We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Game Development is a fascinating and multifaceted journey encompassing various stages to bring a game from concept to reality. Game Developers and enthusiasts need to understand these Game Development Stages to create breathtaking videogame titles. These stages can vary in nature, ranging from the initial spark of an idea to the thrilling release and beyond.
According to Statista, the users in the Video Games market are expected to grow up to a count of 3.10 billion by the year 2027. If you wish to embark on this journey of creating phenomenal video games and uncovering the secrets behind bringing interactive experiences to life, this blog is perfect for you. This blog discusses the Game Development Stages and their importance in the final product's success in detail.
Table of Contents
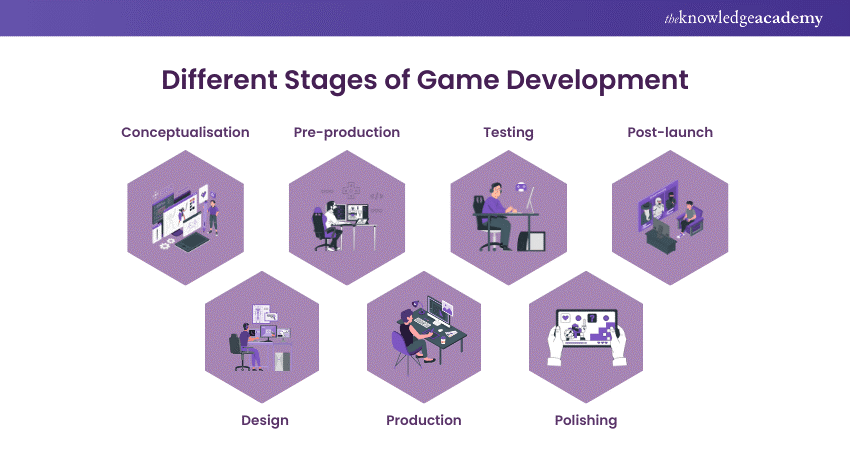
1) Stages of Game Development
a) Conceptualisation
b) Design
c) Pre-production
d) Production
e) Testing
f) Polishing
g) Post-launch
2) Conclusions
Stages of Game Development
Game Development Stages essentially refer to the different phases or steps in creating a video game. Game Development is a complex process that requires careful planning, creativity, and technical skills. These stages outline the major milestones and activities that Game Developers undertake from the initial concept to the game's final release. During the development satges unity projects provide the perfect platform for smoother process.
Interested in Video Games? Learn to make them with Game Development Training!
Conceptualisation stage
Conceptualisation is a vital stage in Game Development, laying the foundation for a successful game. It involves generating and refining ideas, defining the game's genre, target audience, and core gameplay mechanics. Developers create a vision for the game, outlining its story, characters, and art style. Through brainstorming sessions, concepts are explored, evaluated, and filtered based on feasibility, market appeal, and alignment with the team's vision.
Defining the game's genre sets the tone and establishes player expectations. It provides a framework for the game's mechanics and aesthetics to flourish. Understanding the target audience is equally important for Game Development, as it guides gameplay mechanics, narrative elements, and visual aesthetics decisions. By considering the preferences and interests of the intended players,Developers can tailor the game experience to meet their expectations.
Core gameplay mechanics form the backbone of any game. They define the rules, interactions, and progression systems that shape the gameplay experience. The Game Development team crafts the game's story, characters, and art style to further enrich the player's journey, creating a cohesive and immersive world. These elements work in harmony to captivate players and provide a memorable experience.

Design stage
In the design phase, the game concept starts to materialise into a cohesive vision. Developers create a detailed game design document outlining gameplay mechanics, level design, user interface, and audiovisual aesthetics. This blueprint guides the Game Development process, ensuring a focused, immersive player experience.
Gameplay mechanics are meticulously crafted by Game Development team, offering meaningful choices, challenges, and rewards. Level designers create engaging environments that captivate players and drive the narrative. User Interface (UI) designers focus on intuitive and visually appealing interfaces, enhancing player interaction. The art style, character designs, and sound design are carefully considered to create a cohesive and immersive world.
Throughout the design phase, collaboration and iteration are paramount. Regular team meetings and feedback sessions refine the design elements, ensuring cohesiveness and alignment with the game's vision. The design phase lays the groundwork for a successful Game Development process, setting the stage for the next steps, where the game truly comes to life in the Production phase.
Pre-production stage
Pre-production is a critical phase in Game Development where careful planning and preparation lay the groundwork for a successful project. During this Game Development Stage, Developers define the game's concept, establish the scope and goals, assemble the development team, and allocate resources effectively.
a) Establishing identity: One of the primary tasks in pre-production is generating ideas, refining the game's concept, and establishing its unique identity. It determines the game's genre, target audience, and core gameplay mechanics, creating a vision that guides the Game Development process.
b) Setting objectives: Defining the scope and goals is another crucial aspect of pre-production. Developers set realistic objectives, determine the desired features and content, and outline the project's timeline. This ensures the Game Development process remains focused, organised, and on track.
c) Gathering people: Assembling the Game Development team is key to a successful pre-production phase. Developers carefully select individuals with the necessary skills and expertise to contribute to the project. The team may consist of programmers, artists, designers, writers, and other specialised roles. Collaboration and effective communication among team members is essential for a smooth Game Development process.
d) Resource allocation: Allocating resources is also a significant consideration during pre-production. Developers identify the necessary tools, software, hardware, and other resources required for the Game Development process. Proper allocation ensures the team has the necessary assets to execute their tasks efficiently.
Production stage
Game production is the core step in Game Development Stages, where creative ideas become interactive games. This stage has several key phases, each with its own challenges and goals:
a) Prototyping: This is the first test of game mechanics, where Developers experiment and fix any design issues.
b) Visual content creation: This is where the game’s visuals are created, using different methods and tools for 2D and 3D games. 2D games require artistic skills such as sketching, colouring, and animating. 3D games require technical skills such as modelling, texturing, and animating.
c) Game level design development: This is where the game’s levels are designed, each with a purpose and a challenge, forming a coherent and captivating story.
d) Crafting the game’s logic: This is where the game’s logic and mechanics are developed, making sure the game is fun and consistent with its genre and theme.
e) Beyond levels: This is where the game’s narrative and economy are enhanced, adding elements such as plot, rewards, and hints to immerse the player in the game world.
f) Immersive game design: This is where the game’s audio and voice are added, creating soundtracks, sound effects, and voice acting to enrich the game’s realism and atmosphere.
g) Intricacies of coding: This is the final phase, where all the game components are coded and integrated, ensuring a smooth and exciting game experience.
Testing and iteration stage
During the testing and iteration stage, the game undergoes rigorous evaluation to refine and enhance the player experience. The Game Development team conducts functional testing to ensure mechanics work as intended, while performance testing optimises speed and stability. Playtesting gathers valuable feedback from real players, providing insights into gameplay, level design, and overall satisfaction.
The player feedback is used to make necessary adjustments and improvements, addressing any issues or concerns raised during testing. Developers iterate on the game by fine-tuning gameplay mechanics, improving level designs and refining the game's narrative based on the feedback received. This iterative process ensures the game aligns with player expectations and delivers an engaging and enjoyable experience.
Testing and iteration are integral stages in Game Development, allowing Developers to refine the game based on real-world feedback. Through testing and continuous improvement, the game's final version reaches its full potential, providing players with an immersive and captivating gaming experience.
Polishing stage
Polishing is a crucial stage in Game Development that focuses on enhancing the overall quality and refinement of the game. It involves fine-tuning various aspects to deliver a polished and immersive experience for players. During the polishing stage, developers pay meticulous attention to detail, addressing any remaining bugs, improving gameplay mechanics, and enhancing the game's visual and audio elements.
a) Gameplay refinement: Developers analyse player feedback, adjusting game mechanics to ensure a balanced and satisfying experience. They fine-tune controls, responsiveness, and difficulty levels to provide a smooth and enjoyable gameplay flow. Balancing factors such as pacing, challenge, and rewards contribute to the game's overall quality.
b) Visual and audio enhancements: Artists work on improving the game's graphics, animations, and visual effects to enhance immersion and aesthetics. Sound designers focus on enhancing the audio experience by fine-tuning sound effects, music, and voice-overs. The goal is to create a cohesive and captivating audiovisual presentation that complements the gameplay.
c) Bug fixing: Fixing bugs plays a crucial role in the polishing stage. Developers identify and resolve any remaining bugs, glitches, or technical issues that could impact the player experience. Thorough testing and debugging help ensure a smooth and stable game that minimises player disruptions and frustrations.
Code your game into reality with Python Game Development Training with Pygame Course!
Release and post-launch stage
The Release and Post-launch stage marks the culmination of the Game Development journey and is a critical phase in reaching players and ensuring the game's success. It involves preparing the game for distribution, executing marketing strategies, and providing ongoing support and updates to maintain player engagement.
a) Distribution preparation: During the release phase, Developers focus on finalising the game for distribution. This includes preparing the game for various platforms, such as consoles, PCs, or mobile devices, and ensuring compatibility and optimisation. Quality assurance testing is conducted to catch any last-minute issues that may arise.
b) Marketing strategies: Marketing strategies are crucial in promoting the game and reaching the target audience. Developers create marketing materials, such as trailers, screenshots, and promotional campaigns, to generate excitement and awareness. They leverage social media, websites, influencers, and gaming events to maximise visibility and attract players.
c) Post-launch support: Post-launch support is essential for maintaining player engagement and addressing any issues that may arise. Developers actively listen to player feedback, gather data, and provide regular updates and patches to improve the game's performance, fix bugs, and introduce new features. Community management and interaction help foster a dedicated player base, building loyalty and driving word-of-mouth promotion.
d) Expanding the player base: Ongoing marketing efforts continue post-launch to expand the game's reach and attract new players. Developers may release downloadable content (DLC) or expansions to offer additional gameplay experiences and extend the game's lifespan.
Conclusion
The Game Development process consists of several Game Development Stages, each with its own challenges and tasks. From conceptualisation to release and post-launch support, every stage plays a crucial role in bringing the game to life, ensuring its quality, engaging gameplay, and successful reception among players.
Learn to play with media and games with our HTML 5 Apps and Game Training!
Frequently Asked Questions

In Game Development Stages, Pre-production is the planning and design phase, where the game’s concept, genre, audience, mechanics, story, and art style are defined. Production is the implementation phase, where the game’s visuals, levels, logic, audio, and code are created and integrated.

Testing is the quality assurance phase, where the game is checked for bugs, errors, glitches, and performance issues. Testing ensures that the game is functional, stable, and enjoyable for the players.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Game Development courses, including HTML 5 Games training, Gamification training and Unreal Engine 4 Game Development Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Game Development methodologies.
Our Game Development blogs covers a range of topics related to Game Development, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Programming & DevOps skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Programming & DevOps Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Unreal Engine 4 Game Development Training
Unreal Engine 4 Game Development Training
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


