We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
When it comes to analysing problems and identifying solutions, two commonly used methodologies are Causal Analysis and Root Cause Analysis. While they share similarities in their approach, the two have distinct differences. So, how does one decide which one’s better to employ? Worry no more. Read this blog to compare Causal Analysis vs Root Cause Analysis. Also, know how these techniques help to identify the causes of problems or undesired events.
Table of contents
1) What is Causal Analysis?
2) What is Root Cause Analysis?
3) Causal Analysis vs Root Cause Analysis – Key differences
a) Scope and focus
b) Depth of analysis
c) Timeframe consideration
d) Application areas
4) Conclusion
What is Causal Analysis?
Causal Analysis, or cause-and-effect analysis, is a systematic approach to understanding the relationships between causes and effects. It involves investigating and identifying factors contributing to a particular outcome or problem. This analysis aims to uncover the underlying causes that lead to a specific event or result.
This method focuses on examining the connections and relationships between various factors to determine their influence on the outcome. Furthermore, it goes beyond surface-level observations and seeks to understand the root causes that drive a specific occurrence.
Causal Analysis is widely used in various fields, including social sciences, economics, business management, and problem-solving. Through this analysis, researchers and analysts can determine the factors contributing positively or negatively to a particular outcome. As a result, it helps predict potential outcomes and understand the implications of interventions or changes in variables.Explore effective root cause analysis methods to deepen insights into problem origins and enhance strategic decision-making.

What is Root Cause Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the primary cause(s) of a problem or issue. It goes beyond the immediate or surface-level causes and delves deeper to find the underlying issues that contribute to the occurrence of a problem.
In RCA, the focus is on investigating the primary cause or causes responsible for the problem. It aims to uncover the core issues that give rise to a particular problem rather than addressing only the symptoms or superficial aspects.
This analysis technique is widely used in industries such as quality management, manufacturing processes, and safety investigations. It is particularly valuable when dealing with recurring problems or issues that require permanent solutions.
By understanding and addressing the underlying causes, individuals and organisations can achieve long-term improvements and enhance their processes and outcomes.
Understand how to use ITIL to improve your organisation’s efficiency. Register for our ITIL® 4 Foundation Certification Training Course.
Causal Analysis vs Root Cause Analysis – Key differences
While Causal Analysis and Root Cause Analysis both methodologies aim to identify the causes of a problem or issue, they have distinct approaches and focus areas. Here are the key differences between the two:
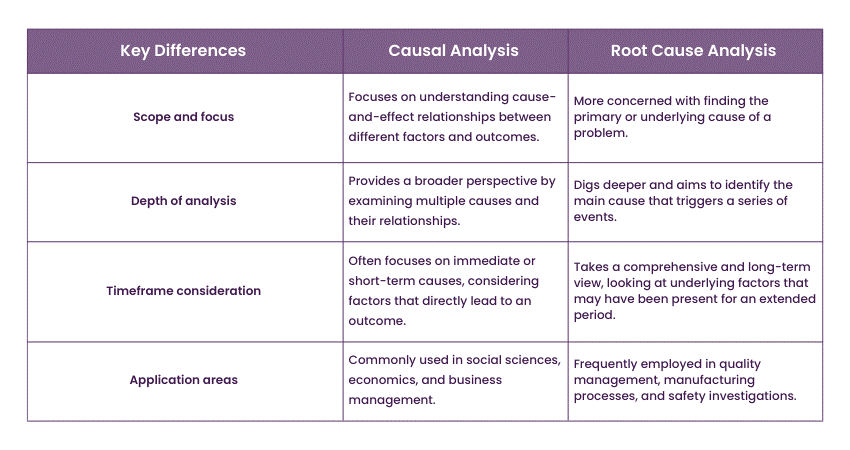
1) Scope and focus
Causal Analysis focuses on understanding the cause-and-effect relationships between different factors and outcomes. It aims to establish connections and identify the reasons behind a specific event or result.
On the other hand, Root Cause Analysis is more concerned with finding the primary or underlying cause of a problem. It goes beyond immediate or surface-level causes and delves deeper to find the underlying issues that contribute to the occurrence of a problem.
Causal Analysis provides a broader perspective by examining multiple causes and their relationships. It considers various factors that contribute to a specific outcome.
In contrast, Root Cause Analysis digs deeper and aims to identify the main cause that triggers a series of events. It focuses on finding the core issues that give rise to a particular problem.
Take your ITIL skills to the next level with our comprehensive ITIL® Certification Training.
3) Timeframe consideration
Causal analysis often focuses on immediate or short-term causes, considering factors directly leading to an outcome.
While Root Cause Analysis takes a more comprehensive and long-term view, it looks at the underlying factors that may have been present for an extended period and influenced the occurrence of a problem.
4) Application areas
Causal Analysis is commonly used in fields such as social sciences, economics, and business management. It helps to understand the relationships between variables and predict potential outcomes.
Root Cause Analysis is frequently employed in quality management, manufacturing processes, and safety investigations. It is particularly useful when dealing with recurring problems and seeking permanent solutions. Explore effective Root Cause Analysis Tools to enhance problem-solving and deepen understanding of complex issues.
Conclusion
Causal Analysis vs Root Cause Analysis provides distinct perspectives on examining causes, with the former exploring relationships and the latter delving into underlying issues. By understanding the differences between the two, organisations can make informed decisions based on the nature of the problem and the desired outcomes.
Unlock effective problem-solving with our Root Cause Analysis Course.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis
Fri 7th Feb 2025
Fri 30th May 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


