We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Securing organisational assets from cyber threats is vital for any enterprise. A central figure in this Cybersecurity landscape is the Penetration Tester. But do you know what these professionals do? The Penetration Testing Job Description generally entails their operation on the frontline of Cybersecurity defences. Their role transcends mere hacking, understanding an organisation's cyber infrastructure intimately, from the software stack to network configurations.
Based on their role, the salaries of Penetration Testers also evolve. According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a Penetration Tester is 56,000 GBP. However, it’s crucial to analyse the Job Descriptions of different companies in order to gain an understanding of the job market.
But how can one know what are the requirements of different companies and their Job Descriptions? Worry no more. Read this blog to discover the Penetration Testing Job Description with example. Explore the key responsibilities, skills, and qualifications needed for a successful career.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding Who is a Penetration Tester
2) The key responsibilities of a Penetration Tester
3) Qualifications of a Penetration Tester
4) Skills expected of a Penetration Tester
5) Career path of a Penetration Tester
6) Salary of a Penetration Tester
7) Penetration Testing Job Description example
8) Conclusion
Understanding Who is a Penetration Tester
A Penetration Tester, colloquially known as an Ethical Hacker, is a Cybersecurity professional responsible for simulating cyberattacks on systems, networks, and applications. They also identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by malicious parties.
Now, unlike Hackers who seek unauthorised access for personal gain or malice, Penetration Testers work with the express permission of the organisation. They aim to uncover weak points and provide recommendations to bolster security.
Armed with a combination of technical knowledge and creative thinking, Penetration Testers mimic various attack techniques, ranging from software exploits to social engineering tactics.
Their objective is twofold: first, examining where a system's defences might fail and then evaluating the potential consequences of such breaches. Following their assessment, they produce detailed reports outlining discovered vulnerabilities, potential risks, and recommended mitigation strategies.
More importantly, to be effective in their roles, Penetration Testers must be versed in various Operating Systems (OSs), programming languages, and hacking tools. Moreover, they need to constantly update their skills and knowledge, keeping pace with the rapidly evolving landscape of Cybersecurity threats. A Penetration Tester plays the invaluable role of a guardian, helping organisations stay one step ahead of potential cyber adversaries.
The key responsibilities of a Penetration Tester
A Penetration Tester is tasked with a multifaceted role in the Cybersecurity realm. Their primary objective is to identify vulnerabilities in systems, but the depth and breadth of their responsibilities go far beyond this simple definition. Let's dive deeper into the key responsibilities of a Penetration Tester:
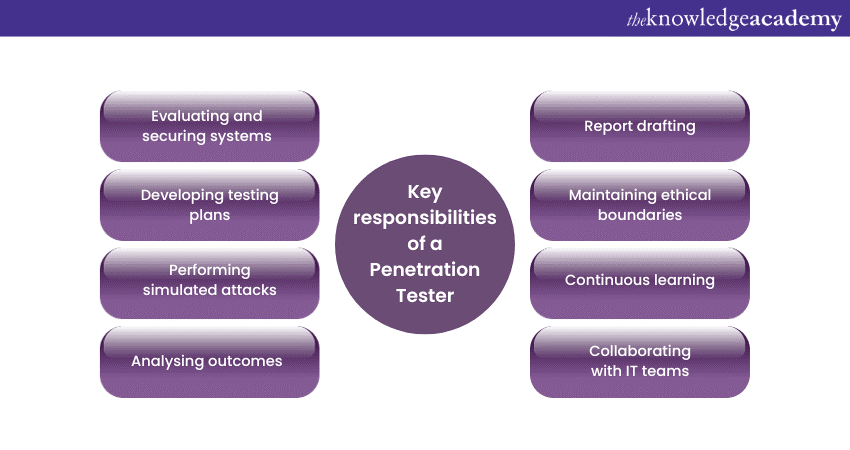
a) Evaluating and securing systems: Before conducting any tests, Penetration Testers work to define the scope of the evaluation. This could range from targeting specific systems to a more general assessment. Their main goal is to uncover weak points that malicious Hackers could exploit.
b) Developing testing plans: Every penetration test should begin with a structured plan, describing the methodologies to be used, tools required, and potential areas of focus. Penetration Testers develop a clear strategy to ensure the testing is both comprehensive and within ethical boundaries.
c) Performing simulated attacks: Armed with the necessary tools and strategies, the Tester simulates cyberattacks. This could involve exploiting software vulnerabilities, cracking passwords, or using Social Engineering techniques to gain unauthorised access.
d) Analysing outcomes: Post-assessment, the Tester evaluates the results, distinguishing between false positives and genuine vulnerabilities. This involves assessing the severity and potential impact of each vulnerability.
e) Report drafting: One of the most crucial responsibilities is the creation of a detailed report post-evaluation. This report not only highlights the vulnerabilities discovered but also provides a clear path to remediation, assisting organisations in addressing their security gaps.
f) Maintaining ethical boundaries: While emulating malicious Hackers, Penetration Testers must always operate within the boundaries of legality and ethics. They should not cause unintentional damage or access data beyond what's been permitted.
g) Continuous learning: The Cybersecurity landscape is ever-changing. Thus, Penetration Testers must remain up-to-date with the latest vulnerabilities, hacking techniques, and tools. Regular training and sometimes certification renewals are integral to their roles.
h) Collaborating with IT teams: A Penetration Tester generally works closely with Information Technology (IT) and Cybersecurity teams within organisations. They share their findings and guide them through the remediation process.
Qualifications of a Penetration Tester
To thrive in the dynamic and challenging world of Cybersecurity, Penetration Testing Job Description requires a combination of formal education, specialised certifications, hands-on experience, and certain soft skills. First, let's explore the qualifications required to excel in this pivotal role:
Formal education
Here is a list of formal educational pre-requisites for a Penetration Tester’s role:
a) Bachelor’s degree: A bachelor's degree in fields like Computer Science, Information Technology, Cybersecurity, or related disciplines provides a strong foundational understanding of computing principles and technologies. The degree is, however, not mandatory, but it is better to acquire one.
b) Master’s degree: Some organisations prefer candidates with a master's degree in Cybersecurity or Information Assurance. These advanced programs often provide deeper insights into threat analysis, digital forensics, and cyber operations.
Certifications and tools required
Here is a list briefly describing the various certifications and tools that equip candidates with a detailed understanding of Penetration Testing:
a) Tools and techniques for Penetrating Testing: Attaining the knowledge of various tools in Penetration Testing, like Metasploit, Sqlmap, Armitage, Netsparker, and many more, helps expand a professional’s toolkit.
b) Fundamentals of Test Automation: Getting trained in the basics of Test Automation by learning about quality improvement, risk reduction, automated test creation and execution helps professionals enhance their technical foundation.
c) Kali Linux fundamentals: Understanding the basics of Kali Linux helps professionals progress to auditing system security and Penetration Testing at an advanced level.
d) Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP): The CISSP Certification trains professionals to design, implement and manage security systems. The Certification provides them with knowledge of Security Compliance and Risk Management.
Learn how to navigate the stages of Security System Management by signing up for our CISSP Training now!
Hands-on experience
Hands-on experience is an indispensable component of a Penetration Tester's qualifications. It offers aspiring Testers practical skills and insights that cannot be solely gained from formal education or certifications. Here's a closer look at the types of hands-on experience beneficial for a budding Penetration Tester:
1) Lab environments and simulations: It includes getting familiar with the following:
a) Self-setup labs: Setting up personal labs using tools like VirtualBox or VMware allows Testers to practice on isolated networks without causing unintended harm. Operating Systems like Metasploitable, Damn Vulnerable Web Application (DVWA), and OWASP WebGoat offer intentionally vulnerable platforms for experimentation.
b) Public labs & platforms: Websites like Hack The Box and TryHackMe provide realistic environments, challenges, and war games to hone skills.
2) Capture The Flag (CTF) challenges: CTFs are competitive events where participants solve Cybersecurity challenges, often mimicking real-world scenarios. These events are invaluable as they teach practical skills, promote out-of-the-box thinking, and introduce testers to a variety of tools and techniques.
3) Internships and junior roles: Starting in entry-level Cybersecurity roles, even if not directly related to Penetration Testing, offers immense learning opportunities. Roles in IT Support, Network Administration, or Cybersecurity Analysis provide foundational knowledge, which becomes invaluable when transitioning to a Penetration Testing Job.
4) Vulnerability assessments: Before diving deep into Penetration Testing, many begin with vulnerability assessments. This involves scanning systems to detect known vulnerabilities. It is a less invasive method than Penetration Testing but still highly informative.
5) Contribution to open-source projects: Actively contributing to or even observing Cybersecurity projects on platforms like GitHub can be enlightening. It offers a chance to understand the development side of the project, which is crucial when trying to exploit or patch vulnerabilities.
6) Real-world testing with permission: Engaging in legal, Ethical Hacking practices is essential. One can offer pro-bono or discounted Penetration Testing services to local businesses, non-profits, or friends with their explicit permission. This not only builds a portfolio but also establishes credibility and trust.
7) Stay updated with emerging threats: Actively engaging with Cybersecurity communities, forums, and platforms such as Reddit's r/netsec or the Stack Exchange's Information Security community can be beneficial. Such platforms often discuss the latest vulnerabilities, tools, and techniques.
Protect yourself against cyber threats by signing up for our Cyber Security Training now!
Skills expected of a Penetration Tester
A Penetration Testing Job Description requires a harmonious blend of technical proficiency, analytical capabilities, and soft skills. Here's a concise breakdown of the skills expected of a Penetration Tester:
Technical expertise
Here are the various aspects that come under the umbrella of technical expertise are as follows:
a) Programming knowledge: Familiarity with languages such as Python, Java, C, and Perl enables scripting and task automation. It also improves the understanding of software vulnerabilities.
b) Operating Systems: Mastery over different OS, especially Linux, is pivotal. Knowledge of system configurations and potential weak points is crucial.
c) Network analysis: A deep understanding of network protocols, topologies, and services ensures thorough Network Penetration Testing.
d) Familiarity with tools: Proficiency with penetration testing tools like Metasploit, Nmap, Wireshark, and Burp Suite to conduct comprehensive tests.
Analytical and problem-solving skills
Here are the two skills necessary for professionals to build in addition to their technical skills:
a) Critical thinking: The ability to think like an attacker, anticipating vulnerabilities and crafting strategies to exploit them.
b) Attention to detail: Spotting minor anomalies or deviations that could indicate a vulnerability is key.
Soft skills
The following soft skills are essential for professionals to transform into holistic employees and team players in their industry:
a) Effective communication: Translating complex technical jargon into understandable terms for non-technical stakeholders and creating detailed reports.
b) Ethical integrity: Abiding by a strong moral code, ensuring testing remains within legal and ethical boundaries.
c) Adaptability: The cybersecurity landscape evolves rapidly. A Penetration Tester must be flexible and willing to learn continuously.
d) Curiosity: A natural inquisitiveness, always seeking to understand "why" and "how," propels testers to dig deeper and uncover hidden vulnerabilities.
Know how to overcome complexities in malware by signing up for our Malware Analysis Training now!
Career path of a Penetration Tester
The work experience of a Penetration Tester is an intricate blend of various assignments, each geared towards identifying and rectifying vulnerabilities in systems, networks, and applications. Here is a list describing the typical work journey of these Cybersecurity professionals:
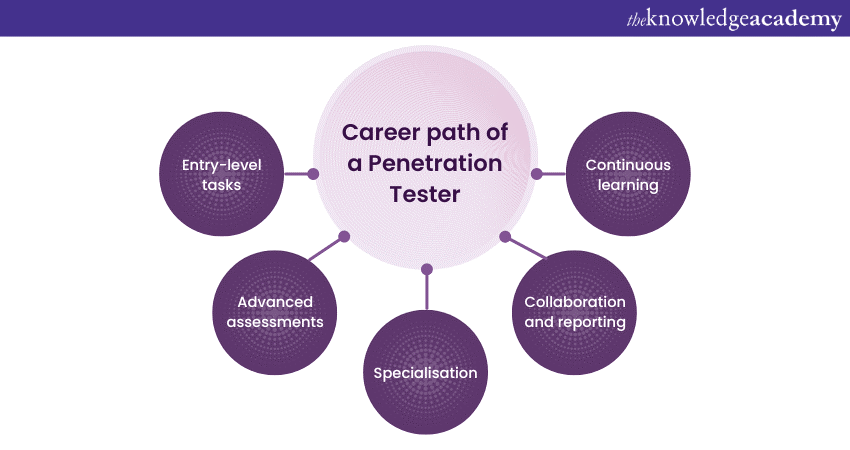
1) Entry-level tasks: In the initial stages, a Penetration Tester often starts with Vulnerability Assessments. This involves using automated tools to scan and identify known vulnerabilities in systems, laying the groundwork for more in-depth penetration tests.
2) Advanced assessments: As they gain proficiency, they undertake full-blown Penetration Tests, crafting and executing strategies to mimic real-world cyberattacks. This could mean exploiting a software vulnerability, conducting a phishing campaign, or even physically attempting to bypass security measures.
3) Specialisation: With time, many Testers specialise in certain domains, be it web applications, network security, mobile devices, or even Internet of Things (IoT) systems. Such niches require deep domain-specific knowledge.
4) Collaboration and reporting: A significant part of their tenure involves collaborating with IT and Cybersecurity teams, discussing findings, and drafting comprehensive reports detailing vulnerabilities, their potential impacts, and recommended mitigation strategies.
5) Continuous learning: Given the ever-evolving threat landscape, Penetration Testers spend considerable time updating their skills, exploring new hacking techniques, and familiarising themselves with the latest tools.
Salary of a Penetration Tester
Here are the Penetration Tester’s Salary brackets based on their level of experience:
|
Role |
Experience level |
Annual salary range |
|
Junior Penetration Tester |
Entry-level (0 to 2 years) |
£25,000 - £35,000 |
|
Penetration Tester |
Mid-level (2 to 5 years) |
£25,000 - £60,000 |
|
Senior Penetration Tester |
Senior-level (5+ years) |
£60,000 - £90,000 |
Source: Indeed UK
Here are the various salaries for Penetration Testers according to cities in the UK:
|
City |
Average annual salary |
|
Bracknell |
£ 69,777 |
|
London |
£ 64,237 |
|
Oxford |
£ 63,223 |
|
Birmingham |
£ 57,894 |
|
Manchester |
£ 55,692 |
|
Leeds |
£ 52,057 |
|
Reading |
£ 47,359 |
|
Milton Keynes |
£ 43,757 |
Source: Indeed UK
Penetration Testing Job Description example
Here is an example of a Penetration Tester’s Job Description by a company in the UK:
Penetration Tester
Based in London (other UK locations considered)
The ZDL Group is looking for a new generation of Penetration Testers to join our rapidly growing team. Whether you are a seasoned professional or at the beginning of your career in Cyber Security, we’re looking to talk with Penetration Testers of all levels.
Why The ZDL Group?
The ZDL Group is a company that recognises employees as the centre of our success. We employ only the best technical experts who have a true passion for Cyber Security. This passion drives our desire to evolve with emerging threats and enables our technical experts to deliver unparalleled services to our clients.
We help our Penetration Testers achieve their full potential by providing paid training and professional certifications, including CREST and OSCP. This ensures our team is at the top of their game on Mobile, Web Applications, Infrastructure, WiFi, Reverse Engineering, Exploit Development, Research, Red Teaming and Social Engineering engagements.
Our Pentest team is made up of specialists in all areas of Penetration Testing, and we are great at sharing knowledge and ideas. You will bring a wealth of knowledge to the team and work with industry experts who will be able to share with you new skills and techniques.
We work with a plethora of interesting clients on ground-breaking projects. If you want exposure to a variety of industry sectors, working on projects that will challenge you to innovate and problem solve, then The ZDL Group can offer you the variety you are looking for.
About you
a) A technical expert in Manual Penetration Testing, both internally and externally
b) Specialist in one or more of the following: Web applications, Infrastructure, Mobile, WiFi, Reverse Engineering or Exploit Development
c) The desire to constantly learn and develop
d) Have a critical eye for detail
e) The ability to explain to all audiences how attacks are carried out and executed (e.g ROP attack)
f) Experience of working in large datacentres with exposure to switch patching and testing procedures
g) Professional experience in buffer overflows, XSS, SQL Injection and the full OWASP Top 10
h) Excellent report writing skills
i) Holding and maintaining OSCP, CREST, or equivalent is desirable
j) Happy to travel to client sites
k) Happy to work from home or local office
l) Punctual and professional
Successful candidates will be required to undergo background screening and offers of employment will be subject to the results of this screening.
Benefits
a) Competitive salary with annual reviews
b) Performance-related bonuses
c) Company pension scheme
d) Private Medical Insurance
e) Company Share Option scheme
f) Length of Service is linked with increases in allocated holiday days
g) Parking/Season ticket scheme
h) Bonuses for employee referrals
i) Structured learning and development plans which can include support for professional qualifications
j) Entertainment and social activities
k) Annual eye tests
Conclusion
We hope that you have now understood how the Penetration Testing Job Description encompasses a blend of technical expertise, ethical responsibility, and continuous learning. As cyber threats evolve, understanding this role's intricacies becomes vital for organisations aiming to safeguard their digital assets against potential breaches.
Learn to protect IT assets and information by signing up for our Ethical Hacking and Penetration Testing Training now!
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fundamentals of Test Automation
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 4th Apr 2025
Fri 3rd Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


