We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

With the increased complexity of business operations and the need for efficient IT systems, the need for such strategies that support business growth and innovation has also increased. This is where TOGAF Architecture Development Method (ADM) Phases come in. There are several TOGAF ADM Phases that help companies walk on the path of growth, innovation, and development.
If you, too, want to see your organisation stepping up the ladder of growth and innovation, read this blog to explore TOGAF ADM Phases in detail. Also, understand the objectives, activities, and deliverables of each phase.
Table of Contents
1) What is TOGAF ADM? An overview
2) TOGAF ADM Phases – Explained
3) Best Practices and tips for implementing TOGAF ADM
4) Key benefits of TOGAF ADM
5) Conclusion
What is TOGAF ADM? An overview
At its core, TOGAF ADM enables organisations to create flexible, scalable, and adaptable architectures for dynamic business environments. It emphasises the importance of aligning IT systems with business strategies, ensuring that technology investments contribute to the organisation’s overall success.
Further, ADM provides a comprehensive set of TOGAF Architecture Principles, guidelines, best practices, and resources that architects can leverage to manage the architecture development process effectively. The method consists of ten distinct phases that provide a logical progression through the architecture development process.
This allows architects to address key aspects such as technology, migration planning, architecture change management, etc. Therefore, businesses can attain improved business-IT alignment, reduced complexity, enhanced interoperability, and increased agility.

TOGAF ADM Phases – Explained
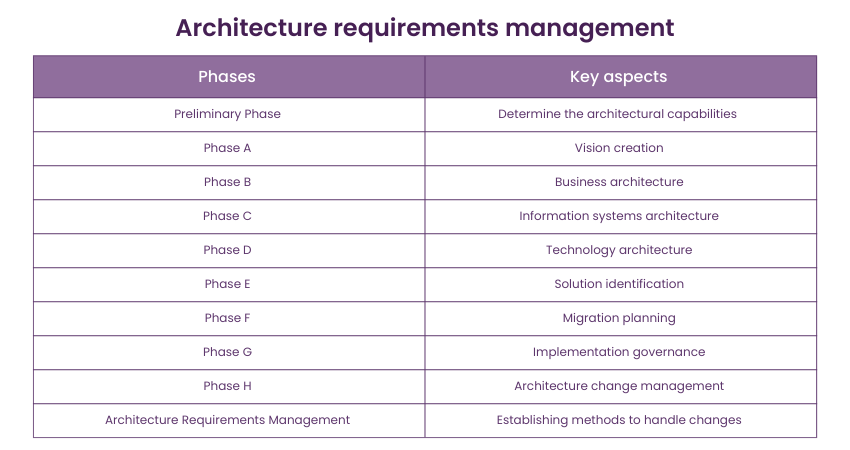
TOGAF phases are the sequential stages or steps within the ADM of the framework. These phases provide a structured approach for architects to develop and manage enterprise architectures. Each phase has specific objectives, activities, and deliverables that guide the architectural development process. There are ten phases of TOGAF ADM, which are as follows:
Preliminary phase
This phase sets the foundation for the architecture development process. Here, the primary focus is determining and establishing the organisation’s architectural capabilities. The goal is achieved through the following practices:
a) Establishing the architecture team
b) Defining the scope and objectives
c) Identifying key stakeholders
d) Identifying and establishing architectural principles
e) Developing strategy and implementation plan for tools and techniques
f) Creating the architecture vision
Phase A: Architecture vision
Phase A revolves around developing a high-level vision for the organisation’s architecture. The objective of this phase is to create a vision for business capabilities and value to be delivered as a result of the proposed enterprise architecture. It involves the following:
a) Identifying Stakeholders, concerns, and business requirements
b) Defining business goals, business drivers and constraints
c) Evaluating enterprise architectural capabilities
d) Creating a preliminary architecture vision and scope
e) Determining value and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for the target architecture
Phase B: Business Architecture
This is the phase where the actual development of the architecture begins. The architects focus on developing a detailed understanding of the organisation’s business architecture. They aim to describe how the enterprise needs to operate to achieve its business goals. It includes performing the following practices:
a) Selecting reference models, viewpoints, and tools
b) Defining business capabilities
c) Identifying business processes
d) Developing target business architecture description
e) Analysing stakeholders
f) Mapping out the relationships between business units
Phase C: Information Systems Architectures
The development of information systems architectures occurs during phase C. The key concern of the architects in this phase is to develop a combination of data and application architecture in either order. Phase C involves performing the following:
a) Selecting reference models, viewpoints, and tools
b) Identifying information requirements
c) Designing information flows
d) Defining application services
e) Creating a logical data model
Phase D: Technology architecture
The objective of phase D is to develop a technology architecture that supports architecture vision and desired business, data and application building blocks. It includes the following practices:
a) Selecting technology platforms
b) Defining infrastructure components
c) Creating a technology roadmap
d) Conducting a formal Stakeholder review
e) Finalising the technology architecture
Phase E: Opportunities and solutions
This phase involves identifying and evaluating potential solutions to address business requirements. At this phase, the architects generate a rough version of the architecture roadmap based on the gap analysis and roadmap components from phases B, C, D. The activities performed during Phase E are as follows:
a) Conducting feasibility studies to determine enterprise change attributes
b) Defining business constraints for implementation
c) Analysing costs and benefits
d) Creating a gap analysis between the baseline and target architectures
e) Formulating implementation and migration strategies
f) Creating the architecture roadmap and implementation and migration plan
Phase F: Migration planning
This phase is dedicated to creating a detailed plan for transitioning from the current architecture to the target architecture. Here, the architecture roadmap is finalised. Further, its implementation and migration are coordinated with the organisation’s change management and implementation approach. It includes the following steps:
a) Finalising management framework interactions for implementation and migration plan
b) Defining transition architectures
c) Sequencing projects according to priority by conducting a cost assessment and risk validation
d) Developing a migration plan with resource allocation
e) Finalising organisation’s readiness and risks for business transformation
Phase G: Implementation governance
This phase focuses on ensuring effective governance and oversight during the architecture implementation. It involves the following practices:
a) Finalising scope and priorities for deployment
b) Monitoring project implementation
c) Managing architectural compliance
d) Implementing business and IT operations
e) Addressing issues and risks that arise during the implementation
Phase H: Architecture change management
Lastly, phase H deals with managing and tracking changes to the architecture over time. The primary goal behind tracking changes is to look after the enterprise architecture capabilities and whether they can meet the current requirements. It involves the following practices:
a) Establishing a change management process
b) Deploying monitoring tools
c) Assessing the impact of changes
d) Developing change requirements to meet performance targets
e) Ensuring that the architecture remains aligned with business objectives
Architecture requirements management
Requirements management is a crucial phase within the TOGAF ADM that focuses on effectively managing and maintaining architectural requirements throughout the architecture development lifecycle. It ensures that the architecture remains aligned with evolving business needs and provides a systematic approach for capturing, analysing, prioritising, and tracking requirements.
The primary objectives of the Requirements Management phase are to identify, document, and validate architectural requirements. This phase helps architects understand the business drivers, goals, and constraints that shape the architecture. It ensures that the architecture addresses the organisation’s and its Stakeholders’ functional and non-functional requirements.
Gain in-depth knowledge of implementing the architecture efficiently. Register for our TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner - Practitioner Training now!
Best Practices and tips for implementing TOGAF ADM
Implementing TOGAF ADM requires careful planning and execution to ensure its successful implementation. Here’s a list of best practices and tips to consider when implementing TOGAF ADM:
a) Familiarity with TOGAF: To successfully implement the various phases of TOGAF, thoroughly understanding the TOGAF framework and its core concepts is essential. This will help the architects establish a solid foundation, ensuring they follow the framework correctly.
b) Define clear objectives: Clearly define the objectives and scope of the organisation’s architecture project. Identify the specific business goals, requirements, and challenges your organisation’s architecture initiative aims to address. This will provide a clear direction and focus for the team’s implementation efforts.
c) Engage Stakeholders: Involve stakeholders from various business units and IT departments early in the process. Gain their support, communicate the benefits of TOGAF ADM, and ensure they understand their roles and responsibilities. Stakeholder engagement is crucial for successful architecture implementation.
d) Tailor TOGAF according to your organisational needs: TOGAF is designed to be customisable to suit your organisation’s needs. Assess your organisation’s specific needs and context and adapt TOGAF ADM accordingly. Tailoring the framework will help you align it with your organisation’s culture, processes, and architecture practices.
e) Establish an architecture governance framework: Implement a robust architecture governance framework to ensure that architecture activities align with business objectives and adhere to established standards. This framework should include clear decision-making processes, roles, responsibilities, and mechanisms for monitoring and controlling architecture development.
f) Plan incrementally: Instead of trying to implement TOGAF ADM in its entirety, consider adopting an incremental approach. Start with a focused scope or a specific architecture project and gradually expand your implementation. This allows for a better understanding and adaptation of the framework while demonstrating tangible value to stakeholders.
g) Ensure the availability of adequate resources: Allocate sufficient resources, including skilled architects, tools, and technologies, to support the implementation of TOGAF ADM. Adequate resources are essential for executing the architecture development activities effectively and achieving the desired outcomes.
h) Foster collaboration and communication: Promote collaboration and open communication among architects, Stakeholders, and project teams. Encourage knowledge sharing, and facilitate regular meetings, workshops, and feedback sessions. This ensures a common understanding, alignment, and buy-in from all involved parties.
i) Leverage architecture repositories and tools: Utilise architecture repositories and modelling tools to document, store, and manage architectural artefacts. These repositories and tools streamline the architecture development process, promote reusability, and enable better visibility and traceability of architectural assets.
j) Monitor and measure progress: Establish metrics and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor the progress and effectiveness of TOGAF ADM implementation in your organisation. Regularly review and assess the outcomes against the defined objectives to identify areas for improvement and course correction.
k) Emphasise continuous learning: Encourage a culture of continuous learning and improvement within your architecture practice. Stay updated with the latest developments in enterprise architecture, attend training sessions, and participate in architecture-related communities to enhance your knowledge and skills.
Key benefits of TOGAF ADM
Implementing the TOGAF Architecture Development Method benefits organisations in several ways. Let’s delve into the benefits of adopting the TOGAF ADM:
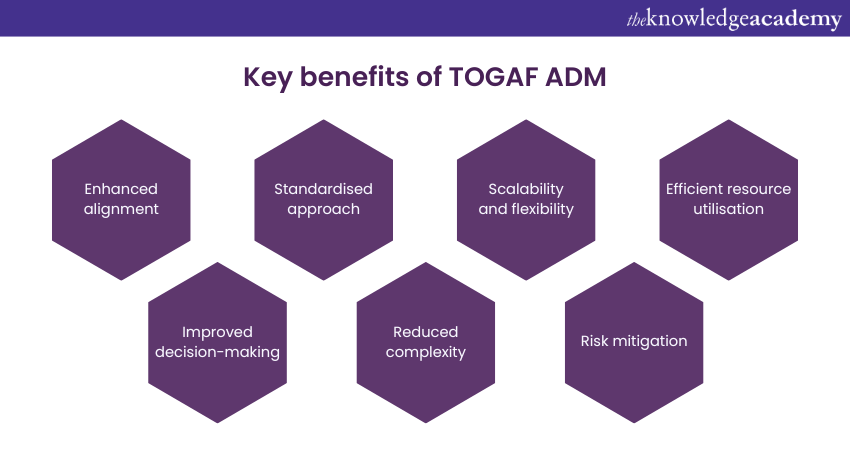
a) Enhanced alignment: The TOGAF ADM provide a structured approach to developing and managing enterprise architectures. It ensures that business needs drive the technology decisions.
b) Improved decision-making: ADM promotes a systematic evaluation of alternatives, considering factors such as business requirements, technology capabilities, and resource constraints. This leads to informed and effective decision-making.
c) Standardised approach: The TOGAF ADM offers a common language and guidelines, enabling better communication and collaboration among stakeholders, architects, and project teams. Therefore, it ensures a uniform development of enterprise architectures.
d) Reduced complexity: ADM breaks down the architecture development process into manageable phases. It provides a clear roadmap and structure, making understanding and navigating complex architectural challenges easier.
e) Scalability and flexibility: The method is scalable and adaptable to organisations of different sizes and industries. It accommodates diverse architectural requirements, allowing organisations to tailor it to their needs.
f) Risk mitigation: ADM identifies and addresses risks early on so that organisations can proactively mitigate potential issues and minimise project risks.
g) Efficient resource utilisation: The ADM promotes efficient utilisation of resources by aligning architecture development efforts with organisational priorities. It helps optimise resource allocation, ensuring that investments are targeted towards areas that deliver the most value to the business.
Conclusion
Understanding the TOGAF ADM Phases is crucial for successful enterprise architecture implementation. Each phase serves a specific purpose, from establishing a clear vision to managing architecture changes. By following the phases and best practices, organisations can align their architecture with business goals and achieve effective decision-making.
Learn how to effectively implement the TOGAF framework in business architecture with our TOGAF® Foundation And Practitioner Training.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Improvement Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner Training
TOGAF® Foundation and Practitioner Training
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Tue 26th Aug 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


