We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today's increasingly digital and interconnected world, Information Technology (IT) and data security are paramount for organisations of all sizes and industries. This has led to the development and adoption of various international standards to help companies meet these challenges. Two such standards, ISO 20000 and ISO 27001, play crucial roles in ensuring IT service management and information security, respectively. Many businesses and industry newcomers still wonder the difference between ISO 20000 vs ISO 27001.
In this blog, we will delve into the differences between ISO 20000 vs ISO 27001, helping you understand their unique purposes and applications.
Table of Contents
1) Introduction to ISO 20000 and ISO 27001
2) Key differences between ISO 20000 and ISO 27001
a) Focus and purpose
b) Scope
c) Certification
d) Risk Management
e) Compliance requirements
f) Customer Focus
3) Conclusion
Introduction to ISO 20000 and ISO 27001
In today's digital age, where businesses and organisations rely heavily on technology and data, the need for robust standards in IT service management and information security has never been greater. This is where ISO 20000 and ISO 27001 come into play as internationally recognised standards that provide essential frameworks for addressing these critical aspects.
ISO 20000: IT Service Management
ISO 20000, formally known as ISO/IEC 20000-1, serves as a global benchmark for IT service management (ITSM). Its primary goal is to ensure that IT services are delivered efficiently and effectively, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction. This standard focuses on establishing best practices and processes throughout the IT service lifecycle, from planning and design to transition, operation, and continual improvement. ISO 20000 is particularly valuable for organisations that provide IT services to both internal and external customers. By adhering to ISO 20000, businesses can streamline their IT operations, minimise disruptions, and enhance their ability to meet customer needs and expectations. Certification to ISO 20000 provides tangible evidence of an organisation's commitment to delivering high-quality IT services.

ISO 27001: Information Security Management
On the other hand, ISO 27001, also known as ISO/IEC 27001, is the globally recognised standard for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). In an era where data breaches and cyber threats pose significant risks, ISO 27001 is instrumental in safeguarding sensitive information.
The primary objective of ISO 27001 is to establish a systematic and comprehensive approach to managing an organisation's information security risks. This involves identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks that could compromise the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. ISO 27001 covers not only digital data but also physical information assets and considers all aspects, including technology, processes, and people.
For organisations that handle sensitive data or are subject to regulatory requirements, ISO 27001 certification is often mandatory or strongly recommended. Achieving ISO 27001 certification demonstrates to stakeholders, including clients and regulatory bodies, that an organisation is committed to protecting sensitive information and has implemented robust security measures.
Key differences between ISO 20000 and ISO 27001
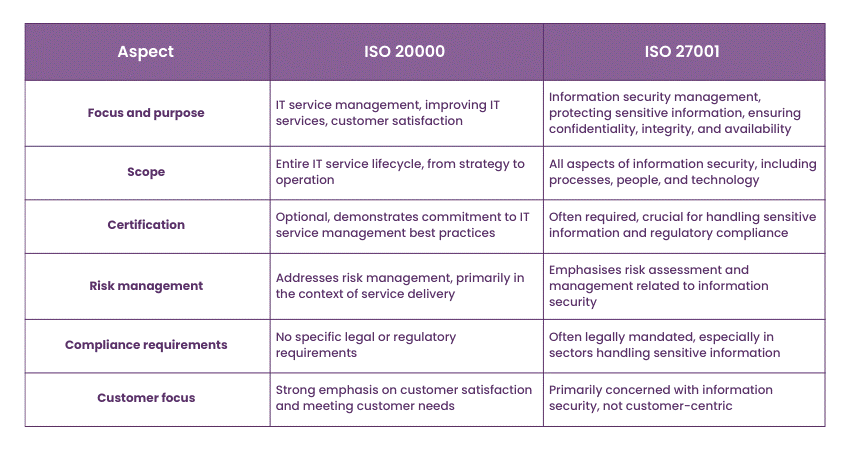
In this section, we will discuss the differences between the two standards based on the following conditions:
Focus and purpose
a) ISO 20000: The focus on IT service management
ISO 20000, formally known as ISO/IEC 20000-1, sets its sights firmly on the realm of IT service management (ITSM). At its core, ISO 20000 is designed to ensure that organisations deliver IT services efficiently, effectively, and with a keen eye on continuous improvement. It serves as a blueprint for managing the complex interplay of IT service processes and procedures to meet the evolving needs of customers.
The primary purpose of ISO 20000 is to enhance customer satisfaction by providing high-quality IT services. This involves optimising various aspects of IT service delivery, such as incident management, problem resolution, change management, and service level agreements. In essence, ISO 20000 helps organisations align their IT services with the expectations and requirements of their clientele, making it a fundamental tool for businesses reliant on robust IT service provision.
b) ISO 27001: The focus on information security
In sharp contrast, ISO 27001, also known as ISO/IEC 27001, has its gaze firmly fixed on information security management. This standard is all about safeguarding an organisation's most valuable asset: its information. Its primary purpose is to establish, implement, maintain, and continually improve an Information Security Management System (ISMS).
ISO 27001 goes well beyond the confines of IT service management. It encompasses the entirety of an organisation's information security landscape, covering electronic and physical data, processes, people, and technology. The core objective is to protect sensitive information by ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Unlock the path to IT service excellence by joining our ISO 20000 Foundation Course today!
Scope
a) ISO 20000 scope
ISO 20000 sets its sights firmly on the arena of IT service management (ITSM). Its reach extends across the entire lifecycle of IT services, encapsulating various phases from inception to operation. This standard is designed for organisations that rely on IT services to support their business functions. ISO 20000 encompasses areas such as service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual improvement.
Within its scope, ISO 20000 addresses critical aspects of IT service management, including incident management, problem resolution, change management, and service level agreements (SLAs). It offers a structured framework to help organisations enhance their IT service delivery, streamline processes, and ultimately, meet the expectations of their customers.
b) ISO 27001 scope
On the other side of the spectrum, we have ISO 27001, which takes a much broader approach. ISO 27001's scope encompasses the entirety of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). Its focus is not limited to IT services but extends to all types of information, whether electronic or physical. This information includes data related to customers, employees, business operations, and any other sensitive information that an organisation may possess.
ISO 27001 deals with a wide array of concerns within its scope. These include risk assessment, access control, data encryption, physical security, and incident response. Its primary aim is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive data while managing risks associated with information security.
Unlock your career potential with our ISO 20000 Lead Auditor Course and become a certified expert in IT service management.
Certification
Certification demonstrates an organisation's commitment to international standards and best practices. Both ISO 20000 and ISO 27001 offer certification processes but serve vastly different purposes and have distinct requirements.
ISO 20000 certification
ISO 20000 certification focuses on IT service management (ITSM) and aims to ensure that an organisation's IT services are delivered efficiently and effectively. Here are key differences in the certification process for ISO 20000:
a) ISO 20000 certification is primarily concerned with the IT service management processes within an organisation. It evaluates how well an organisation plans, designs, transitions, operates, and improves its IT services in areas like incident management, problem resolution, and change management.
b) ISO 20000 places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction. The certification process assesses whether IT services align with customer needs and expectations. Customer feedback and service improvement are integral parts of ISO 20000 certification.
c) ISO 20000 certification is not mandatory for all organisations. IT service providers often seek it to enhance their service quality and demonstrate their commitment to best practices. Certification can be a competitive advantage when bidding for contracts, especially when dealing with clients prioritising service excellence.
d) To obtain ISO 20000 certification, organisations undergo a thorough audit by an accredited certification body. The audit assesses the organisation's compliance with ISO 20000 standards and its effectiveness in delivering IT services.
ISO 27001 Certification
ISO 27001 certification, on the other hand, focuses on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). It is designed to protect sensitive information within an organisation. Here are key differences in the certification process for ISO 27001:
a) ISO 27001 certification encompasses all aspects of information security, including people, processes, and technology. It applies to protecting all types of information, electronic and physical, regardless of its form.
b) ISO 27001 is often mandatory for organisations that handle sensitive information. Compliance with ISO 27001 can help organisations meet legal and regulatory requirements concerning data protection and privacy. Industries such as finance, healthcare, and government commonly require ISO 27001 certification.
c) A significant focus of ISO 27001 certification is on risk assessment and management related to information security. Organisations must identify information security risks, evaluate their potential impact, and implement controls to mitigate them effectively.
d) ISO 27001 certification involves a rigorous audit process, during which an accredited certification body evaluates an organisation's ISMS. Achieving and maintaining ISO 27001 certification demonstrates an organisation's commitment to safeguarding sensitive data.
Unlock your career potential with ISO 20000 Internal Auditor certification and lead the way in IT service excellence.
Risk Management
Risk Management is a critical aspect of both ISO 20000 and ISO 27001, but these two international standards approach it from different angles and with varying levels of depth and emphasis.
a) ISO 20000
ISO 20000, the standard for IT service management, incorporates Risk Management as a part of its framework, but it primarily focuses on risks related to IT service delivery. Here are the main aspects of Risk Management within ISO 20000:
b) Service delivery risks: ISO 20000 emphasises identifying, assessing, and managing risks associated with the delivery of IT services. This includes risks related to incidents, problems, and changes in service, all of which can impact service quality and customer satisfaction.
c) Alignment with business objectives: ISO 20000 encourages aligning Risk Management with an organisation's broader business objectives. It aims to ensure that IT services support the overall goals and strategies of the business.
d) Continual improvement: The standard promotes the concept of continual improvement, where organisations regularly review and enhance their Risk Management processes to adapt to changing circumstances and evolving technology.
e) Customer focus: ISO 20000 places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction. Risk Management efforts are geared towards meeting customer expectations and delivering high-quality IT services.
f) ISO 27001
ISO 27001, on the other hand, is solely dedicated to information security management. Here are the key differences in how ISO 27001 addresses Risk Management:
g) Comprehensive information security Risk Management: ISO 27001 offers a comprehensive approach to information security Risk Management. It requires organisations to identify, assess, and manage risks related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of sensitive information.
h) Legal and regulatory compliance: ISO 27001 places a significant emphasis on compliance with legal and regulatory requirements related to information security. This includes data protection laws, industry-specific regulations, and contractual obligations.
i) Risk assessment methodology: ISO 27001 prescribes a specific risk assessment methodology, including the calculation of risk levels based on the likelihood and impact of identified risks. This structured approach ensures a thorough evaluation of information security risks.
j) Information security controls: ISO 27001 mandates the implementation of information security controls to mitigate identified risks. These controls cover areas such as access control, data encryption, incident response, and security awareness training.
Compliance requirements
ISO 20000 compliance requirements
ISO 20000, which focuses on IT service management, does not have specific legal or regulatory requirements associated with it. Instead, compliance revolves around adhering to best practices and industry standards to improve IT service management processes continually. The goal is to align these processes with the needs and expectations of customers.
While ISO 20000 compliance may not be legally mandated, it plays a significant role in building trust and credibility with clients and stakeholders. Many organisations seek ISO 20000 certification to demonstrate their commitment to delivering high-quality IT services. This certification is often a requirement when bidding for contracts or when working with clients who prioritise service quality.
To achieve ISO 20000 compliance, organisations typically undergo an assessment by an accredited certification body. This assessment evaluates the organisation's IT service management processes against the requirements outlined in the standard. Any identified gaps or areas for improvement must be addressed to attain certification.
ISO 27001 compliance requirements
In contrast, ISO 27001, the information security management standard, often comes with strict compliance requirements. This is especially true for organisations that handle sensitive information, such as personal data, financial records, or healthcare information. Compliance with ISO 27001 can be legally mandated or required by industry regulations and data protection laws.
ISO 27001 compliance involves establishing, implementing, maintaining, and continually improving an Information Security Management System (ISMS). This system includes policies, procedures, and controls designed to protect sensitive information from threats and vulnerabilities. Organisations must conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security risks and implement appropriate security measures to mitigate them.
Certification to ISO 27001 is often a prerequisite for organisations that handle sensitive data. Achieving compliance not only demonstrates a strong commitment to information security but also helps organisations avoid legal penalties related to data breaches and non-compliance with data protection regulations.
Customer focus
One of the notable distinctions between ISO 20000 and ISO 27001 lies in their approach to customer focus. While both standards acknowledge the significance of meeting customer requirements, they do so in different contexts.
a) ISO 20000: The standard places a strong emphasis on customer satisfaction within the realm of IT service management. ISO 20000's core objective is to enhance the quality of IT services delivered by organisations. It emphasises aligning IT services with customer needs and expectations. By doing so, it ensures that the IT services not only meet technical specifications but also contribute to the overall success of the customer's business. Customer feedback and feedback-driven improvements are integral components of ISO 20000's customer-centric approach.
b) ISO 27001: While ISO 27001 acknowledges the importance of protecting customer data and maintaining its confidentiality, it is not primarily customer-centric in the same way as ISO 20000. ISO 27001's primary focus is on safeguarding an organisation's information assets, ensuring data integrity, confidentiality, and availability. While it indirectly serves customers by protecting their data, its primary objective is to manage information security risks comprehensively.
Enhance your organisation's Information Security with ISO 27001 Training Today!
Conclusion
ISO 20000 and ISO 27001 are two distinct international standards that serve different purposes within the realms of IT service management and information security. Hopefully, this blog helped you understand the differences between ISO 20000 vs ISO 27001 and make informed decisions regarding certification and compliance, ensuring that your organisation's IT services and information assets are effectively managed and protected.
Upgrade your IT service management skills with ISO 20000 Training and excel in delivering high-quality IT services.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 20000 Foundation
ISO 20000 Foundation
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


