We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +61 272026926 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Cyber-crimes have become an ever-rising threat to enterprises due to rapidly advancing technologies. According to Statista, cybercrime is expected to surge drastically by 2023, with its global cost rising from £ 7 trillion to £ 19.77 trillion. As cybercrime grew more threatening, measures to stop them, have become equally robust, referred to as Cyber-Security. Certain legal and governing bodies have pre-established standards for such measures and demand compliance with these Cyber-Security standards.
These standards protect sensitive data from unauthorised access, provided that large enterprises follow strict Cyber-Security Compliance. Cyber Security Compliance means meeting the standards and regulatory requirements established by an agency, legislation or group of authorities. Read more!
Table of contents
1) What is Cyber Security Compliance?
2) Cyber security and compliance standards
3) Importance of Compliance in Cyber Security?
4) Conclusion
Wish to learn more about Cyber threats? Take our course in Cyber Security Awareness!
What is Cyber Security Compliance?
Measures are taken to ensure protection against potential threats to a computer network and its systems are collectively called cyber security. It has become a vital part of modern network infrastructure and is now regulated by law and public expectations. These mandatory standards for cyber security, defining the network infrastructure, and employee policies are now called Cyber-security Compliances.
Such compliances involve step-by-step processes such as risk assessment of an enterprise's current network architecture, reporting the flaws within the system and network, tallying the needs and necessity of the company with its demands and budget, and finally making necessary changes, ensuring a company adheres to a certain standard. Suppose the network security architecture is found to be vulnerable to cyber-attacks. In that case, a company might hire a cyber security architecture specialist, referred to as a cyber security architect or simply a security architect.
A security architect uses various methods like penetration testing and ethical hacking to protect a network from malicious cyber-attacks and unauthorised access. Suppose a cyber security architecture fails to adhere to a compliance standard. In that case, the architect is responsible for making some changes based upon the need of the said company and training non-technical employees about new security-abiding policies.
These regulations help a company be more compliant with cyber security standards, making their services reliable. This helps a company build trust in the general public, ensuring their sensitive data stays safe and well-defended. Public faith plays a huge part in the necessity of Cyber Security Essentials compliance, as a company that ends up having a data breach puts its customer at unfathomable risks, making people unlikely to trust them or use their services again.
Interested in becoming a security architect? Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect SC100 is the right fit for you!
Implementing Cyber Security Compliance
Cyber-Security compliance focuses on implementing certain framework standards upon an enterprise which stores and works with sensitive data. These standards are based on an analysis of a business's working environment, policies and the type of data processed in that enterprise. Once the needs of an enterprise are established, certain steps are followed to ensure the company adheres to cyber-security standards, and they are as follows.
1) Creation of a compliance team
Creating a dedicated team is the first step to implementing a cyber security standard. This team aims to reinforce the organisation’s adherence to the cyber-security standard. Additionally, due to the constant virtualisation of enterprises across the globe, the team must be well integrated with all other team and their workflow. This ensures and promises protection against cyber-attacks in all instances possible.
2) Risk assessment in an organisation
The second step is evaluating the current cyber security architecture within an enterprise. This helps the compliance team document the current flaws of a company and potential improvements within the enterprise.
This process generally involves assessing an enterprise’s cyber architecture, consisting of the data, system and networks. The list of flaws is then sorted by protection priority, based on legal obligations. The compliance team reinforces their security in the respective order of priority.
3) Establishing security control
Once the risk and risk levels have been evaluated, necessary changes are made within a company. These changes come in the form of security-based controls that check for authorisation on different levels. Some examples of such security-based controls are password-based access, data encryption and metric identification, such as optical and fingerprint detection, and firewalls within the network.
4) Policy creation
Security Compliances are just benchmarks for cyber security in essence, hence in order for them to have any effect, they need to be implemented first. Even a perfect framework for cyber-security isn’t useful at all if it isn’t implemented correctly on a physical and social level.
The physical level implementation for the cyber security framework is done through security control, while social implementation is done by establishing policies. These policies act as guidance and protocols for most employees in case of data breaches. A cyber security policy is often revised and updated to ensure it stays updated against potential threats.
5) Monitoring and reporting
A well-established framework and a well-defended system today might be a victim of a new form of cyber threat tomorrow. Cyber threats evolve and scale with technology. Thus cyber-security measures need to evolve with them. For instance, a previously unnoticed vulnerability would eventually mean a new method for cyber-criminals to obtain and exploit data. Such instances are regarded as Zero-day attacks.
A cyber-criminal may even rework an existing strategy, such as merging two previously used ransomware into newer, stronger ransomware, thus bypassing the previous security measures. Monitoring the state of a computer network and its system is extremely necessary to avoid such instances. If a cyber threat such as a data breach occurs, such an occurrence can be immediately reported, letting a compliance team create new countermeasures against them.
Wish to master the art of preventing Cyber-attacks? Then register for the CCNA Cybersecurity Operation Training today!
Cyber Security and compliance standards
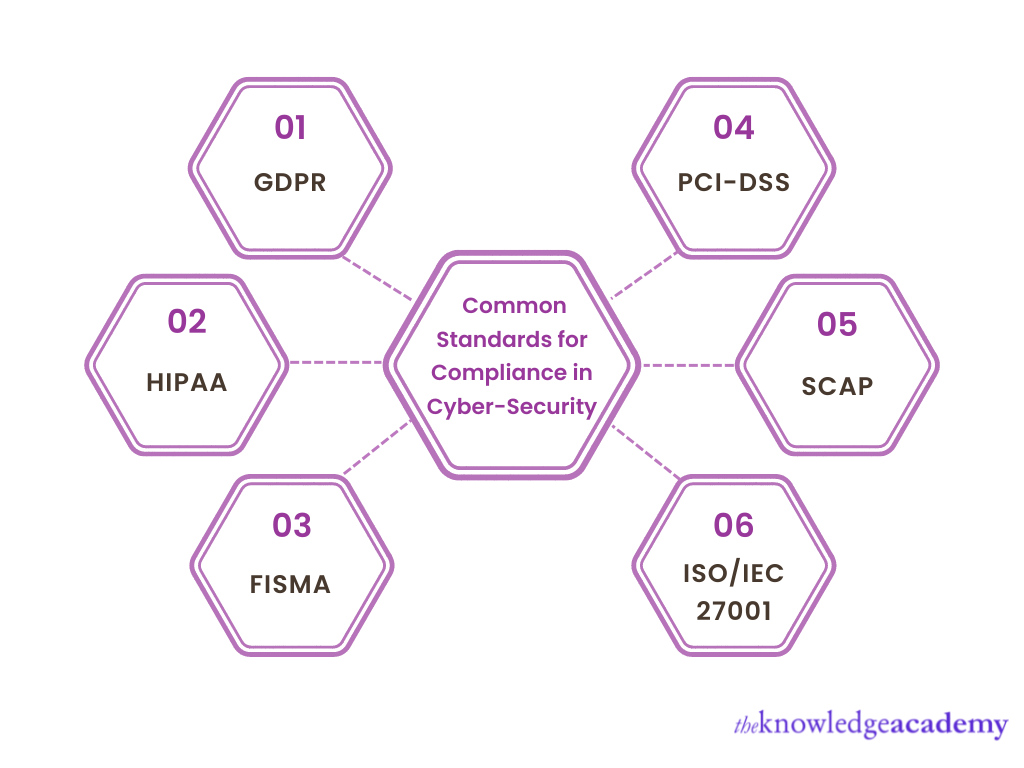
Despite many cyber security standards across different premises, all Cyber-Security Compliances have one goal, to ensure a system and its network is well defended against external threats and internal failures.
However, enterprise cyber-security standards vary based on the data type it uses, its location, and the market it operates in. Cyber-attacks pose a core threat to personal information such as a person’s full name, address, phone number or social security. Different Cyber-Security Compliance is established on factors for enterprises. Some of such standards are as follows.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
GDPR is a legal framework that establishes principles for handling European person’s sensitive data. According to GDPR, A company must provide clear terms and conditions about its data collection policies and allow the person to change the availability status of their data. The person’s consent directly determines the usage of their personal information. It was established in 2016, and its standards and compliance apply to the European Union (EU) and all Economic Area Countries (EEA).
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
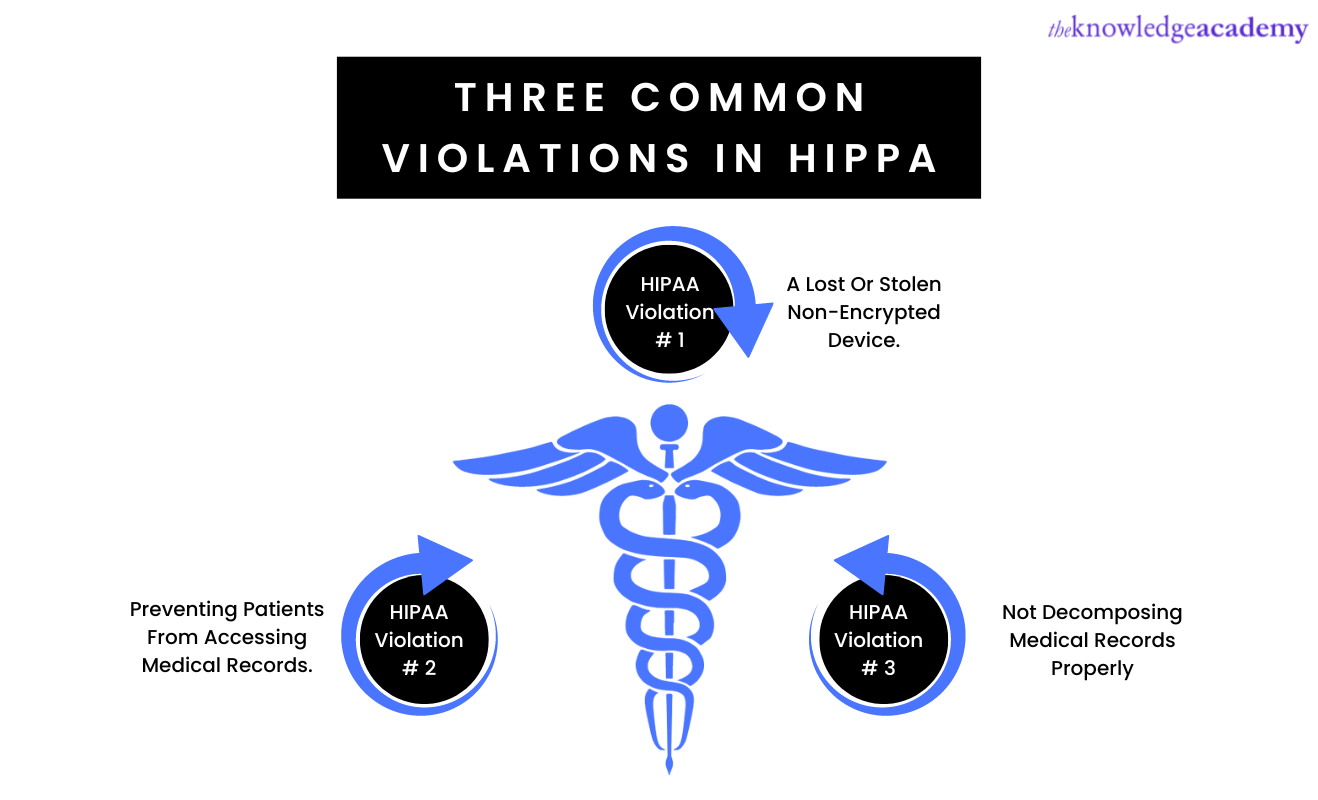
HIPAA standards and their compliance apply to all transactions for all health-relevant information. This applies to medical facilities like healthcare providers and healthcare clearinghouses. It implements that all transactions of health info must be covered electronically. Some such transactions are receiving payment, processing claims and sharing vital information like medical history and prescription records. This reinforces the concealment of any health-relevant information. HIPPA was signed into law in the year 1996 in the United States.
Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA)
FISMA is a large-scale framework which protects security and economic interest-based information from data breaches. FISMA compliance is strictly implemented within the federal system of the United States. It is a minimum security standard to prevent cyber threats on any national-level system and its data. FISMA was published in the year 2002.
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS)
PCI-DSS is a security standard established for credit-card protection to protect cardholders’ data. PCI-DSS is administrated by PCI (Payment Card Industry) standards council, and its compliance applies to all merchants handling payment-based information. These standards consist of elements such as a firewall, data encryption, password usage and access restriction to credit card information it was established in the year 2006.
Security Content Automation Protocol (SCAP)
SCAP standard is used to determine flaws within the software, which can pose a risk to security policies. It enables automated management for any vulnerabilities within an organisation's information system and checks the state of security policy compliance.
Internationaal Organization for Standardization (ISO/IEC 27001)
ISO 27001 signifies the adherence to cyber security-based rules and policies on all levels in an enterprise, such as people, processes, tools and the system itself. It’s an international Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) standard focusing on building a resilient cyber security management system. It was established in the year 2005 and it belongs to the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 27000 family of standards.
Importance of Compliance in Cyber Security?
Strong compliance with cyber security has many benefits, not limited to simply being well-defended from cyber-attacks. Some of such alternative benefits are as follows.
1) Positive public reputation: Compliance with cyber security standards promises a good reputation. This results in gaining customers' trust and thus gaining loyal customers.
2) Legal obligations: Cyber-security compliance is mandated by law in the majority of locations across the globe. The guiding standard for these laws may vary, but it is generally a good idea to abide by legal regulations and compliance. Many of these laws also impose heavy penalties for failing to adhere to them.
3) Reliable and trustworthy business: A well-defended business will earn customer trust and be a more reliable choice for other businesses and partnerships.
4) Efficient architecture: Cyber-security compliances rigorously analyse the state of network architecture. Hence any changes made within it result in more streamlined data and better data flow. This benefits the working process and data handling within the company, hence increasing the all over productivity.
5) Advantage against the competition: In this competitive day and age, people can choose a service from many options. Thus, customers are more likely to choose services from a company with databases better defended from cyber-attacks, giving a business a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Legal bodies and public expectations today mandate cybersecurity frameworks. Failure to comply with cyber security can often pose huge threats to an enterprise's customers and employees. Cyber Security Compliance can be confusing to relatively new firms and old firms alike. Still, this blog hopefully helped you better understand cyber security compliance, thus helping you establish a better, robust cyber security architecture.
Interested in becoming a Cyber-Security specialist? Join our Cyber Security Training course!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course






 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


