We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever thought about the Difference Between Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing? Both carry importance in our interconnected world but have different functions. Cloud Computing permits data and applications to be accessed over the Internet from any location. Mobile Computing, conversely, emphasises the utilisation of handheld gadgets for retrieving and handling information while in motion. It is important for businesses and individuals aiming to optimise technological benefits to grasp these distinctions.
This blog aims to examine the main differences between Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing, enabling you to make well-informed choices in today's digital landscape.
Table of Contents
1) What is Cloud Computing?
2) What is Mobile Computing?
3) Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing
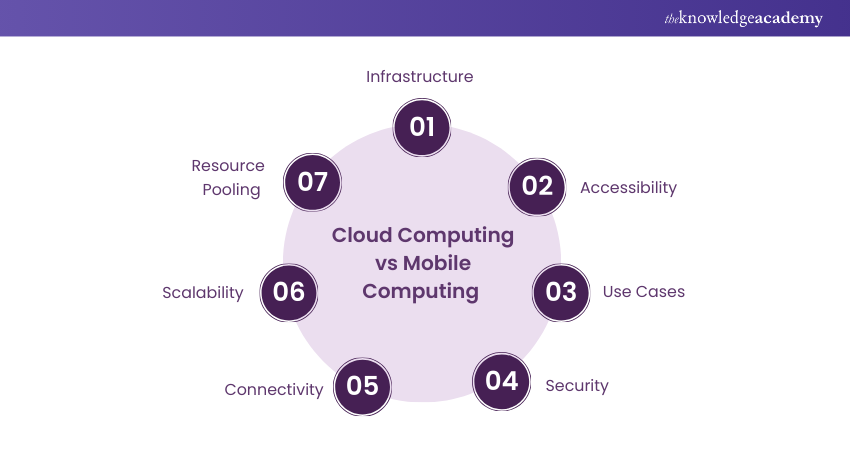
a) Infrastructure
b) Accessibility
c) Use Cases
d) Security
e) Connectivity
f) Scalability
g) Resource pooling
4) Use Cases of Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing
5) Conclusion
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing has revolutionised data and application management by shifting from local storage to online solutions. It offers a range of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, and software, all delivered over the Internet. Instead of depending on local hardware, users access resources through remote servers in data centres. This approach enables access to data and applications from virtually anywhere with an Internet connection.

1) Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The key characteristics of Cloud Computing are as follows:
a) On-demand Self-service: Users can provision and manage computing resources as needed without requiring human intervention from service providers.
b) Broad Network Access: Cloud services are accessible over the internet from a variety of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers.
c) Resource Pooling: Cloud providers utilise multi-tenant models, where resources are pooled and dynamically allocated to serve multiple users, optimising efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
d) Rapid Elasticity: Cloud resources can be quickly scaled up or down to accommodate changing demands, ensuring flexibility and cost efficiency.
e) Measured Service: Users pay only for the resources they consume, which are typically measured in terms of processing power, storage, bandwidth, or active users.
2) Advantages of Cloud Computing
Cloud Computing offers numerous advantages, including:
a) Cost-efficiency: Organisations can reduce capital expenditures on hardware and software, as they only pay for the resources they use.
b) Scalability: Resources can be easily scaled up or down to adapt to changing workloads or business needs.
c) Accessibility: Cloud services are accessible from anywhere, facilitating remote work, collaboration, and access to critical data.
d) Reliability and Redundancy: Cloud providers offer high levels of uptime and redundancy, minimising the risk of data loss or service interruptions.
e) Automatic Updates and Maintenance: Service providers manage hardware and software updates, ensuring that users always have access to the latest features and security patches.
Start delivering patient-centric solutions today with our Cloud Computing Course - Sign up now!
What is Mobile Computing?
Mobile Computing involves the use of devices, applications, and services specifically designed for on-the-go use. This technology has revolutionised our interaction with digital information, enabling access to data and task completion from virtually anywhere without being confined to a fixed location. It’s a game-changer in modern connectivity.
1) Characteristics of Mobile Computing
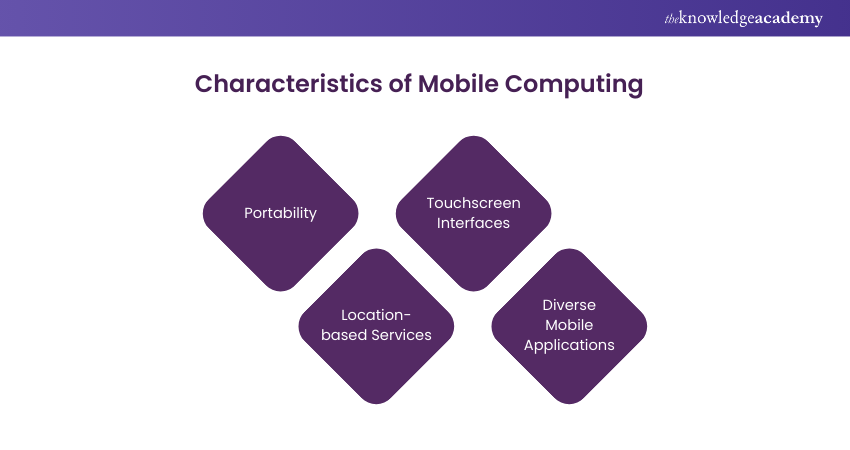
Key characteristics of Mobile Computing include:
a) Portability: Mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, are compact and lightweight, allowing users to carry them easily.
b) Location-based Services: Mobile Computing leverages GPS and other location technologies to offer services tailored to the user's current location, like navigation apps and location-based notifications.
c) Touchscreen Interfaces: Mobile devices are equipped with touchscreen interfaces, making them user-friendly and intuitive.
d) Diverse Mobile Applications: A vast ecosystem of mobile applications (apps) exists, catering to a wide range of needs, from productivity to entertainment.
Advantages of Mobile Computing
Mobile Computing offers numerous advantages:
a) Convenience and Mobility: Users can access information, communicate, and complete tasks on the go, enabling greater flexibility in work and personal life.
b) Real-time Information Access: Users can receive real-time updates and access the latest information, keeping them informed and up-to-date.
c) Enhanced User Experience (UX): Touchscreen interfaces, intuitive design, and interactive apps create a seamless and engaging User Experience.
d) Integration With Sensors and Hardware: Mobile devices incorporate various sensors like accelerometers, gyroscopes, and cameras, allowing innovative applications and features, such as augmented reality.
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing
Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing are two influential paradigms that have reshaped the digital landscape. Understanding their unique solutions is vital for individuals and organisations navigating diverse computing demands in the digital world. . In this in-depth exploration, we will delve into the distinctions in infrastructure, accessibility, use cases, security, connectivity, scalability, and resource pooling.
1) Infrastructure
Cloud Computing operates on a centralised infrastructure, relying on large data centers managed by providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. These data centres are often spread across different regions, as well as house servers, storage, and networking equipment. Users access cloud resources remotely, with providers managing the infrastructure.
Mobile Computing relies on a decentralised infrastructure. Processing power, memory, and storage are built directly into mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. While mobile devices can connect to cloud services, they function independently for many tasks due to their self-contained hardware. This independence reduces reliance on external data centres, enabling mobile devices to operate autonomously.
2) Accessibility
One of the hallmark features of Cloud Computing is its broad network access. Cloud services are accessible from virtually any device with internet connectivity. Whether you are using a desktop computer, a tablet, a smartphone, or even a smart home device, as long as they are connected to the internet, you can access cloud-based resources. This accessibility allows users to tap into cloud services from different locations and devices, promoting flexibility and convenience.
Mobile Computing is intrinsically linked to the capabilities of the mobile device in use. The accessibility of Mobile Computing is limited to the functionality and connectivity of the device itself. While mobile devices can connect to cloud services, they are subject to the constraints of their hardware and network capabilities, making them most effective for on-the-go tasks and interactions.
3) Use Cases
Cloud Computing is best suited for tasks that require extensive computing power, vast storage, and centralised data management. Common use cases include data storage, web hosting, big data analytics, Machine Learning(ML), and hosting complex applications. Businesses often leverage Cloud Computing for their servers and data storage to ensure scalability, redundancy, and cost-efficiency.
Mobile Computing is tailored for on-the-go activities and personal productivity. It excels in location-based services, quick access to information, and user-centric tasks. Typical use cases include GPS navigation applications, mobile gaming, social media interaction, and mobile productivity apps like note-taking and task management.
4) Security
Security in Cloud Computing is a shared responsibility between the service provider and the user. Providers ensure the security of the infrastructure, including data centres and network security, by implementing physical protection and data redundancy measures. Users, on the other hand, are responsible for securing their data through robust authentication and access control mechanisms.
In Mobile Computing, the onus of security primarily falls on the user. Due to the portable nature of mobile devices, they are susceptible to loss or theft, making device security crucial. Users must employ screen locks, encryption, and app-level security measures. Although mobile operating systems offer features like biometric authentication, the user’s role in safeguarding data and devices remains paramount.
5) Connectivity
Cloud Computing relies heavily on stable Internet connectivity. Users need a reliable and fast Internet connection to access cloud services effectively. The user experience (UX) is directly influenced by the availability and speed of the Internet. While some cloud services offer offline functionality, this feature varies across different applications.
Mobile Computing is designed for flexible connectivity. Mobile devices can access cloud services online but also function well with limited or no connectivity. Many mobile applications are optimised for offline use, syncing data with the cloud once a connection is restored. This ensures a more seamless user experience, even with intermittent Internet access.
6) Scalability
Cloud Computing offers unmatched scalability, allowing businesses to quickly adjust resources based on changing needs. This flexibility ensures cost-efficiency by enabling payment only for utilised resources, seamlessly adapting to demand fluctuations.
In contrast, mobile computing faces challenges related to scalability. Mobile devices have fixed processing power, storage, and memory, which cannot be easily expanded. While the number of mobile devices can increase, each device’s capabilities remain limited.
7) Resource Pooling
Cloud Computing optimises efficiency through resource pooling, where service providers share resources among multiple users. This dynamic allocation model reduces costs as users access shared resources like servers and storage, which are distributed based on demand.
In contrast, Mobile Computing operates with standalone devices, each managing its own resources. While mobile devices can connect to cloud services, they do not engage in resource pooling. Each device functions independently, relying on its internal capabilities.
Elevate your skills and master the latest strategies with our Mobile Marketing Course - Join now!
Use Cases of Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing
Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing have reshaped the digital landscape, offering diverse applications. Cloud Computing excels in data storage, web hosting, analytics, and AI. Mobile Computing empowers location-based services, mobile banking, social media, gaming, fitness, productivity, and immersive experiences.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
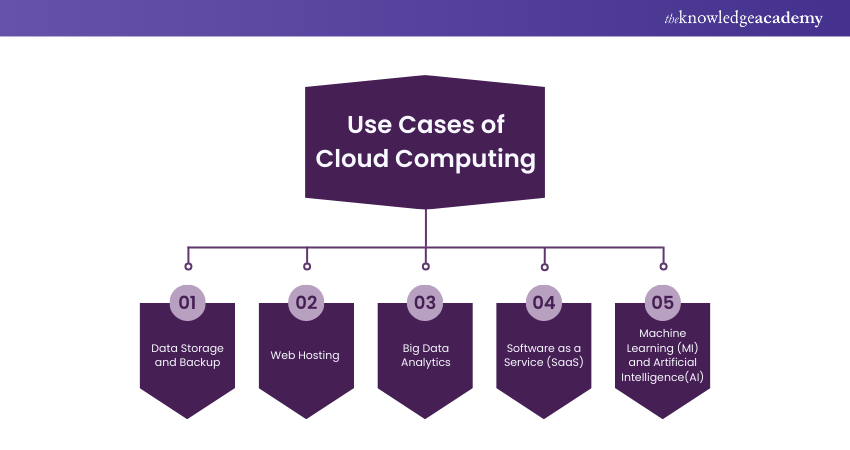
Cloud Computing offers a diverse range of applications for individuals and businesses, transforming the way we interact with digital resources. Here are some of its key use cases:
a) Data Storage and Backup: Cloud Computing plays a crucial role in data storage and backup, ensuring secure and accessible data for users and organisations. Services like Google Drive and Dropbox simplify data management.
b) Web Hosting: Cloud Computing is the backbone of scalable and reliable web hosting services. Platforms such as AWS and Microsoft Azure empower businesses with high-performance infrastructure for websites and applications.
c) Big Data Analytics: Organisations leverage Cloud Computing to analyse vast volumes of data efficiently. Cloud-based analytics platforms like Amazon Redshift and Google BigQuery provide valuable insights and data-driven decision-making.
d) Software as a Service (SaaS): SaaS applications, hosted in the cloud, offer accessible software solutions for various devices. Applications like Microsoft Office 365 and Salesforce reduce the need for local installations.
e) Machine Learning (MI) and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Cloud Computing provides computational power and tools for Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence. Developers use cloud services for training models and deploying AI-driven solutions across industries.
Turn your ideas into powerful apps with our Mobile App Development Training today!
Use cases of Mobile Computing:
Mobile Computing has revolutionised how we engage with digital resources on the go. Here are some key use cases that illustrate its versatility:
a) Location-based Services: Mobile devices equipped with GPS technology offer location-based services like navigation apps and location-aware marketing, enhancing User Experiences.
b) Mobile Banking and Payments: Mobile Computing facilitates secure access to banking services and mobile payments, enabling users to manage finances and make contactless transactions through apps like PayPal and Apple Pay.
c) Social Media: Mobile Computing has reshaped social media engagement, with apps like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter designed for mobile devices, fostering connectivity and interaction.
d) Mobile Gaming: The mobile gaming industry has surged, with smartphones and tablets becoming gaming platforms of choice. Popular titles like "Candy Crush" and "Fortnite" showcase the diversity of mobile gaming.
e) Health and Fitness: Mobile Computing is integral to the health and fitness sector, offering apps like Fitbit and Apple Health that allow users to monitor physical activity, health metrics, and fitness goals.
f) Mobile Productivity: Mobile devices come equipped with productivity apps for note-taking, document editing, and task management. Apps like Evernote, Microsoft Office Mobile, and Google Workspace enhance productivity on the go.
g) Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR): Mobile devices support AR and VR applications, revolutionising gaming, education, and entertainment experiences. Apps like Pokémon GO and Oculus offer immersive and interactive adventures through mobile technology.
Conclusion
It is important to grasp the Difference Between Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing in order to navigate modern digital landscapes. Cloud Computing serves as a centralised hub that provides extensive resources and scalability, while Mobile Computing offers the convenience and flexibility of accessing information while on the move. Collaboratively, they improve our digital interactions, increasing efficiency and flexibility. Understanding their unique and complementary functions enables you to make smart choices, maximising the use of technology in personal and professional environments.
Open the door to endless technological opportunities with our Cloud Computing Training - Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions

The outlook for Cloud Computing looks bright, thanks to advancements in edge computing, AI integration, and increased adoption of Hybrid Cloud. As more companies move to the Cloud, the need for scalable, secure, and efficient Cloud solutions will lead to innovation and shape the digital environment.

Mobile Computing's future potential is extensive, fueled by the increasing number of IoT gadgets, artificial intelligence, and improved connectivity. With the advancement in mobile device technology, complex applications, remote work, and smart environments will be enabled, reshaping industries and daily interactions by enhancing mobility and connectivity.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cloud Computing Courses, including the Cloud Computing Training, Certified Artificial Intelligence (AI) For Cloud Professionals Training, and Google Cloud Platform Fundamentals. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is Cloud Computing.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cloud, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 5th Dec 2024
Thu 13th Feb 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


