We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +61 272026926 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

The term “Computer Worm” conjures images of stealthy, self-replicating threats that burrow through networks with alarming efficiency. But what exactly is this, and how does it differ from other cyber threats? At its core, this type of malware replicates itself to spread to other computers, often exploiting vulnerabilities in network security. Have you ever wondered how these worms navigate the vast expanse of the internet to find their next host?
This blog delves into the intricate workings of these digital parasites. It will explore the sophisticated mechanisms that enable a Computer Worm to spread without human intervention, the potential havoc it can wreak, and the subtle signs that may indicate an infection. Let’s dive in to know more!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Computer Worm?
2) How does a Computer Worm Spread?
3) Types of Computer Worm
4) Computer Worm Examples
5) Signs of a Worm Infection
6) How to Remove a Computer Worm?
7) How to Prevent Computer Worm Infections?
8) What's the Difference Between a Worm and a Virus?
9) Conclusion
What is a Computer Worm?
A Computer Worm is a type of malware that independently infiltrates and proliferates across computer networks, exploiting security gaps to duplicate itself. Unlike viruses, worms operate autonomously, not needing to attach to other programs for distribution. They pose a significant threat due to their ability to self-replicate and disperse rapidly without human intervention, affecting computers, smartphones, and tablets alike.
These Computer Worms, which are a subset of Trojan malware, are notorious for their capacity to spread swiftly and silently. They can self-propagate through internet connections or local networks, bypassing the need for human activation. As Trojans deceive users into executing them by appearing as trustworthy software, worms leverage network vulnerabilities as their attack vectors.
How Does a Computer Worm Spread?
Computer Worms are malware that can be spread through various means, such as software vulnerabilities, spam emails, instant messages, or files downloaded from unsecured sources. These worms can also be distributed through Social Engineering, which involves tricking people into taking actions they would not usually take. This can include tactics like phishing, which consists of transmitting fraudulent emails or messages that seem to be from a trustworthy source. Some worms can replicate themselves on networks by exploiting security holes in software or spreading through shared access points.
Worms can infect systems through third-party devices like Universal Serial Bus (USB) sticks or external hard drives. To avoid potentially harmful Computer Worms, it is crucial to be wary when opening emails or downloading files from untrusted sources. Let’s learn about how it spreads:
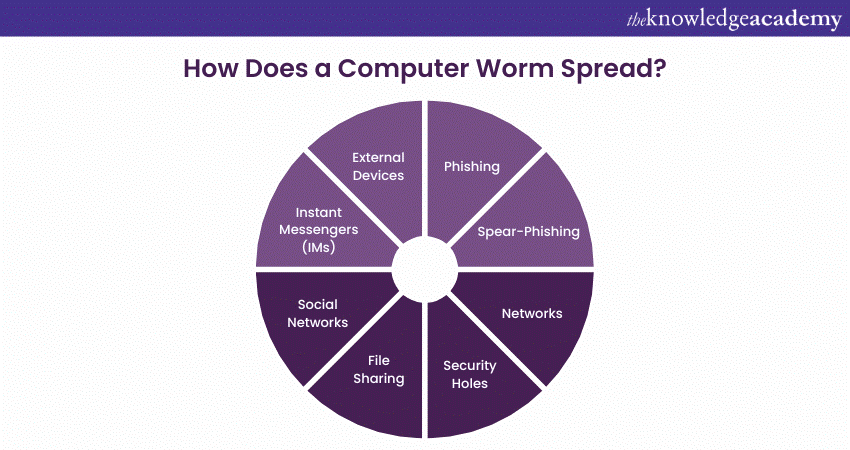
a) Phishing: In cybersecurity, social engineering attacks are a growing concern. These attacks involve using deceptive tactics to manipulate users into clicking on malicious links or visiting websites developed to infect their devices with malware. Social engineering attacks are becoming more prevalent with the increasing popularity of Instant Messaging (IM) platforms like Internet Relay Chat (IRC). One must know the warning signs to protect oneself from these threats and take precautions to safeguard our devices and personal information.
b) Spear-Phishing: Spear Phishing is an email or electronic communication scam targeting a specific individual, organisation, or company. The perpetrator's objective is to obtain confidential data for malicious purposes, but they may also aim to install dangerous software on the victim's computer. Spear Phishing is a highly targeted and personalised cyber-attack that often employs social engineering tactics and research to appear legitimate and trustworthy to the victim.
c) Networks: Computer networks are highly vulnerable to attacks by worms, which can enter the network via shared access, security holes in programs, and file sharing. These malicious entities can exploit software vulnerabilities to spread across networks, causing widespread damage. In addition, worms can be manually installed by unauthorised personnel who have gained access to a computer. Once a worm spreads across a network, it can affect every device that is connected to it.
d) Security Holes: Exploiting software vulnerabilities is a method that some worm versions use to access a computer system.
e) File Sharing: Computer Worms that spread via file sharing will duplicate themselves and store them in a shared folder before sending it out across a peer-to-peer network.
f) Social Networks: Worms have caused issues on several social networking sites, including MySpace, which hosts user content.
g) Instant Messengers (IMs): Text messages and instant messaging services, such as Internet Relay Chat, are prime vectors for transmitting malicious software, including worms (IRC).
h) External Devices: Worms can infect external hard drives and USB sticks.
Sign up for our comprehensive Cyber Security Risk Management Training and empower yourself with the knowledge to safeguard your digital assets.
Types of Computer Worm
There are several types of adversarial Computer Worms; the following are some of the important types of Computer Worms:
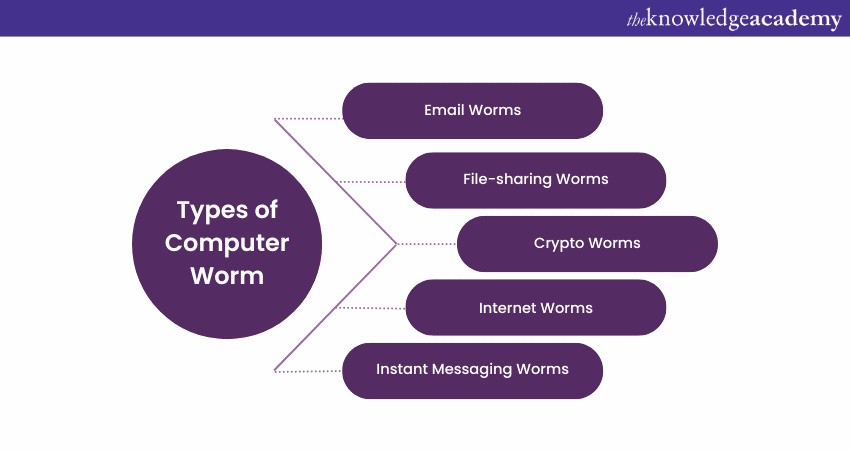
1) Email Worms
Email worms replicate themselves by generating new messages and sending them to all the addresses stored in a user's contact list. Successful email worms often use social engineering and phishing methods to entice users to click the attached file. The emails include a malicious executable file that infects the new machine when the receiver downloads the attachment.
2) File-sharing Worms
As a means of propagation, worms can replicate their files in shared folders and swiftly spread across peer-to-peer networks. These malicious programs, intentionally camouflaged as data files, are created by their authors to infect many computers.
Join our Computer Forensics Foundation Training and master the art of digital investigation – sign up now!
3) Crypto Worms
A crypto worm is a type of malware that targets a computer system and encrypts the data, making it inaccessible to the user. Hackers often use This type of worm in ransomware attacks, where they seize control of the victim's information and demand payment in exchange for a decryption key that can open the files. These episodes can have excruciating consequences for individuals and organisations, resulting in critical data loss and significant financial costs.
4) Internet Worms
A particular category of Computer Worms has a specific purpose of targeting widely used websites with weak Cyber Security measures. The ultimate goal of these worms is to infiltrate the website's system, which then allows them to spread to any computer that has accessed the site and infect them as well.
5) Instant Messaging Worms
Like email worms, Instant Messaging (IM) worms conceal themselves within attachments or links. Once opened, the worm will spread to the contacts within the infected person's list. The main distinction is that instead of email, it enters through an instant message on a chat platform.
Computer Worm Examples
The history of Computer Worms dates back over fifty years, with the inaugural worm, Creeper, emerging in 1971. Although not designed to be harmful, Creeper set the stage for subsequent impactful attacks. Here’s a refined overview of some notable worms:
a) Morris (1988): Created by Robert Morris, this worm unintentionally overloaded 6,000 UNIplexed Information Computing System (UNIX), leading to crashes and damages worth £78,826.50 to £78,82,650.00 million.
b) SQL Slammer (2003): This worm caused widespread internet disruption and router crashes globally, infecting 75,000 victims within minutes.
c) Mydoom (2004): Targeting Windows systems, Mydoom became one of the fastest-spreading worms, causing an estimated $38 billion in damages. It persists, accounting for a significant portion of malicious emails.
c) Storm Worm (2007): Utilising a catastrophic European storm as a lure, the Storm Worm infected millions of computers through deceptive emails.
e) Duqu (2011): A sophisticated worm, Duqu is believed to be related to Stuxnet, which disrupted Iranian nuclear facilities. It gathers intelligence potentially useful for attacking industrial controls.
f) ILOVEYOU (2000): Masquerading as a love letter, this worm rapidly infected over 50 million PCs, accruing a removal cost of approximately £1,18,23,900.00 billion.
Advance your career with our Digital Forensics Training – register today and dive into comprehensive modules and practical exercises.
Signs of a Worm Infection
Endpoint protection solutions are critical in defending against Computer Worms. To ensure these security measures are effective in thwarting worms (and other threats), one should access the dashboard and review the most recent endpoint protection report.
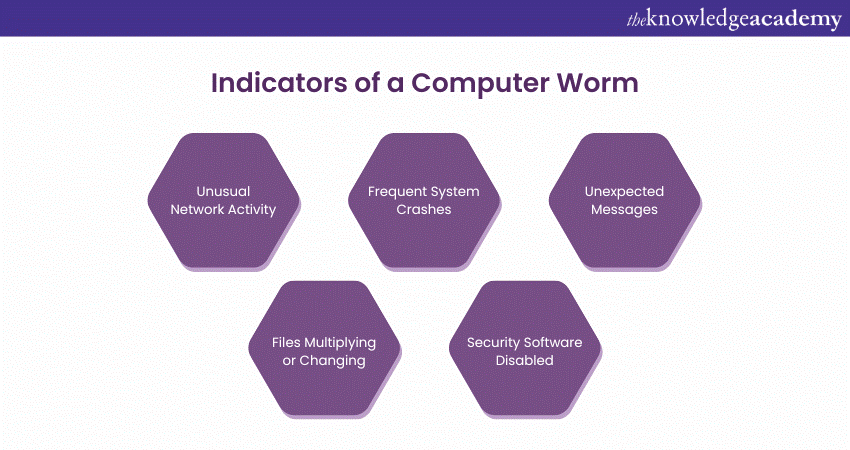
Conversely, if an endpoint protection solution fails to identify and halt a Computer Worm, certain indicators may become apparent:
a) Diminished system performance due to elevated Central Processing Unit (CPU) resource consumption
b) Files and folders that are concealed or absent
c) Unsolicited emails being dispatched to your contacts
d) Unexpected crashes of computer applications
e) Unfamiliar files or programs appearing on the computer that were not installed by you.
f) Automatic execution of programs or launching of websites
g) Atypical browser functionality or erratic program behaviour
How to Remove a Computer Worm?
Eradicating a Computer Worm can be challenging. In severe instances, it may necessitate reformatting the system, leading to the reinstallation of all software. During the initiation of an incident response, it’s advisable for security teams to utilise a verified secure computer to download necessary updates or software onto an external storage device, which can then be installed on the compromised system.
If the specific Computer Worm is identifiable, there may be targeted guidelines or utilities available that facilitate its removal without the need for a complete system reset.
Prior to attempting worm removal, ensure the system is disconnected from the internet, as well as any wired or wireless networks. Additionally, detach any temporary storage mediums like USBs or external hard drives, and conduct separate scans for infections.
After isolating the system, proceed with the following steps:
a) Update all antivirus definitions
b) Perform a scan using the updated antivirus program
c) Employ the antivirus to eliminate any detected malware, malicious code, and worms and to sanitise any infected files.
d) Verify that the operating system and all software are current and that patches have been applied.
How to Prevent Computer Worm Infections?
Maintaining robust Cyber Security practices is crucial for shielding systems against Computer Worms. Adopting the following strategies can bolster defences against the menace of worm infiltrations:
a) Regularly update the operating system and apply software patches
b) Implement firewalls to guard against malevolent software
c) Utilise antivirus software to block the execution of harmful software
d) Avoid engaging with email attachments or links within various messaging platforms that could introduce malicious software to the system.
e) Employ encryption to secure confidential information on computers, servers, and mobile devices.
What's the Difference Between a Worm and a Virus?
Here are five key differences between a Computer Worm and a virus:
a) Propagation: A Computer Worm can spread independently and self-replicate without human intervention. In contrast, a virus requires human action to spread, such as opening an infected file.
b) Host Dependency: Viruses need a host file or program to attach themselves to and remain dormant until triggered. Worms do not require a host and are stand-alone malicious programs.
c) Objective: While both can cause damage, worms primarily aim to consume system resources and slow down the system, whereas viruses tend to modify or delete data.
d) Control: Worms can sometimes be controlled remotely, but viruses cannot be controlled once they have infected a system.
e) Detection and Protection: Both worms and viruses can be detected and removed by antivirus software, but worms can also be blocked by firewalls due to their network-based nature of spreading.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Computer Worms are rather sophisticated entities capable of causing widespread disruption. Awareness and vigilance are the best allies in combating these silent invaders. So, stay informed, stay secure, and ensure that the cyber environments remain resilient against the relentless tide of these worms.
Master the techniques to thwart Cyber-attacks with our Malware Analysis Training – secure your spot now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Yes, Computer Worms still exist. They are malicious software that replicate themselves to spread to other computers, often causing harm.

Computer Worms can be extremely harmful as they may consume system resources, steal sensitive data, or install additional malware.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cyber Security Trainings, including the Cyber Security Awareness Course, Cyber Security Risk Management Course, and Social Engineering Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Internet Security.
Our IT Security & Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to Computer Worms, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your IT Security & Data Protection skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 7th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 12th Sep 2025
Fri 14th Nov 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


