We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine a vast treasure trove filled with diamonds of raw data just waiting to be unearthed. But how do you sift through the mountains of information and unearth the hidden gems? That's where Data Mining Architecture comes in! What is Data Mining Architecture? It's the intricate blueprint that guides you in extracting valuable insights from seemingly endless data sets.
This comprehensive blog delves into the What is Data Mining Architecture. We'll explore the key components, the processes involved, and how they work together to transform raw data into actionable knowledge. Get ready to unlock the secrets of Data Mining Architecture and become a master treasure hunter in the vast ocean of information!
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Mining Architecture?
2) Working of Data Mining Architecture
3) Types of Data Mining Architecture
4) Components of Data Mining Architecture
5) Benefits of Data Mining
6) Drawbacks of Data Mining
7) Conclusion
What is Data Mining Architecture?
Data Mining Architecture involves selecting, exploring, and modelling extensive datasets to uncover previously unknown patterns or relationships, generating valuable insights for the database owner. This process entails using automated or semi-automated techniques to analyse vast amounts of data, identifying significant trends and actionable information.
The architecture typically includes several layers: data sources (databases, data warehouses), a Data Mining engine (executing algorithms), pattern evaluation (assessing useful patterns), a user interface (facilitating user interaction), and a knowledge base (storing domain knowledge and rules). This structured approach ensures efficient and accurate Data Analysis, transforming raw data into meaningful insights.
Working of Data Mining Architecture
When a user submits Data Mining queries, these requests are directed to the Data Mining engine for pattern analysis. The Data Mining engine, a software application, utilises the existing database to find solutions to the query. The process involves several steps:
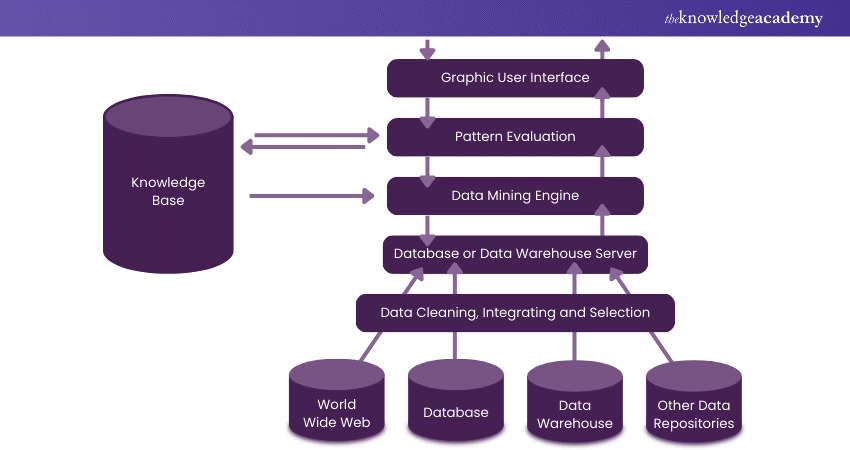
a) Query Processing: User requests are sent to the Data Mining engine.
b) Data Analysis: The engine analyses the data by accessing the database to uncover patterns or relationships.
c) Metadata Retrieval: The necessary metadata is retrieved and sent to the Data Mining engine for further processing.
d) Pattern Assessment: The engine may interact with pattern assessment modules to evaluate and decide the outcomes of the analysis.
e) Result Delivery: The final results are formatted into a user-friendly format and delivered to the front end through an appropriate interface.
Types of Data Mining Architecture
After understanding the workings of Data Mining Architecture, let's explore its types, each offering varying levels of integration and efficiency for different tasks.
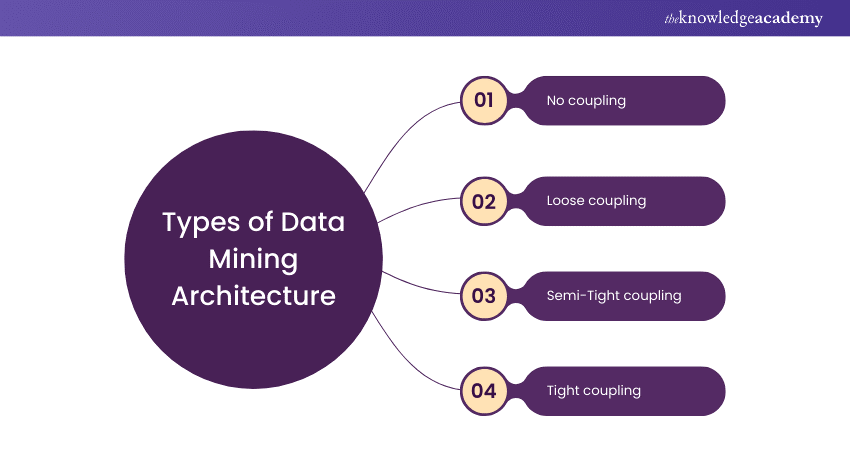
No coupling
The no coupling Data Mining Architecture retrieves data directly from specific data sources, bypassing the database. While this method can be straightforward, it is generally inefficient and lacks accuracy.
It is used for very simple Data Mining tasks that do not require complex processing or integration. Due to its limited capabilities, no coupling is considered the weakest form of Data Mining Architecture.
Loose coupling
In loose coupling architecture, the Data Mining system interacts with the database to retrieve data, which is then stored in separate systems for processing. This approach is characteristic of memory-based Data Mining, where the data is temporarily held in memory for analysis.
While it offers more flexibility than no coupling, it may still face limitations in handling large datasets and ensuring consistent performance.
Semi-Tight coupling
This architecture leverages the advanced features of data warehouse systems, such as sorting, indexing, and aggregation. Semi-tight coupling allows intermediate results to be stored in the database, improving performance and efficiency. By utilising the data warehouse's capabilities, this architecture strikes a balance between performance and complexity, making it suitable for more sophisticated Data Mining tasks.
Tight coupling
In tight coupling architecture, the data warehouse is a core component of the Data Mining system. This architecture fully integrates Data Mining tasks with the data warehouse, using its features to perform complex analyses.
Tight coupling provides enhanced scalability, high performance, and integrated information management. It is the most robust and efficient architecture, capable of handling extensive and intricate Data Mining processes, making it ideal for enterprise-level applications.
Enhance your knowledge of Architect roles with our BCS Practitioner Certificate In Enterprise And Solution Architecture - sign up now!
Components of Data Mining Architecture
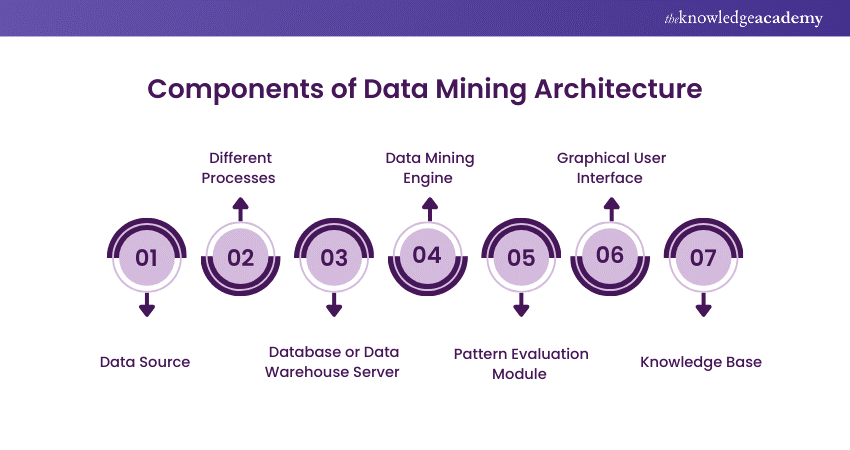
Let's now explore the key components of Data Mining Architecture, which are essential for processing and analysing data efficiently to extract valuable insights and patterns.
Data Source
Data sources for Data Mining include databases, data warehouses, the World Wide Web (WWW), text files, and other documents. Successful Data Mining requires a large volume of historical data, which organisations typically store in databases or data warehouses.
A data warehouse can contain multiple databases, text files, spreadsheets, or other data repositories. Even plain text files or spreadsheets can hold valuable information. The internet is another primary data source.
Different Processes
Before data is passed to the database or data warehouse server, it must undergo cleaning, integration, and selection. Since data comes from various sources and formats, it cannot be used directly for Data Mining because it may be incomplete or inaccurate. Therefore, data needs to be cleaned and unified.
Excess data is collected from various sources, and only the relevant data is selected and sent to the server. These processes are complex and involve several methods to ensure proper selection, integration, and cleaning.
Database or Data Warehouse Server
The Database Server or Data Warehouse Server often serves as a central hub for collecting data from various sources. Its primary function is to store and manage data while also providing tools for querying and manipulation in a user-friendly manner.
The choice between using a database or a data mart depends on the data's complexity and volume, as well as the need for fast, real-time analysis versus historical analysis.
Data Mining Engine
The Data Mining engine is a crucial component of any Data Mining system. It includes modules for performing various Data Mining tasks such as association, characterisation, classification, clustering, prediction, and time-series analysis.
The engine is central to Data Mining Architecture, comprising tools and software used to extract insights and knowledge from collected data.
Pattern Evaluation Module
The pattern evaluation module measures and analyses patterns using threshold values. It collaborates with the Data Mining engine to focus on interesting patterns. This module often uses threshold measures to filter out patterns and may be integrated with the mining module, depending on the Data Mining techniques used.
Efficient Data Mining involves pushing pattern evaluation as much as possible into the mining process to focus the search on relevant patterns.
Graphical User Interface
The Graphical User Interface (GUI) offers a user-friendly platform, making it accessible even for those without computer expertise. It allows users to create Data Mining queries, apply techniques, generate visualisations, and navigate data and hypothetical scenarios.
A well-structured GUI ensures smooth and efficient Data Mining operations, enabling analysts to interpret data quickly and make informed decisions.
Knowledge Base
The knowledge base supports the entire Data Mining process by guiding searches and evaluating pattern significance. It may contain user views and experiences that enhance the Data Mining process.
The Data Mining engine uses inputs from the knowledge base to improve result accuracy and reliability. The pattern evaluation module frequently interacts with the knowledge base to obtain and update information.
Elevate your IT skills! Register for the BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains to build a strong foundation in IT architecture and advance your career.
Benefits of Data Mining
Here are a few key points highlighting the advantages of Data Mining Architecture:
a) Insight Discovery: Data Mining uncovers unexpected patterns within vast datasets, providing invaluable insights that conventional methods might miss.
b) Predictive Analysis: Facilitates businesses in forecasting trends, consumer behaviour, and future outcomes, enabling pre-emptive actions for customer needs, market changes, and business opportunities.
c) Improved Decision-making: Provides data-driven evidence for informed decision-making, leading to more effective and beneficial strategies.
d) Enhanced Marketing and Sales: Enables customer segmentation by behaviour and preferences, resulting in personalised offers and better customer engagement.
e) Risk Management: Identifies risk patterns, helping reduce the impact of risks such as fraud detection, credit risk assessment, and market volatility.
f) Operational Efficiency: Optimises processes by detecting inefficiencies, streamlining workflows, and automating repetitive tasks, lowering costs and improving productivity.
g) Competitive Advantage: Early market trend anticipation and uncovering customer pain points provide a competitive edge and drive new business initiatives.
h) Customer Insights: Offers deep understanding of customer behaviour, preferences, and sentiments, allowing businesses to tailor products, services, and promotions.
i) Innovation and Product Development: Captures user feedback and market competition data to fuel innovation and guide product development, ensuring alignment with customer attitudes.
Drawbacks of Data Mining
While Data Mining offers a range of benefits, it also comes with several drawbacks and challenges that organisations need to be aware of:
a) Privacy Issues: Invasion of user privacy through unauthorised data extraction raises ethical and legal concerns.
b) Security Risks: Collecting and storing large volumes of data exposes systems to cyberattacks, data leaks, and loss of sensitive information.
c) Data Quality: The effectiveness of Data Mining depends on the quality of data; incorrect or biased data can lead to misleading results.
d) Cost: High costs of Data Mining Tools and the need for specialised personnel can be a significant setback.
e) Complexity: Extracting meaningful insights requires skilled data scientists to run algorithms and interpret results.
f) Misuse of Information: Data Mining insights can be used unethically for manipulation, targeting, or discrimination.
g) Over-reliance on Data: Excessive focus on data can lead organisations to neglect human intuition, experience, and the human factor.
h) Legal and Ethical Issues: Accessing confidential information or using data beyond permissible limits can violate laws and moral principles.
i) Maintenance: Maintaining Data Mining systems requires ongoing updates, data renewal, and the assurance of the reliability of mining processes.
Conclusion
In summary, Data Mining Architecture is the backbone of efficient and effective Data Analysis, transforming raw data into valuable insights. By understanding What is Data Mining Architecture, its components and various types, organisations can leverage this architecture. This can help uncover hidden patterns, predict future trends, and make informed decisions.
Unlock the power of data! Join our Data Mining Training today and transform raw information into valuable insights for your business success.
Frequently Asked Questions

Here are the four Data Mining techniques:
1) Classification
2) Clustering
3) Association Rule Learning
4) Regression

Yes, Data Mining often requires coding to implement algorithms and process data, though there are tools available that minimise or abstract away direct coding for users.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Analysis Courses including BCS Certificate in Business Analysis Practice, BCS Foundation Certificate in Agile and BCS Foundation Certificate in IS Project Management. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into BCS Code of Conduct.
Our Business Analysis Blogs cover a range of topics related to Data Mining Architecture, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Analysis skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains
BCS Foundation Certificate in Architecture Concepts and Domains
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


