We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a bustling city powered by a vast network of highways, railroads, and power lines, all seamlessly interconnected to support millions of lives every day. Now, envision the digital counterpart of that city – Big Data Infrastructure. This intricate web of technologies and systems is what fuels the immense flow of data that businesses, governments, and organisations rely on to make informed decisions, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge.
With global data volume projected to reach a staggering 181 zettabytes by 2025, as per Statista, the importance of a robust Big Data Infrastructure has never been more critical. It’s the backbone that supports the growing demands of data processing, storage, and analysis, transforming raw data into actionable insights that can shape the future. Let’s dive in!
Table of Contents
1) What is Big Data Infrastructure?
2) Understanding the Importance of Big Data Infrastructure
3) How to Build Big Data Infrastructure?
4) Fundamentals of Big Data Infrastructure
5) Real-world Examples of Successful Big Data Infrastructures
6) Conclusion
What is Big Data Infrastructure?
Big Data Infrastructure refers to the fundamental framework of technologies and resources designed to handle vast volumes of data efficiently and effectively. In this data-driven era, where information flows from various sources at an unprecedented pace, the need for a robust infrastructure to manage, store, process, and analyse this data becomes paramount.
At its core, Big Data Infrastructure comprises a combination of hardware, software, and networks, all working harmoniously to support the data lifecycle. This includes data ingestion, where data is collected from diverse sources like the following:
a) Data Storage: Information is stored in distributed systems capable of handling massive data sets.
b) Data Processing: Complex computations and analysis take place.
c) Data Retrieval: Valuable insights are extracted.
The significance of Big Data Infrastructure lies in its ability to empower organisations with actionable insights, enabling data-driven decision-making across industries. By harnessing its potential, businesses can optimise processes, identify patterns and trends, personalise customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge.
In essence, this infrastructure is the backbone of the data revolution, paving the way for innovation, growth, and transformative opportunities in a world where information reigns supreme.
Understanding the Importance of Big Data Infrastructure
In today's data-driven world, the importance of Big Data Infrastructure cannot be overstated. As the volume, velocity, and variety of data continue to escalate. Further, businesses face the challenge of effectively managing and harnessing this vast information. So, let’s explore why it is crucial for organisations:
a) Data Management: It provides a robust framework for efficient data management, ensuring seamless storage, retrieval, and processing of vast volumes of information.
b) Real-time Insights: With distributed processing capabilities, the infrastructure enables organisations to analyse data in real time, leading to faster decision-making and swift responses to changing trends.
c) Enhanced Customer Experiences: Leveraging Data Analytics through Big Data Infrastructure helps businesses gain valuable insights into customer preferences and behaviours. This allows them to deliver personalised and tailored experiences.
d) Predictive Analytics: It also empowers businesses to employ predictive analytics, anticipating future trends and potential challenges, thus enabling proactive decision-making and risk mitigation.
e) Competitive Advantage: By harnessing the power of its infrastructure, companies can gain a competitive edge. It is because they make data-driven decisions that optimise operations, identify new opportunities, and stay ahead in the market.
f) Innovation and Research: Researchers and scientists Benefit from Big Data Infrastructure to process and analyse large datasets, facilitating groundbreaking discoveries and advancements across various fields.
g) Resource Scalability: It offers scalable resources, allowing organisations to adjust storage and processing power as per changing data demands, ensuring cost-effectiveness.
h) Data Security: Implementing proper security measures within Big Data Infrastructure safeguards sensitive data and protects against potential cyber threats, ensuring compliance with data regulations.
i) Business Growth: The ability to harness and utilise data effectively through Big Data Infrastructure directly contributes to business growth. It helps drive efficiency, productivity, and revenue generation.
j) Data-driven Decision making: It enables data-driven decision-making processes and reduces reliance on intuition and gut feelings. This also fosters a culture of data-centricity within organisations.
Learn to create Data Models with our Big Data Architecture Training – Sign up now!
How to Build Big Data Infrastructure?
Building a robust Big Data Infrastructure is a multi-faceted process that requires careful planning, consideration, and adherence to best practices. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to accomplish this:
a) Define Objectives: Clearly outline your business objectives and data requirements. Understand the types of data you need to manage, process, and analyse, ensuring your infrastructure aligns with these specific needs.
b) Choose the Right Technologies: Select appropriate technologies that cater to your data processing requirements. Consider factors such as data volume, velocity, variety, and the complexity of the analysis you aim to perform.
c) Scalability and Flexibility: Future-proof your infrastructure by ensuring it can scale seamlessly to accommodate growing data volumes and adapt to evolving technological advancements.
d) Data security and Compliance: Prioritise data security and implement robust measures to protect sensitive information. Comply with relevant data regulations to maintain data integrity and build trust.
e) Data ingestion Mechanisms: Develop efficient data ingestion mechanisms to capture and transport data from various sources into your infrastructure in real time.
f) Distributed Storage: Opt for distributed storage systems that can handle large volumes of data and ensure high availability, reducing the risk of data loss.
g) Processing Power: Equip your infrastructure with sufficient processing power to efficiently handle complex data analysis and computations.
h) Data governance and Quality: Implement proper data governance practices to maintain data quality, establish data lineage, and ensure adherence to data standards.
i) Monitoring and Performance Optimisation: Regularly monitor your infrastructure's performance and optimise resources to enhance efficiency and minimise latency.
j) Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test and validate your infrastructure to identify and rectify potential bottlenecks or issues before deploying it for full-scale operations.
Learn and understand the basics of Data Science with our Data Science Analytics Course today!
Fundamentals of Big Data Infrastructure
Mastering the fundamentals of Big Data Infrastructure is essential for handling vast and intricate data collections. This section highlights the main elements and fundamental principles of successful Big Data Management Systems.
1) Key Components of Big Data Infrastructure
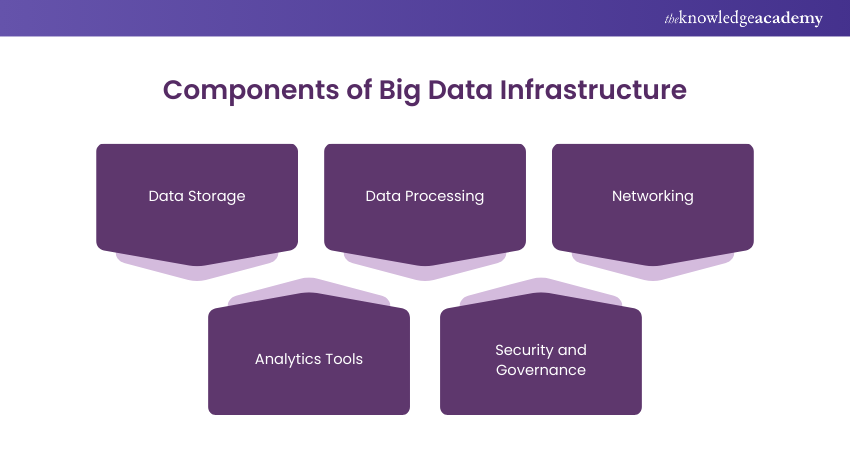
1) Data Storage: Includes databases and data lakes that hold extensive amounts of data in various distributed environments. By adding more nodes, the capacity of these systems can be increased through horisontal scaling.
2) Data Processing: Big data requires high-performance computing to execute complex algorithms effectively. Apache Hadoop and Apache Spark are commonly utilised distributed computing frameworks. These systems handle information on numerous servers at once, increasing effectiveness. ETL operations in cloud settings have grown in importance, simplifying data processes and preparing data for analysis.
3) Networking: Adequate bandwidth and networking technologies are required for the fast transfer of large data volumes within the infrastructure.
4) Analytics Tools: These programs scrutinise large datasets to reveal patterns, connections, and understandings. Machine learning algorithms, statistical tools, data mining techniques, and predictive analysis are all encompassed.
5) Security and Governance: It is crucial to protect data privacy and adhere to regulations like GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA. Adherence to these standards is required and comes with substantial consequences for violations.
2) Architectural Principles
1) Scalability: Scalability is essential for the infrastructure to grow alongside increasing data volume.
2) Fault Tolerance: Systems need to be able to tolerate data loss or hardware failures.
3) Performance: Enhancing performance by maximising data storage, processing, and analysis speed.
4) Flexibility: Flexibility is provided to accommodate different types of data and analytical tasks.
5) Cost-efficiency: Guarantee economic viability and anticipate forthcoming expenses.
3) Models of Infrastructure
1) On-premises: Data centres that are owned and operated by the organisation, providing complete control.
2) Cloud-based: IaaS offers remotely managed, scalable, and virtualised resources provided by third-party vendors.
3) Hybrid: Hybrid technology integrates both on-premises and cloud resources for a mix of control, scalability, and cost-efficiency.
Keen to have deeper knowledge of Data analytics, refer to our blog on "data Architecture"
Real-world Examples of Successful Big Data Infrastructures
Real-world examples of successful Big Data Infrastructures abound, with prominent companies and organisations leveraging these cutting-edge technologies to revolutionise their operations and deliver outstanding results. Here are some compelling examples:
a) Netflix: The entertainment giant employs a robust Big Data Infrastructure to analyse user preferences, viewing habits, and content interactions. This enables Netflix to provide highly personalised recommendations, enhancing user satisfaction and retention.
b) Amazon: As one of the world's largest e-commerce platforms, Amazon utilises Big Data Infrastructure to optimise its supply chain, forecast demand, and manage inventory efficiently. This data-driven approach ensures timely deliveries and exceptional customer experiences.
c) Google: Google’s search engine handles an immense amount of data each day. By employing sophisticated Big Data Infrastructure, Google can process user queries quickly and accurately, delivering relevant search results in real time.
d) Facebook: With billions of active users, Facebook relies on Big Data Infrastructure to analyse vast amounts of user-generated content, identify trends, and target advertisements with precision, resulting in a highly profitable advertising model.
e) NASA: The space agency employs Big Data Infrastructure to process and analyse complex data from satellites, telescopes, and rovers. This data analysis has led to a deeper understanding of the universe and groundbreaking scientific discoveries.
f) Uber: Uber relies on Big Data Infrastructure to optimise ride-sharing routes, predict rider demand, and dynamically adjust pricing. This data-driven approach enhances efficiency and reliability for both drivers and riders.
g) Walmart: This retail giant utilise Big Data Infrastructure to analyse customer purchase patterns, optimise inventory management, and offer personalised promotions, ensuring a seamless shopping experience for customers.
These real-world success stories demonstrate the transformative power of Big Data Infrastructure. By effectively harnessing the potential of data, these organisations have gained a competitive edge, improved customer experiences, and driven innovation, showcasing the immense value of data-driven decision-making in diverse industries.
Conclusion
The significance of Big Data Infrastructure cannot be underestimated in today's data-centric world. Embracing and optimising it is not merely a choice but a necessity for organisations seeking to thrive in the digital age and unlock the full potential of their data-driven future.
Learn to plan and implement a Big Data approach with our Big Data Analysis Course – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Organisations are increasingly understanding data as a crucial competitive edge, aiming to harness its value. A carefully designed Data Infrastructure strategy is crucial as data expands rapidly from edge to cloud. Infrastructure that is not aligned properly can impede flexibility and confine data in separate units.

Data Infrastructure consists of tangible, informational, and operational systems that uphold data within a company. It includes everything from data centre equipment and networks to Business Software and Analysis instruments. The elements may differ, but each provides staff, guidelines, and procedures.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data & Analytics Training, including the Data Science Analytics, Big Data Analysis, and Data Analytics With R. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analyst Job Description.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data, Analytics & AI skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 23rd Jan 2025
Thu 20th Mar 2025
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


