We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +61 272026926 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In this digital age, where innovation knows no bounds, the agricultural landscape is experiencing a remarkable evolution, and at the heart of this evolution lies the groundbreaking concept of IoT in Agriculture.
The fusion of Internet of Things (IoT) technology with age-old farming practices has given rise to a new era of smart and interconnected agricultural systems. This is why, according to Statista, the revenue in the IoT market is projected to reach £ 932.36 billion in 2023.
So, if you are willing to explore the wonders of Internet of Things in Agriculture and technology leverage data-driven decision-making, and minimise waste, it’s time to explore about this field in detail. Don’t know how? Read this blog to learn about IoT in Agriculture, its definition, applications, benefits, and the promising future it holds for sustainable farming practices.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding IoT in Agriculture
2) Applications of IoT in Agriculture
3) Benefits of IoT in Agriculture
4) Challenges and considerations of IoT in Agriculture
5) Future trends and innovations with IoT in Agriculture
6) Conclusion
Understanding IoT in Agriculture
The Internet of Things refers to interconnected devices embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity capabilities that enable them to collect and exchange data. In the context of agriculture, IoT is crucial in transforming traditional farming practices by enabling smart and data-driven decision-making.
Internet of Things technology is applied in the agricultural sector by deploying various IoT Devices and systems. These devices, such as soil moisture sensors, weather stations, and livestock trackers, gather real-time data from the field. The collected data is then transmitted to a central hub or cloud platform.
Further, the data is analysed using advanced analytics techniques to generate valuable insights for farmers. These insights enable precision farming practices, resource optimisation, early detection of diseases, and improved decision-making. As a result, using Internet of Things, farmers can leverage the following:
a) Monitor and handle their crops and livestock in real time
b) Improve productivity and efficiency
c) Precisely manage resources
d) Reduces water and energy wastage
e) Minimise the use of pesticides and fertilisers
f) Make informed decisions
g) Optimise yield
h) Enhance overall sustainability in agriculture
Try our Advanced Technologies Courses and discover various cutting-edge innovations!
Applications of IoT in Agriculture
Internet of Things technology has revolutionised the agriculture industry by introducing innovative applications that enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Let's explore the diverse applications of IoT in different areas of agriculture:
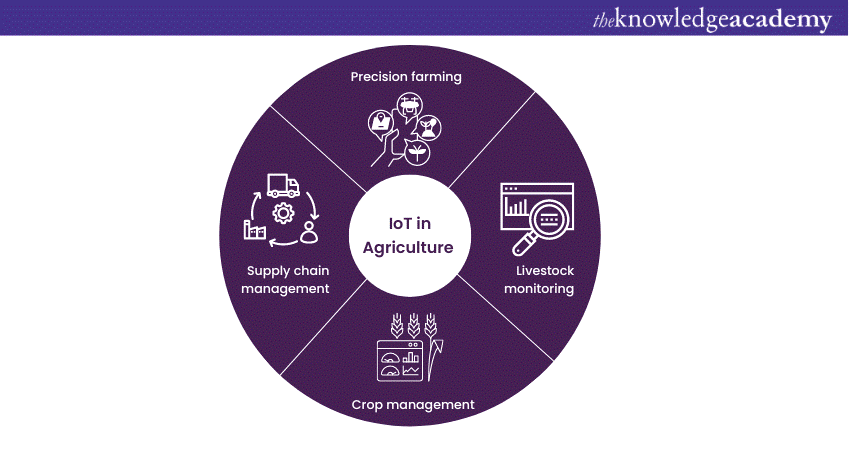
Precision farming
IoT in Agriculture enables precision farming practices by providing real-time data on temperature, soil moisture and nutrient levels. Farmers can optimise irrigation and fertilisation, resulting in improved crop yields and reduced resource wastage.
Livestock monitoring
Internet of Things devices, such as smart collars and ear tags, allow farmers to monitor the health, location, and behaviour of livestock. Further, real-time data on factors like body temperature, heart rate, and feeding patterns enable early detection of diseases, improved breeding programs, and efficient herd management.
Crop management
Internet of Things sensors and drones assist in monitoring crop growth, pest infestation, and disease outbreaks. Farmers can take timely actions based on the collected data, such as targeted pest control measures and precise application of fertilisers and pesticides. As a result, they can optimise crop health and reduce environmental impact.
Supply chain management
IoT in Agriculture facilitates the tracking and monitoring of agricultural products throughout the supply chain. Sensors and RFID tags provide real-time information on temperature, humidity, and location. Therefore, these devices ensure proper handling, storage, and transportation, leading to reduced spoilage and improved quality control.
Try our Internet of Things (IoT) Training and unleash new possibilities in this technological world!
Benefits of IoT in Agriculture
The adoption of IoT in Agriculture brings forth a multitude of advantages and benefits that revolutionise traditional farming practices. Let's explore the various ways in which Internet of Things enhances agricultural operations:
a) Resource management: IoT in Agriculture enables precise resource management by offering real-time data on soil moisture, weather conditions, and crop health. Farmers can optimise irrigation, fertilisation, and pest control measures. This leads to reduced water usage, minimised waste, and improved resource efficiency.
b) Productivity enhancement: Internet of Things sensors and devices offer continuous monitoring and automation capabilities, leading to increased productivity. Farmers can remotely monitor and control farm operations and streamline workflows. They can also take informed decisions based on accurate and timely data.
c) Data-Driven Decision-Making (DDDM): IoT generates vast amounts of data that can be examined to gain valuable insights. Farmers can leverage data analytics and predictive models to optimise crop management strategies, improve yield prediction, and mitigate risks. Moreover, data-driven decision-making ensures better resource allocation and higher crop productivity.
d) Economic benefits: IoT-driven farming practices can lead to cost savings by optimising resource usage, reducing waste, and minimising manual labour. Improved crop yield, enhanced quality, and efficient supply chain management contribute to increased profitability for farmers.
e) Environmental sustainability: IoT in Agriculture enables sustainable farming practices by promoting efficient resource usage, minimising chemical inputs, and reducing environmental impact. Precision irrigation, targeted pest control, and optimised fertiliser application help conserve water, protect soil health, and reduce the ecological footprint of agriculture.
f) Social impact: This technology can also improve food security and nutrition by enhancing crop production and ensuring the availability of quality produce. It enables farmers to meet the growing demands of a rapidly expanding population, contributing to food sufficiency and stability.
Try our 5G Wireless Training and gain in-depth knowledge of wireless communication!
Challenges and considerations of IoT in Agriculture
Implementing IoT in Agriculture brings forth its own set of challenges and considerations that need to be addressed for successful integration. Let's explore some of these challenges and discuss key considerations in implementing this technology:
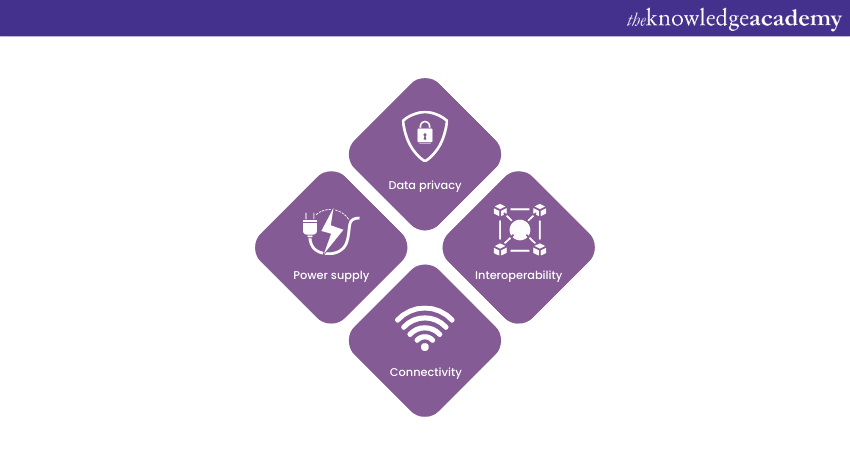
Data privacy and security
As Internet of Things involves collecting and transmitting sensitive data, ensuring data privacy and security is crucial. Farmers must implement robust security measures to protect their data from unauthorised access or cyber threats. They should also consider data ownership and establish clear data sharing and storage protocols.
Interoperability
The protocols and standards in an IoT device may vary with each manufacturer, making interoperability a challenge. It is essential to select devices and platforms that support open standards and can seamlessly integrate with existing farm systems to avoid compatibility issues.
Connectivity and infrastructure
Reliable connectivity is vital for Internet of Things systems to function effectively. However, rural farming areas may face challenges in accessing stable internet connectivity. The lack of infrastructure, such as cellular networks or broadband, can hinder the implementation and operation of IoT devices. Building robust connectivity infrastructure in these areas becomes imperative for successful IoT integration in agriculture.
Power supply
IoT devices require a continuous power supply to operate effectively. In remote farming areas with limited access to electricity, providing reliable power sources or implementing energy-efficient solutions like solar panels becomes essential to support IoT deployments.
Future trends and innovations with IoT in Agriculture
The future of IoT in Agriculture is brimming with exciting possibilities as technology continues to advance. Let's delve into some of the emerging trends and innovations that are set to shape the future of this technology:
Advancements in sensor technologies
Sensor technologies are becoming more sophisticated, compact, and cost-effective. In real time, miniaturised sensors can monitor various parameters such as soil temperature, humidity, moisture and nutrient levels. These advancements enable farmers to make data-driven decisions and optimise resource usage.
Data analytics and automation
IoT-generated data holds immense potential in agriculture. Advanced data analytics techniques can extract meaningful insights from vast datasets. As a result, they can aid in predictive modelling, disease detection, yield forecasting, and optimal resource allocation.
Moreover, when coupled with automation, Internet of Things enables autonomous farming operations, such as automated irrigation systems or precision spraying can reduce human labour and improve efficiency.

AI, machine learning, and robotics
Artificial intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms are becoming integral to this technology in agriculture. These technologies enable intelligent decision-making, predictive analytics, and adaptive control systems.
Additionally, robotics and autonomous vehicles can perform tasks like crop monitoring, weed detection, and harvesting. As a result, they improve productivity and reduce manual labour requirements.
Connectivity standards and integration
The seamless integration of Internet of Things with other technologies is essential for holistic agricultural solutions. Standardisation of connectivity protocols and interoperability between IoT devices and systems facilitate data exchange. They also allow for greater integration across different platforms and applications. Integrating cloud computing, edge computing, and blockchain technologies further enhances data storage, processing capabilities, and transparency in the agricultural ecosystem.
Conclusion
The future of IoT in Agriculture is bright and promising. This technology has a profound impact on agriculture as it optimises resource usage, enables data-driven decisions, and enhances productivity. Overcoming challenges and embracing future trends will unlock its full potential, paving the way for a sustainable and efficient agricultural ecosystem.
Want to learn how to implement IoT technologies across platforms? Try our Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Advanced Technology Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training
Internet of Things IoT Systems and Applications Training
Thu 30th Jan 2025
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 8th May 2025
Thu 10th Jul 2025
Thu 11th Sep 2025
Thu 6th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


