We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +43 720 115337 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Understanding the complexities of business technology management can be daunting. That's where frameworks like COBIT come into play. But do you know What is COBIT? It stands for Control Objectives for Information and Related Technologies. Initially developed by the Information Systems Audit and Control Association (ISACA), it is a comprehensive framework that helps govern and manage a company's Information Technology (IT) operations.
COBIT assists organisations in achieving their objectives for the Governance and Management of enterprise IT resources. It provides a toolset that aligns IT processes with business goals while helping organisations adhere to relevant laws, regulations, and policies.
Considering the huge benefits that this framework can provide, organisations willing to provide exceptional IT services must learn about it in extreme details. This blog will help you understand What is COBIT, its benefits, principles, frameworks, and compare it with other IT Governance frameworks.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is COBIT
2) Key principles of COBIT
3) Benefits of implementing COBIT
4) COBIT frameworks and components
5) COBIT vs. Other IT Governance frameworks: Key differences
6) Conclusion
Undestanding What is COBIT?
COBIT's meaning is deeply rooted in its primary objective: to bridge the gap between business and Information Technology (IT). It provides a robust framework that assists organisations in optimising the value they derive from their IT initiatives while ensuring compliance, risk management, and alignment with business objectives. COBIT emerged as a response to organisations' challenges in managing their IT functions.
Key principles of COBIT
The success of any framework lies in its guiding principles, which shape its philosophy, approach, and application. COBIT is no exception. It is built upon four key principles that serve as the foundation of its methodology, providing organisations with a structured approach to effective IT Governance and Management. Let's explore Principles of COBIT in detail:

Principle 1: Meeting stakeholder needs
COBIT is a framework that helps organisations align their IT processes with the needs and expectations of their stakeholders. It helps create value and balance business and IT goals. COBIT also helps improve stakeholder satisfaction, trust, and support for IT projects.
Principle 2: Covering the enterprise end-to-end
COBIT takes a holistic view of the enterprise and considers all aspects of IT Governance and Management. It ensures that no areas are overlooked and that all relevant processes are incorporated given in the framework.
COBIT encourages organisations to avoid siloed thinking and consider the broader impact of their IT decisions. By assessing the interconnectedness of IT processes across the organisation, organisations can identify synergies, eliminate redundancies, and create a cohesive IT ecosystem.
Principle 3: Applying a single integrated framework
Rather than reinventing processes from scratch, COBIT encourages organisations to leverage existing standards, regulations, and best practices. This principle promotes integration with other established frameworks, reducing complexity and redundancy.
Organisations can adopt COBIT alongside other frameworks like ITIL, ISO 27001, or NIST Cybersecurity Framework. This integration streamlines efforts, reduces duplication of work, and ensures that IT Governance and Management efforts are consistent and harmonised.
Principle 4: Enabling a holistic approach
COBIT promotes a seamless integration between Governance and Management activities. It acknowledges that Governance sets the direction while management implements the processes, and the two must work in harmony to achieve optimal results.
Organisations can implement COBIT by integrating governance and management processes. By aligning strategic decisions with operational execution, organisations ensure that IT initiatives are well-planned, effectively executed, monitored, and improved.
Principle 5: Separating Governance from Management
COBIT provides a clear distinction between Governance and Management. This distinction is crucial for the effective oversight and operation of enterprise IT. Governance primarily ensures that organisational objectives are set appropriately, and stakeholder needs are met.
On the other hand, management is more operationally focused. It encompasses the planning, building, running, and monitoring of activities and ensuring that they align with the direction set by the governing body.
Master COBIT principles and advance your IT Governance expertise with our comprehensive COBIT Training – register today!
Benefits of implementing COBIT
Implementing COBIT offers many benefits to organisations that seek to enhance their IT Governance and management practices. Let's delve deeper into the Benefits of COBIT:
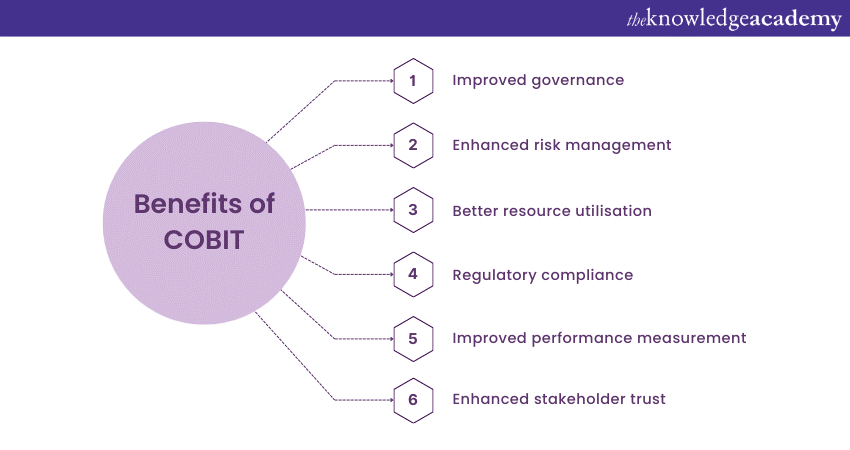
1) Improved Governance
COBIT strongly emphasises effective Governance, which is essential for organisations to make informed decisions, allocate resources wisely, and ensure accountability. By providing a structured approach to Governance, COBIT enables organisations to establish clear lines of authority, decision-making processes, and responsibilities.
This leads to a more transparent and efficient Governance structure. This, in turn enhances the organisation's ability to manage risks, align IT strategies with business goals, and make optimal decisions.
2) Enhanced risk management
Effective risk management is critical for mitigating potential threats and minimising the impact of unexpected events. COBIT's focus on risk management as a core Governance objective ensures that organisations identify, assess, and address risks related to their IT activities.
By implementing COBIT's risk management practices, organisations can proactively identify vulnerabilities and implement controls to prevent or mitigate the impact of risks. This proactive approach enhances the organisation's resilience and ability to navigate challenges effectively.
3) Better resource utilisation
Resource allocation is a crucial aspect of IT Governance, as organisations must use their resources efficiently to achieve optimal outcomes. COBIT guides how to allocate resources based on business priorities and strategic goals.
This ensures that resources such as time, finances, and personnel are directed toward initiatives aligning with the organisation's objectives. As a result, organisations can minimise resource wastage, enhance operational efficiency, and achieve a higher return on investment.
4) Regulatory compliance
In today's regulatory landscape, organisations face numerous compliance requirements related to data protection, security, and industry-specific regulations. COBIT assists organisations in navigating these complexities by providing a structured approach to compliance management.
By aligning its processes with relevant regulations and standards, an organisations can ensure that they meets legal and industry requirements. This helps reduce the risk of legal and financial penalties and enhances the organisation's reputation as a responsible and compliant entity.
5) Strategic alignment
Aligning IT initiatives with business goals is a challenge that many organisations face. COBIT addresses this challenge by emphasising the importance of strategic alignment as a Governance objective.
The framework ensures that IT strategies are developed and executed harmoniously with the organisation's broader objectives. This alignment fosters a more cohesive approach across different departments, As a result, organisation can foster collaboration, more effective use of resources, and a greater likelihood of achieving organisational success.
6) Improved performance measurement
Measuring the performance of IT processes is essential for continuous improvement and accountability. COBIT provides a structured approach to performance measurement through its metrics and indicators.
These metrics enable organisations to monitor the effectiveness of their Governance and Management practices, identify areas for improvement, and track progress over time. By analysing these metrics, organisations can make data-driven decisions, optimise processes, and ensure that their IT activities contribute to their success.
COBIT frameworks and components
The COBIT framework is a robust and comprehensive model designed to guide organisations in achieving effective IT Governance and Management. It comprises several interconnected components, each crucial in ensuring alignment between business objectives and IT activities. The following are the key components that make up the COBIT framework:
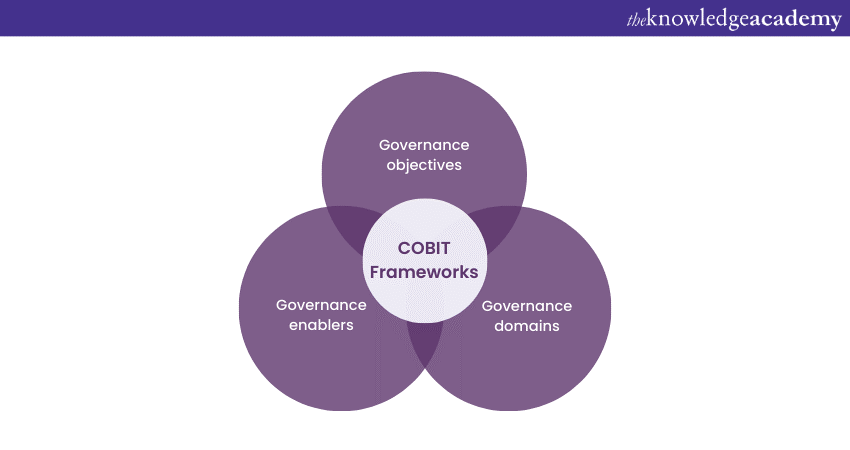
a) Governance objectives: COBIT defines five Governance objectives that guide the development and implementation of IT-related processes. These objectives encompass strategic alignment, value delivery, risk management, resource management, and performance measurement.
b) Governance domains: COBIT organises IT activities into seven Governance domains, each addressing a specific IT Governance and Management aspect. These domains include evaluating, directing, and monitoring the organisation's IT resources to ensure alignment with business objectives.
c) Governance enablers: Governance enablers represent how organisations achieve their Governance objectives. They are categorised into seven enablers, namely principles, policies, processes, organisational structures, culture, information and services, infrastructure, and applications.
COBIT vs. Other IT governance frameworks: Key differences
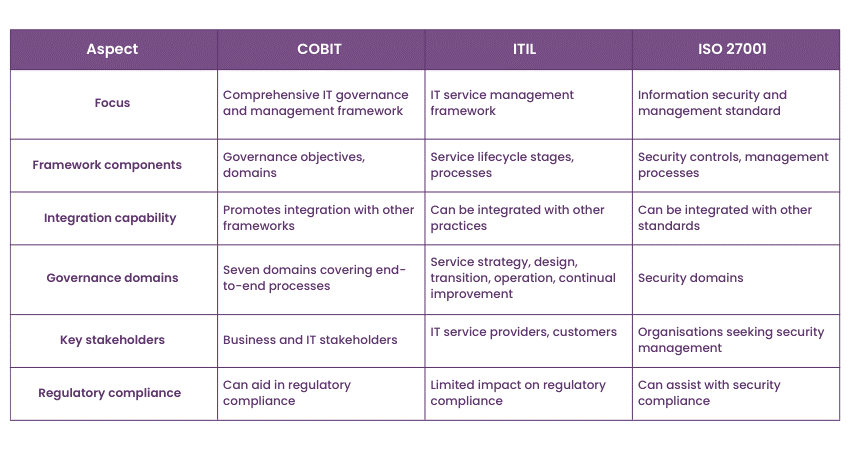
In IT Governance, various frameworks and standards have emerged to help organisations effectively manage their information and technology assets. COBIT is a prominent player, offering unique features and capabilities that differentiate it from other IT Governance frameworks. Such frameworks include the Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL) and ISO 27001. Understanding the distinctions between COBIT and these frameworks is essential for organisations seeking to make informed decisions about their IT Governance strategy.
1) COBIT
COBIT focuses on control objectives and IT alignment with business goals. It provides a comprehensive framework that covers a wide spectrum of IT-related processes and activities. COBIT emphasises the importance of Governance, risk management, and compliance, helping organisations ensure that their IT initiatives contribute to overall business value while minimising risks. The following are the key characteristics of COBIT:
a) Control objectives: COBIT sets clear and specific control objectives for IT processes, aiding in achieving consistent levels of control and compliance.
b) Process-oriented: It defines a comprehensive set of processes organised into four domains, encompassing the entire IT management lifecycle.
c) Holistic approach: COBIT covers a wide range of IT-related areas, including Governance, risk management, resource optimisation, and performance measurement.
2) ITIL
ITIL, on the other hand, centres around IT Service Management (ITSM). It provides a set of practices for delivering and managing IT services in alignment with business needs. ITIL emphasises the importance of customer satisfaction and continual service improvement. The following are its key characteristics:
a) Service-centric: ITIL's main focus is on delivering quality IT services that meet customer requirements and contribute to business objectives.
b) Service lifecycle: It defines a lifecycle approach to service management, including stages like service strategy, design, transition, operation, and continual service improvement.
c) Process integration: ITIL highlights processes that ensure efficient service delivery, incident management, problem resolution, and change management.
Transform your IT service management proficiency with our ITIL Certification Training. Join now to advance your skills!
3) ISO 27001
The ISO 27001 is an Information Security Management System (ISMS) standard recognised globally. It offers a systematic approach to managing and protecting sensitive information within organisations. Its key characteristics are as follow:
a) Security management: ISO 27001 helps identify, assess, and manage information security risks.
b) Risk-centric: It requires organisations to establish a risk management framework that addresses security threats and vulnerabilities
c) Compliance and certification: ISO 27001 offers a certification process demonstrating an organisation's commitment to best practices for information security.
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog and, understood What is COBIT, explored its principles, frameworks and benefits. As organisations strive to balance the potential of technology with the need for robust control and Governance, COBIT offers a structured approach that facilitates collaboration, enhances decision-making, and ensures the achievement of strategic objectives. Its comprehensive framework provides a roadmap for enterprises to navigate the complex intersection of technology and business successfully.
Elevate your IT Governance skills with COBIT Foundation Training- sign up now for a comprehensive learning experience.
Frequently Asked Questions

COBIT has four levels of hierarchy which include the following:
a) Enterprise goals: These are the strategic objectives of the organisation, such as increasing customer satisfaction, reducing costs, or enhancing innovation
b) Alignment goals: These are the outcomes that I&T should deliver to support the enterprise goals, such as delivering reliable information, enabling business agility, or optimising IT assets
c) Governance and management objectives: These are the activities that need to be performed to achieve the alignment goals, such as ensuring stakeholder transparency, managing performance, or overseeing risk
d) Governance and management processes: These are the processes that implement the governance and management objectives, such as plan and organise, acquire and implement, deliver and support, and monitor and evaluate

The time required to learn the COBIT 5 material depends on the individual and the level of certification they are pursuing. Generally, training courses are delivered over 3 days. However, some providers may offer tailored and blended learning solutions that can vary in duration. If you are self-studying for the exam, you will need to review the relevant ISACA publications, which can be purchased from their website.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various COBIT Training, including COBIT® Foundation. The course caters to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into COBIT vs ITIL
Our IT Service Management blogs covers a range of topics related to COBIT, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Service skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Service Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 COBIT® Foundation
COBIT® Foundation
Thu 6th Mar 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 4th Sep 2025
Thu 13th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


