We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ever feel overwhelmed by the sheer volume of data bombarding us today? This is the age of Big Data, and it's revolutionising every industry. But how do we harness its power? Enter Big Data and Machine Learning.
This blog explores the fascinating relationship between Big Data and Machine Learning. We'll explore how Big Data provides the raw materials, the vast datasets, that fuel Machine Learning algorithms. These algorithms, in turn, unlock hidden patterns and insights from Big Data, empowering businesses to make smarter decisions. Ready to learn how Big Data and Machine Learning are transforming our world? Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Big Data and Machine Learning
2) Key Concepts of Big Data and Machine Learning
3) Big Data Analysis vs Machine Learning vs Artificial Intelligence
4) Interplay of Big Data and Machine Learning
5) Use cases of Big Data with Machine Learning
6) Conclusion
Understanding Big Data and Machine Learning
Big Data and Machine Learning are two transformative technologies that have revolutionised how we collect, process, and extract insights from vast datasets. To comprehend their significance, it's essential to break down each concept individually. Let's have a detailed look at each one of them:
Big Data encompasses the immense volume, velocity, variety, and veracity of data generated in our digital age. This data can range from social media interactions and sensor readings to financial transactions and healthcare records. The challenge lies in managing, storing, and processing this data efficiently, which requires specialised tools and techniques like distributed computing and cloud platforms.
On the other hand, Machine Learning is the engine that drives intelligence within Big Data. It's a subset of Artificial Intelligence that empowers computers to understand patterns and make predictions without explicit programming. Machine Learning algorithms enable systems to recognise speech, understand images, recommend products, and much more.
The synergy between Big Data and Machine Learning is undeniable. Big Data provides the raw material - the fuel - that Machine Learning algorithms need to operate effectively. These algorithms, in turn, extract valuable insights, uncover hidden patterns, and enable data-driven decision-making.
Understanding Big Data and Machine Learning is not just a technological feat but a fundamental shift in how we approach information and knowledge. Together, they offer the potential to transform industries, improve healthcare, enhance customer experiences, and solve some of the most complex problems facing society today. As we continue to delve deeper into these technologies, their impact on our lives will only become more profound.
Key Concepts of Big Data and Machine Learning
In the realm of Big Data and Machine Learning, several key concepts underpin the understanding and application of these transformative technologies. These concepts are essential for anyone seeking to harness their power effectively. Let's have a quick look at these concepts:
a) Data Preprocessing: Data often comes in a raw and unstructured form, requiring Preprocessing to make it suitable for analysis. This step involves data cleaning, transformation, and normalisation, ensuring that the data is precise, consistent, and ready for Machine Learning algorithms.
b) Feature Engineering: Feature Engineering is the process of selecting, creating, or modifying specific attributes (features) from raw data to improve the performance of Machine Learning models. Effective Feature Engineering can significantly impact the accuracy and efficiency of a model.
c) Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning: Machine Learning can be broadly categorised into Supervised and Unsupervised Learning. Supervised Learning involves training models on labelled data, where the outcome is known. In contrast, Unsupervised Learning deals with unlabelled data, seeking patterns and relationships without predefined guidance.
d) Neural Networks: Neural Networks, particularly Deep Learning models, have gained prominence in recent years. They are inspired by the structure of the human brain and are capable of solving complex tasks, including Natural Language Processing (NLP and image recognition.
e) Model Evaluation and Hyperparameter Tuning: Choosing appropriate Evaluation metrics and fine-tuning model parameters are critical aspects of Machine Learning model development. Effective evaluation ensures the model's performance aligns with the desired objectives, while Hyperparameter Tuning optimises its efficiency.
Big Data Analysis vs Machine Learning vs Artificial Intelligence
It’s crucial to understand that Big Data, Machine Learning (ML), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are distinct disciplines that have evolved over time.
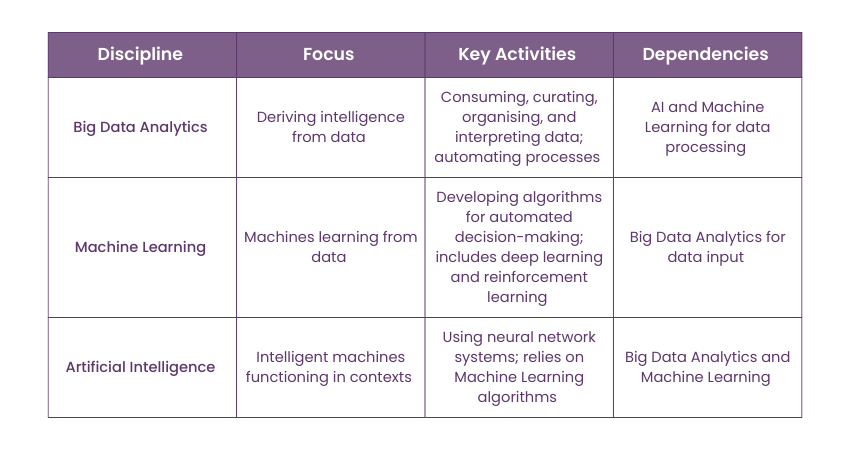
a) Big Data Analytics: Deriving intelligence from data has been a quest of modern computation for decades and to a lesser extent, a goal of AI and Machine Learning (ML) research. However, analytics is a distinct discipline. Data scientists and engineers in this field focus on consuming, curating, organising, and interpreting both structured and unstructured data. The aim is to use various consumption and categorisation methods to derive meaningful insights that enhance decision-making processes. Many analytics platforms now automate processes, allowing non-technical users to control dashboards and visualisations without needing to understand the underlying mechanisms.
b) Machine Learning (ML): Machine Learning involves developing algorithms that can ingest data and use it to inform automated, strategic decision-making. This discipline focuses on how computers can use data to learn strategies and behaviours within specific contexts. Subdisciplines within Machine Learning (ML) include deep learning and reinforcement learning.
c) Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI, a hot topic since the early- and mid-20th century, is closely related to but distinct from Machine Learning (ML). While Machine Learning focuses on how machines can learn behaviours, AI explores how intelligent machines can function across various contexts. AI relies on Machine Learning algorithms and the neural network systems they create. Both AI and Machine Learning depend on Big Data Analytics to process data and provide diverse insights and approaches.
Interplay of Big Data and Machine Learning
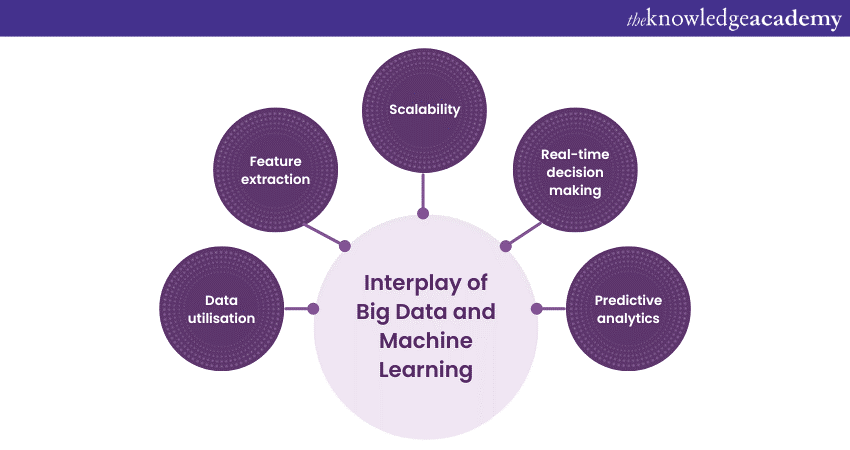
The interplay of Big Data and Machine Learning (ML) represents a transformative synergy that has revolutionised industries and fundamentally altered our approach to data-driven decision-making.
At its core, Big Data involves the accumulation of vast amounts of data from diverse sources, characterised by its volume, velocity, variety, and veracity. Once seen as a challenge, this data abundance is now a valuable resource. Enter Machine Learning (ML), a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that enables machines to learn from this data, automatically adapting and improving their performance without explicit programming. The synergy between Big Data and Machine Learning is evident in several critical aspects:
a) Data Utilisation: Machine Learning thrives on data. The more data available, the more accurate and insightful the models become. Big Data provides the massive datasets necessary for training and refining Machine Learning algorithms, allowing these models to uncover intricate patterns and trends previously inaccessible.
b) Feature Extraction: Big Data often comprises a multitude of data types, from structured to unstructured. Machine Learning algorithms excel at feature extraction, identifying relevant information from this complex data landscape and transforming it into actionable insights.
c) Scalability: Big Data platforms such as Hadoop and Spark provide the infrastructure needed to process and store massive datasets. Machine Learning algorithms can seamlessly integrate with these platforms, ensuring scalability and performance even when dealing with petabytes of data.
d) Real-time Decision Making: The velocity at which Big Data is generated necessitates real-time analysis. Machine Learning models can continuously adapt and learn, making instant decisions based on the latest data inputs, a crucial capability in fields like finance and Cyber Security.
e) Predictive Analytics: By analysing historical and real-time data, Machine Learning (ML) models can predict future trends and events with remarkable accuracy. This capability is instrumental in areas such as demand forecasting, healthcare diagnosis, and predictive maintenance in manufacturing.
Learn to evaluate risk and predict outcomes based on data by signing up for the Predictive Analytics Training now!
Use cases of Big Data with Machine Learning
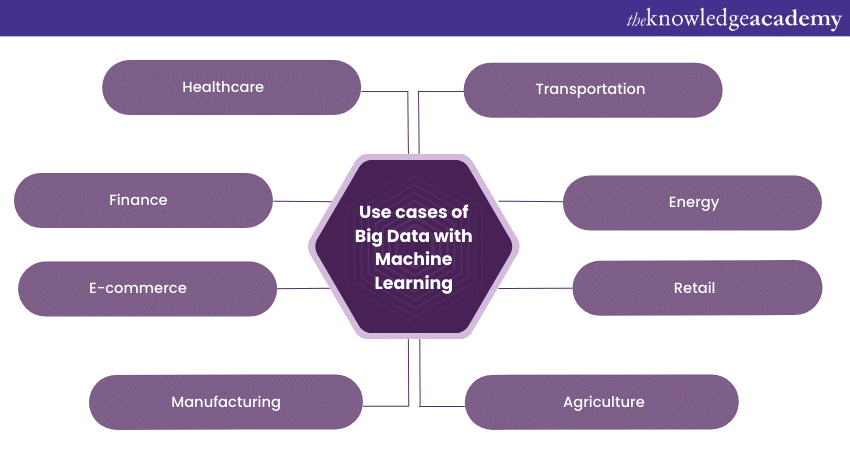
The integration of Big Data with Machine Learning has ushered in a new age of data-driven decision-making across various industries. Let's explore some compelling use cases where these technologies are making a significant impact:
a) Healthcare: The healthcare sector has been revolutionised by Big Data and Machine Learning. These technologies are used to analyse vast volumes of patient data, including medical records, genomic information, and real-time sensor data. Machine Learning models can predict disease outbreaks, assist in early diagnosis, and even suggest personalised treatment plans. This data-driven approach enhances patient care, reduces costs, and saves lives.
b) Finance: In the financial industry, Big Data and Machine Learning are employed for fraud detection and prevention. By analysing transactional data, user behaviour, and historical patterns, algorithms can identify unusual activities and trigger alerts. Additionally, Machine Learning is used for algorithmic trading, where models make split-second decisions based on market data to optimise trading strategies.
c) E-commerce: Online retailers leverage these technologies to enhance customer experiences. Recommendation systems powered by Machine Learning analyse user behaviour, purchase history, and product attributes to suggest personalised products to customers. This not only increases customer engagement but also boosts sales and revenue.
d) Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance is a game-changer in manufacturing. By collecting and analysing data from sensors embedded in machinery, Machine Learning models can predict when equipment is likely to fail. This allows proactive maintenance of machines. As a result, it reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and improves overall production efficiency.
e) Transportation: The transportation industry benefits from Big Data and Machine Learning through various applications. Route optimisation algorithms help reduce fuel consumption and transportation times. Traffic prediction models enable real-time rerouting to avoid congested areas, improving logistics efficiency. Additionally, autonomous vehicles rely on Machine Learning to navigate and make decisions based on sensor data.
f) Energy: In the energy sector, these technologies are used to optimise energy consumption. Smart grids use Machine Learning to analyse real-time data from sensors to balance supply and demand, reducing energy wastage. Furthermore, predictive analytics helps energy companies anticipate equipment failures and optimise energy production. This ultimately lowers costs and reduces carbon emissions.
g) Retail: Retailers use Big Data and Machine Learning for demand forecasting. By analysing historical sales data alongside external factors such as weather and holidays, businesses can optimise inventory levels. They can also reduce stockouts and enhance supply chain efficiency. This leads to enhanced customer satisfaction and profitability.
h) Agriculture: Precision agriculture leverages Big Data and Machine Learning to maximise crop yields. By collecting data from sensors, drones, and satellites, farmers can make informed decisions about planting, pest control and more. Machine Learning models can process this data to provide actionable insights, improving crop quality and sustainability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Big Data and Machine Learning represent a dynamic duo, reshaping how we leverage data. Their applications are diverse and far-reaching, from healthcare to finance, e-commerce to manufacturing. Thus, understanding the key concepts and exploring real-world use cases is essential for individuals and organisations looking to harness the power of these technologies.
Acquire the basic knowledge of Data Analytics by signing up for our Data Analytics for Marketing Professional Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Apache Spark supports Machine Learning through its MLlib library, providing scalable and easy-to-use algorithms. It integrates well with big data platforms, enabling efficient processing and analysis of large datasets for machine learning (ML) tasks.

Big Data refers to vast, complex datasets from diverse sources, characterised by volume, velocity, variety, and veracity. An ML dataset is a subset of data specifically curated for training and testing machine learning (ML) models, focusing on quality and relevance.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data & Analytics Courses, including Hadoop Big Data Certification Training, Apache Spark Training and Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Key Characteristics of Big Data.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data and Machine Learning, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Big Data and Machine Learning skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Big Data Analysis
Big Data Analysis
Fri 6th Dec 2024
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


