We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

What could be the cornerstone of a safer, more robust, and resilient banking world? The answer emerged in the wake of the 2007-2009 global financial crisis: Basel III. Crafted by the Basel Committee, this framework significantly raised the standards for capital reserves, ensuring banks can weather even the most turbulent times.
Dive into this blog to explore the essence of Basel III Capital Requirements. Discover how it enhances liquidity and fortifies financial stability, revolutionising the global finance landscape. Read on to see how Basel III is reshaping the rules of the banking game!
Table of Contents
1) What is Basel III?
2) What are Basel III Requirements?
3) Why Basel III Endgame Matters for Everyday Investors?
4) How Does Basel III Affect the Global Banking Landscape?
5) Basel III: Pillar-by-pillar Breakdown
6) Conclusion
What is Basel III?
To know in detail about the Basel III Requirements, you need to know about Basel III. It is an international regulatory convention with a set of reforms that was introduced to the financial world in 2009. These reforms aim to mitigate risks which are present in the international banking sector. These risks are mitigated by asking the banks to maintain a particular leverage ratio along with maintaining certain levels of reserve capital in hand.
What are Basel III Requirements?
Minimum Capital Requirements Under Basel III
First let's look at the two main silos of bank capital to work with:
1) Tier 1: This is a bank’s core capital, equity, and reserves that appear on its financial statements. This capital is more liquid, allowing a bank to weather stress during significant losses.
2) Tier 2: It's the bank's supplementary capital such as unsecured subordinated debt instruments and undisclosed reserves. This is less secure than Tier 1.
Under the proposed Basel III Endgame, banks with over $100 billion in assets must increase their reserves to cover potential losses. Additionally, banks would need at least 6% of their risky assets in Tier 1 capital. The minimum for total capital (Tier 1 + Tier 2) would stay at 8%.
Capital Buffers to Weather Financial Storms
Basel III introduces new capital buffer requirements that banks must maintain above the minimum capital ratios. These buffers ensure that banks build up capital reserves during good times that they can draw down during periods of financial and economic stress:
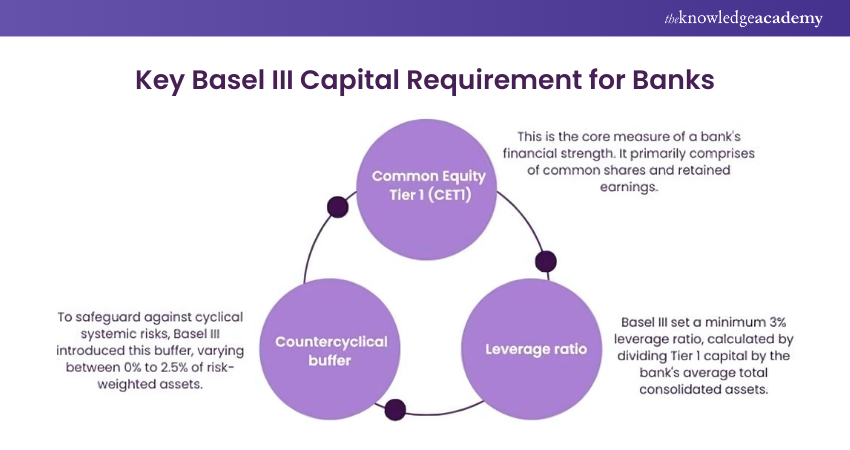
a) Capital Conservation Buffer (CCB): The proposal requires banks to maintain a CCB of 2.5% of risk-weighted assets with only CET1 capital. This buffer is in addition to the minimum CET1 ratio of 4.5%, effectively raising the CET1 requirement to 7%. Banks that dip into their CCB face restrictions on share buybacks, dividend payouts, and discretionary bonus payments to ensure they have this on hand.
b) Countercyclical Capital Buffer (CCyB): During periods of excessive credit growth, regulators can make it mandatory for banks to hold additional capital. The proposal would apply the CCyB to every bank with asset of $100 billion or more. The CCyB can range from 0% to 2.5% of risk-weighted assets and will be released during times of stress to help banks continue lending.
c) Global Systemically Important Bank (G-SIB) Surcharge: A risk-based capital surcharge for G-SIBs is maintained by the proposal. This extra capital buffer, ranging from 1% to 3.5% of risk-weighted assets, reduces the risks that large, interconnected banks pose to the financial system.
Leverage and Liquidity Measures
Basel III introduced new leverage and liquidity requirements for protection against excessive and risky lending while ensuring that banks have enough liquidity to weather financial stress periods. It sets a higher leverage ratio for G-SIBs, the ratio being Tier 1 capital divided by bank’s total assets (with a minimum ratio requirement of 3%). Consider the following points:
a) A liquidity coverage ratio necessitates banks to hold a sufficient reserve of high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) for surviving a period of significant liquidity stress lasting 30 calendar days.
b) HQLA includes central bank reserves, cash, and specific government securities that can be easily converted to cash with little to no loss of value.
c) The net stable funding (NSF) ratio is another liquidity-related provision. It compares the bank’s available stable funding with the stable funding amount that it must hold based on outstanding maturities, liquidity, and risk level of its assets.
d) The bank’s NSF ratio must be at least 100%.
Why Basel III Endgame Matters for Everyday Investors?
Despite the intricate nature of bank capital regulations, the Basel III Endgame proposal carries significant benefits for the broader economy and financial markets. Here's a closer look at some of them:

1) Confidence in the Financial System: A resilient banking system can continue lending during economic downturns. This can help mitigate the severity and duration of recessions, and such increased confidence can contribute to stable financial markets, which benefits all investors.
2) Economic Growth: Critics argue that the higher Basel III Capital Requirements would lead some banks to cut their lending activities, which will slow economic growth in the short term. However, studies show that banks might lend more with a cushion to backstop their lending activities.
3) Financial Stability: The Basel III Endgame rules strengthen the banking system's resilience against economic shocks by enabling banks to hold more high-quality capital. A durable banking system is vital for the smooth functioning of the economy. For investors, a more stable financial system mitigates the risk of market disruptions that could impact their portfolios.
Enhance your knowledge on Compliance Training – register now in our Compliance Training.
How Does Basel III Affect the Global Banking Landscape?
The introduction of Basel III has brought about significant shifts in the global banking landscape, touching various facets of banking operations, Risk Management, and capital allocation. Here's an overview of its impact:

a) Strengthened Capital Base: One of the primary objectives of Basel III was to enhance the quantity as well as the quality of capital that banks are required to hold. This has led to banks globally raising capital, either through equity issuance or by retaining earnings, making them more resilient to potential financial shocks.
b) Enhanced Liquidity Management: The introduction of liquidity ratios such as Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR) and the Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) has forced banks to reassess their funding models. Many banks have increased their holdings of high-quality liquid assets and shifted towards more stable, long-term funding sources.
c) Reduced Excessive Leverage: The leverage ratio has acted as a backstop to the risk-weighted capital ratios, curbing banks from taking on excessive on- and off-balance-sheet leverage.
d) Shifting Business Models: Higher capital and liquidity requirements have led to reduced profitability in certain banking segments. As a result, some banks have divested or scaled down their activities in areas like proprietary trading, while others have shifted towards more fee-generating activities.
e) Enhanced Risk Management: Basel III places a strong emphasis on stress testing and enhanced risk disclosures. Banks globally now have more sophisticated Risk Management tools and practices, ensuring a more holistic understanding of their risk profiles.
f) Global Standardisation With Local Nuances: While Basel III provides a global framework, its implementation may vary by country based on local nuances. This has led to a more standardised, yet flexible, approach to banking regulation across the globe.
Basel III: Pillar-by-pillar Breakdown
As a global regulatory framework the Basel III framework continues the three-pillar structure introduced by its predecessor, Basel II. Here's a breakdown of each pillar:
Pillar 1: Minimum Capital Requirements
The following are the minimum Basel III Capital Requirements for banks:
a) Credit Risk: Sets out the approach banks can use to calculate their capital requirements to cover the risk of default. This includes the Standardised Approach, Foundation Internal Ratings Based (FIRB), and the Advanced Internal Ratings Based (AIRB).
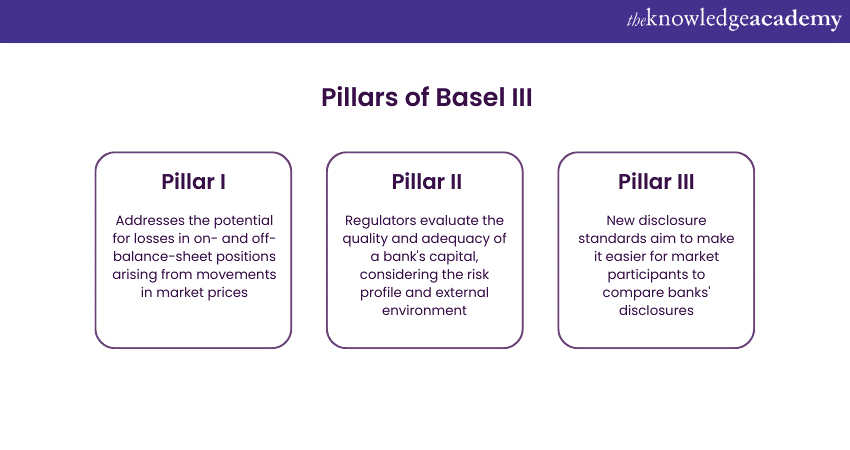
b) Market Risk: Addresses the potential for losses in on- and off-balance-sheet positions emerging from movements in market prices. The standardised measurement method and the approach of internal models are the primary methods for calculating capital requirements.
c) Operational Risk: Concerns potential losses due to failed or inadequate internal processes, systems, people, or external events. Methods for calculating capital include the Standardised Approach, the Basic Indicator Approach, and the Advanced Measurement Approach.
d) Leverage Ratio: A non-risk-based backstop measure to ensure banks maintain a minimum amount of capital against their total leverage exposure.
Pillar 2: Supervisory Review process
The following points describe the supervisory review process:
a) Risk Assessment and Capital Planning: Encourages banks to develop internal processes to assess their risk profile and ensure that they hold adequate capital in relation to their risk profile.
b) Supervisory Review: Regulators will evaluate the quality and adequacy of a bank's capital, considering the risk profile and external environment. If the regulatory assessment determines that a bank's capital is below the necessary level, they may require it to hold more.
c) Stress Testing: Banks are required to conduct stress tests to evaluate potential vulnerabilities under adverse scenarios.
d) Enhanced Supervision: Introduces a more intensive and intrusive approach to supervision, ensuring that systemic risks are identified and mitigated early.
Pillar 3: Market Discipline
The following points highlight the third pillar of Basel III Capital Requirements:
a) Disclosure Requirements: Encourages transparency by mandating banks to disclose key information about their risk exposures, risk assessment processes, and capital adequacy.
b) Enhanced Comparability: New disclosure standards aim to make it easier for market participants to compare banks' disclosures.
c) Transparency and Accountability: By making their risk exposures and management strategies public, banks are held accountable, and market participants can better assess the risk profile of each institution.
Enhance your knowledge on the effectiveness of Compliance System- Register now in our Security Governance and Compliance Training.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Basel III Capital Requirements proved instrumental in fortifying global banking resilience following the 2007-2008 financial crisis. These standards aim to shield banks from potential crises by mandating higher-quality capital and liquidity buffers, ensuring sustained financial stability against economic downturns in the banking sector.
Join our Corporate Governance Training to master the principles of effective corporate governance, to enhance decision-making, and drive sustainable success.
Frequently Asked Questions

Basel II Requirements is necessary as it asks the financial institutions to use standardised measurements for market risk, operational risk and credit. This accord also allows financial institutions use advanced Risk Management approaches which frees up capital investment.

Banks can focus on these following points:
a) A dedicated team can be employed to track any changes or updated Basel III Capital Requirements.
b) With regular awareness programs, banks can help their teams to align updated Basel III Capital Requirements.
c) Banks can analyse any gaps to evaluate the potential impact of any change in the Basel III Capital Requirements.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Compliance Courses, including the introduction to Basel III Course and the Introduction to Basel IV Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Compliance Framework.
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to Basel regulations, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your regulatory compliance knowledge base, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 PCI DSS Implementer
PCI DSS Implementer
Thu 28th Nov 2024
Thu 6th Feb 2025
Thu 3rd Apr 2025
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


