We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on + 1-866 272 8822 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Ethical hacking is a useful tool that helps to improve network security by identifying and solving system vulnerabilities. This industry requires a thorough understanding of intricate security systems and the skill to think like an attacker. As a result, the Ethical Hacker Interview process is sometimes seen as an insurmountable hurdle.
The fear of the questions that you might face can be very daunting, and the pressure of tackling complex queries unprepared might cost you valuable opportunities. Hence, we have curated this blog to help you through your journey. In this, we have discussed the top 20 Ethical Hacker Interview questions and answers. It will help you walk into your next interview with confidence and secure your dream job in Cybersecurity.
Table of Contents
1) Common Ethical Hacking Interview questions
2) Behavioural and scenario-based questions
3) Technical questions and practical demonstrations
4) Conclusion
Common Ethical Hacking interview questions
As the need for quality Cybersecurity increases, organisations are turning more and more toward Ethical Hacking to protect their information from dangerous attacks on the internet. Ethical Hackers are considered significant people in this regard, as they are the ones who identify weak points in systems, strengthen security, and ensure that computer systems and networks are secure. An Ethical Hacker Interview would generally ask some of the usual questions to see if a candidate is rightly fit for the job or possesses the right skills.
Let's get into Ethical Hacking and check out the usual interview questions that will help spot the best people for this very important area of Cybersecurity.
Question 1: What is the difference between white, black and grey hat hackers?
White hat hackers are normally helpful and ethical in nature. They help identify vulnerabilities and protect systems, networks, and applications from unauthorised access. Working with permission is key to ensuring the safety and integrity of the target.
On the other hand, black hat hackers mostly indulge in illegal activities, usually with some form of personal benefit or malevolence in mind to capitalise on some opportunity. Grey hat hackers fall in between: to some degree, they breach systems without permission, but they are not malicious and, in some cases, might even report the flaws they find.
Question 2: Explain the steps involved in an Ethical Hacking process
The Ethical Hacking process typically includes the following steps:
a) Reconnaissance: This is the first step, where hackers collect basic information like IP addresses, domain details, and network infrastructure of the target.
b) Scanning: Next, they scan the network to find open ports and running services to spot possible weak points.
c) Enumeration: Here, they gather more specific data, such as usernames, network shares, and system settings.
d) Vulnerability Assessment: Hackers then use various tools and manual methods to pinpoint security loopholes in the system.
e) Exploitation: Using these vulnerabilities, they try to break into the system to gain unauthorised access.
f) Post-exploitation: Once inside, they work to keep their access, increase their control, and dig deeper into the system.
g) Reporting: Finally, they compile a report detailing the vulnerabilities found, their potential impact, and suggestions for fixing them.
Take the next step towards a secure future - join our CompTIA Security+ Certification Course today!
Question 3: How do you stay updated with the recent hacking techniques and security trends?
"A good Ethical Hacker must keep up with cutting-edge techniques in hacking and security trends. That is why I take an active part in the discussion through different online forums, security communities, and social media group discussions where professionals share their views and get abreast of the ongoing trends.
I have been reading a few industrial publications, research papers, and blogs from reputable sources on a regular basis. I have also been attending security conferences, webinars, and training courses. This is meant to widen my scope of knowledge and keep me abreast of a fast-changing security environment.”
Question 4: What are some common types of cyber-attacks, and how would you defend against them?
The most common types of cyber-attacks include phishing, malware attacks, Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, Structured Query Language (SQL) injection, and social engineering. All these forms of attacks can be protected using a multi-layered approach. In this regard, installation of strong firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention, and antivirus among others in the network and host spaces may help prevent attacks and even detect any such attacks that break through.
Another aspect is regular security patching, secure access controls, and user awareness training. Moreover, regular vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, and security audits help organisations foresee and address potential vulnerabilities before they cause problems.
Question 5: Describe the concept of social engineering and how it can be used to exploit vulnerabilities
Social engineering is a method for intruding into the human psyche to gain access to confidential information or to potentially harm security. The attacker uses impersonation, pretexting, and baiting to leverage the susceptibility of human trust, bypassing technical security controls.
For instance, a Social Engineer may take the guise of a trusted work colleague or an IT support engineer and manipulate people into revealing their passwords or granting unauthorised access. Mitigation against social engineering requires broad training and user awareness, strong mechanisms for authentication, and rigorously followed security policies.
Learn the foundation of Ethical Hacking with the Ethical Hacking Professional Course!
Question 6: What are the key components of a penetration testing report?
A penetration testing report often contains the following components:
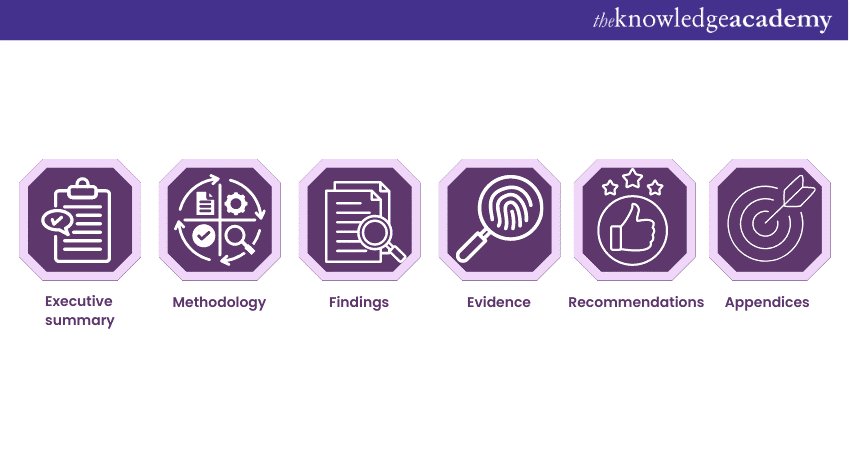
a) Executive summary: A high-level summary of the findings that identifies critical vulnerabilities and their potential impact.
b) Methodology: Describes how the penetration testing process approach, tools, and techniques are to be explained.
c) Findings: Highlight the vulnerabilities identified with detailed documentation of these vulnerabilities, including severity, impact and recommendations on corrective measures.
d) Evidence: Supporting data for the findings, such as screenshots or logs.
e) Recommendations: They should include clear, actionable recommendations on what is to be done to remedy the identified vulnerabilities and improve security.
f) Appendices: Any other additional information required to provide a context to the findings and which will support them. This may include certain things like network diagrams, test configurations, and technical details.
Question 7: How would you handle a situation where you discover a critical vulnerability in a client's system?
"When faced with a critical vulnerability, one must handle this sensitively. The first thing I would do is document the vulnerability along with its potential impact. Then, I would report this information to the client or the point of contact directly by clearly and descriptively reporting the vulnerability with any relevant technical details.
I would make recommendations and work closely with the client to develop an appropriate remediation plan. Open communication, professionalism, and confidentiality are very important parts of the process.”
Question 8: Discuss the importance of password security and suggest best practices
Password security is normally important because it protects sensitive information and prevents unauthorised access. Key to that would be the point at which weak or compromised passwords would come up as a window of opportunity for system access or a data breach. Best practices in this regard are using complex passwords with upper and lowercase characters, numbers, and special characters.
Passwords need to be unique for all accounts and should be changed periodically. Multi-factor authentication provides that additional layer of security. Use of password management tools can further increase password security significantly.
Question 9: What are some encryption algorithms commonly used in securing data?
There are several encryption algorithms that are commonly used to secure data. One of the most widely adopted symmetric encryption algorithms for its strength and performance is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES). RSA is an asymmetric encryption algorithm scheme that is mostly used for secure key exchange and digital signatures.
Triple Data Encryption Standard (DES) means that the DES cypher is applied three times so as to increase security. Blowfish has always been known for its flexibility and effectiveness in symmetric encryption algorithms. ECC is strong in security with shorter key lengths due to being an asymmetric encryption algorithm applicable to resource-constrained environments like mobile devices.
Question 10: How would you conduct a wireless network security assessment?
A wireless network security assessment involves a general process: the identification of possible vulnerabilities in a system and ways to mitigate them. This should consist of identifying wireless networks and their APs, carrying out the process of reconnaissance in the information-gathering stage on the networks, and analysing the encryption protocols.
It also involves the penetration testing of vulnerability exploitation, rogue AP detection, wireless traffic analysis for any suspicious activity, and even the deployment of wireless intrusion detection systems, monitoring and reporting 24/7 for results and recommendations.
Try our Mastering Metasploit Framework Course and use Metasploit in penetration testing!
Behavioural and scenario-based questions
The following section explores some of the behavioural and scenario questions that arise during an ethical hacking interview. These questions are probing and go a bit further than technical knowledge, opening up a candidate's mind about decision-making, communication skills, and suitability in real-world situations.
These Ethical Hacker Interview questions provide the recruiter with a view of your experiences, problem-solving approaches, and ethical judgment. In return, the interviewer can get a gauge of the suitability of the candidate for the hard and dynamic field of Ethical Hacking.
Question 11: Describe a challenging Ethical Hacking project you have worked on
This question seeks to understand your perspective on the job, including both positive and negative aspects of the role. A well-crafted response should elucidate why the particular project was satisfying and highlight motivational factors that aided in overcoming challenges.
Sample answer: "I have recently conducted an Ethical Hacking project, which involved assessing the security of the online banking system for a certain financial institution. The goal was to identify all possible vulnerabilities that might pose a threat to the clients’ data. After conducting in-depth analysis and penetration testing, I identified a severe vulnerability in the login mechanism. I reported these findings and gave detailed recommendations for mitigation.”
Question 12: How do you handle disagreements or conflicts with team members during an assignment?
This question seeks to understand your approach to teamwork, including both positive and challenging aspects.
Sample answer: "I employ open communication and collaboration to solve conflicts. I actively listen to team members, express my thoughts, and seek common ground or alternative solutions. Maintaining professionalism and respect are crucial during discussions to reach a resolution and focus on project objectives.”
Question 13: Explain how you would respond to a suspected security breach
This question aims to gauge your approach to handling critical situations and your ability to navigate challenges in the role.
Sample answer: "This situation demands timely, well-coordinated action when suspected breaches in security occur. If I were to identify a suspected breach, I would isolate the affected system and then go ahead with the scope and possible entry point investigation of the breach. Of course, it goes without saying that I would do so in coordination with the incident response team. Steps of mitigation that I would take include patching vulnerabilities, changing access credentials, and beefing up security controls. Transparent communication with stakeholders and long-term preventive measures are also essential.”
Question 14: Share an example of when you had to prioritise multiple tasks with tight deadlines
This question delves into the candidate's capacity to manage time effectively and handle pressure in a professional setting.
Sample answer: I executed several activities in the data encryption project by assessing the urgency of the data that should be protected. This was done courtesy of a well-elaborated schedule, whereby I would delegate responsibilities in part of the Cybersecurity architects for an even distribution of workloads. The key to making any changes in priorities based on updated information or challenging situations that are courtesy of the encryption project is adaptability and flexibility, thereby ensuring that one can meet deadlines accordingly.”
Question 15: How do you maintain ethical standards while performing hacking activities?
This question delves into the moral compass of an individual when engaging in hacking activities, which often involves navigating through ethical dilemmas.
Sample answer: "I work only within the legal frameworks, having obtained appropriate authorisations and consents, and obtain authorisations and consent in order to maintain ethical standards. Hacking engagements are defined in terms of their scope, and I handle sensitive information with discretion.
I consistently follow responsible disclosure practices, including timely reporting of vulnerabilities and never capitalising on them for personal gain. I keep updating my capabilities in line with industry best practices. In addition, I will continue to learn and develop professionally by keeping abreast with all the latest trends in ethical hacking techniques and requirements.”
Technical questions and practical demonstrations
Technical knowledge and practical skills are important for one to be successful in Ethical Hacking. One should be familiar with varied hacking techniques, vulnerabilities, and defensive strategies. Sometimes, in interviews, a certain portion is left for technical questions and practical demonstrations to check the ability and skills of a candidate.
This part evaluates whether the candidate can apply his knowledge in a real-time scenario and gives a demonstration of his practical problem-solving skills. Let us explore them in detail:
Question 16: Walk us through the process of conducting a vulnerability assessment
"Some of these steps to take in conducting a vulnerability assessment would be gathering information regarding the target system or network, including an IP address, domain name, and network infrastructure. Thereafter, an automated vulnerability scan would be run to find common vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses.
Once the vulnerabilities are identified, I would assign priorities based on the level of vulnerability and potential impact. I would then go on to manually test for the validation and verification of the vulnerabilities. Finally, I would document my findings with recommendations on mitigation to be made and finally implement assistance on mitigation with security measures against the vulnerabilities.”
Question 17: Demonstrate your knowledge of network protocols and their vulnerabilities
Protocols serve as the backbone for device-to-device communications within a network. Some common protocols—namely, Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP), Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), and Domain Name System (DNS)—are known to be vulnerable. For example, TCP/IP is vulnerable to IP spoofing and SYN floods. HTTP can be exploited by the methods of injection, while FTP can be susceptible to brute-force attacks.
DNS is very vulnerable to DNS spoofing or cache poisoning, and if understood, the same helps to evaluate and secure an organisation's network infrastructure. The vulnerabilities related to such can be mitigated by applying proper security controls such as encryption, access control, and proper patching.
Learn about information security with the CISM Certified Information Security Manager Course!
Question 18: Perform a basic SQL injection attack on a test environment
The recommended response to this interview question is that Structured Query Language (SQL) injection is illegal. SQL injection being a web application vulnerability permits an attacker to change user input, . This also allows unauthorised access, data leakage, or database manipulation. Hackers can insert SQL commands if there are some input fields that are poorly defined or non-validated.
SQL injection can be mitigated by using input validation and parameterised queries. Input validation will be effective to sanitise the user input and ensure that it is as per the expected formats. Parameterised queries maintain separate user input from the SQL query, hence preventing the execution of malicious code.
Question 19: Explain the concept of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and explain how it can be mitigated
XSS is a kind of web application attack where a script is injected into web pages and executed with the intent of causing some harm. This occurs when user input has not been validated or sanitised and is then reflected on a web page without encoding. Some of the malicious activities that could be affected by XSS attacks include session hijacking, cookie theft, defacement, and malware distribution.
Input validation and output encoding should be done to eliminate XSS. Input validation ensures that data supplied by users is free from harmful scripts, whereas output encoding ensures that data rendered on web pages is properly encoded such that injected scripts would not be executed.
Question 20: Conduct a wireless network sniffing demonstration
When addressing this interview question, it’s important to highlight the legal and ethical considerations surrounding network sniffing. Wireless network sniffing entails the capture and analysis of data packets traversing a wireless network. This method enables potential attackers to eavesdrop on network traffic, which may expose confidential details such as passwords, email content, or financial information. Tools like Wireshark or tcpdump are mostly used for this purpose, capturing packets in promiscuous mode.
To counteract wireless sniffing threats, it’s essential to employ encryption protocols like WPA2 or WPA3, which secure network traffic, rendering it indecipherable to unauthorised individuals. Additional security measures, like MAC address filtering and the deactivation of superfluous wireless protocols, serve as robust access control strategies that bolster network security.
Conclusion
The Ethical Hacker Interview process is a critical mechanism for organisations to appraise the Cybersecurity acumen, ethical integrity, and technical prowess of candidates. It offers a platform to gauge an individual’s analytical thinking, collaborative efficiency, and proficiency in identifying security loopholes and implementing countermeasures. The recruitment of adept Ethical Hackers is a pivotal step in fortifying an organisation’s Cybersecurity infrastructure.
Become certified in cyber security with our CISSP Training today!







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


