We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Is your business stuck in a tangled web of inefficiency? Do tasks seem to stall unpredictably, and clear communication feels like a distant dream? These are classic signs that your Business Processes need a refresh. Business Process Modelling Techniques offer a powerful solution, providing a clear roadmap to streamline your operations.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into various Business Process Modelling Techniques, helping you choose the right tool to unravel the complexities of your organisation. We'll explore popular techniques like BPMN and flowcharts, analyse their strengths, and guide you in selecting the method that best suits your specific needs.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Business Process?
2) The Purpose of Business Process Modelling in Companies
3) Business Process Modelling Technique
a) Gantt charts
b) Flowcharts
c) Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
d) Unified Modelling Language (UML) Diagrams
e) Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN)
f) Functional Flow Block Diagrams (FFBDs)
g) Integrated Definition for Function Modelling (IDFM)
h) Petri Nets
i) Role Activity Diagrams (RADs)
j) Coloured Petri Nets (CPN)
4) Conclusion
What is a Business Process?
A Business Process is an uninterrupted connection of activities or tasks that brought together lead to a certain organisational objective. It is, therefore, the elementary building block of firm operations, including the procedures and steps needed to deliver a product or service to a customer. These processes are designed to be repeatable and often standardised, ensuring consistency and efficiency in execution.
Business Processes are classified into core processes, which deliver value directly to customers, and supporting processes, which help the internal functions of the organisation. Usually, the process mappings are documented and visualised by different Modelling techniques to provide more understandability, manageability, and improvement. This visualises spotting all inefficiencies, even redundancies, and sometimes bottlenecks. This will be effective to put measures that streamline the workflow, improving service delivery and hence performance of the organisation. Essentially, the Business Processes refer to the orchestrated effort that propels the engine for day-to-day operations and long-term success of a company.
The Purpose of Business Process Modelling (BPM) in companies
Business Process Modelling (BPM) in an organisation defines the system approach for documenting, analysing, and making logical decisions concerning its business activities. It is to outline the clear graphic of the corporate activities, which could be published, in capturing the sequence of activities, the flow of information, and the responsibility of different roles. The roles of the objectives of BPM are multifaceted:
a) Better process comprehension: BPM comes in handy for stakeholders to comprehend the processes in a more shared way, where they can communicate and collaborate.
b) Enhances efficiency: BPM is a workflow optimisation toward higher efficiency due to the removal of bottlenecks and redundancies in time and cost.
c) Support for standardisation: It guarantees the uniformity of processes within an organisation in order to comply with quality and conformity with the law.
d) Enables automation: BPM lays the foundation for automating repetitive tasks and enabling accuracy, conserving human resources for more valued works.
e) Drives continuous improvement: It lays the base for continued evaluation and optimisation of the processes that encourage a culture of excellence and innovation.
Streamline your operations and boost efficiency with our Business Process Mapping Training – Sign up now!
Business Process Modelling Technique
Business Process Modelling Techniques are very valuable arsenals in an organisation's toolkit, empowering insights into understanding, documenting, analysing, and optimisation of their operational workflows. Let's have a look at these techniques to give their perspective:
1) Gantt charts
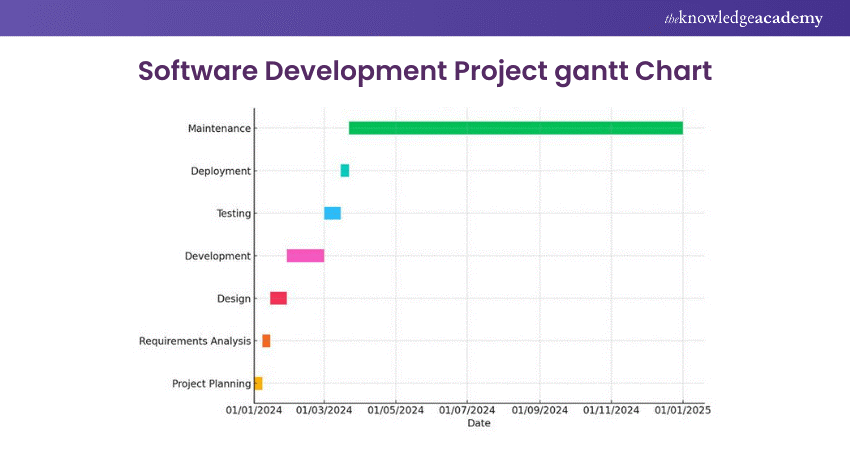
Colourful, graphic, and very intuitive charts are used as very valuable aids in project management. They offer an overall picture of project time for the assignment of tasks by the project manager, resource allocation, and monitoring of the project effectively. Gantt Charts help in clear communication between the project stakeholders, outlining when each project commences and finishes through the use of bar chart format in order to allow a successful execution of the project.
Here is an example of Software Development project depicted on a Gantt Chart:
2) Flowchart
This is a powerful way of diagramming the succession of stages in a process from initiation to completion. They even use various shapes and arrows to explain the kind of activities and decision points within the process; stakeholders are able to see the flow of these activities and, therefore, be in a position to tell of potential bottleneck or inefficiency. Flowcharts are very useful tools in the analysis and optimisation of process systems, because they provide an organised framework explaining intricate workflows and even pointing out the areas that need improvements. Flowcharts help enhance organisational efficiency and effectiveness. Flowcharts can be used to help in explaining Business Processes, software algorithms, or procedures for decision-making.
Get ready for your interview with our top Business Analyst Interview Questions.
3) Data Flow Diagrams (DFD)
DFDs offer a structured approach to visualising data movement within information systems. It shows the hierarchical flows of how the data passes from processes, through stores and external entities, giving insight into sources, changes or transformations, and destinations of the data. While they do not provide temporal details, DFDs are very good at giving an overview of the data flow that is clear and elaborative, hence quite invaluable for requirements analysis, system design, and communication among the technical and non-technical stakeholders.
4) Unified Modelling Language (UML) diagrams
The UML diagrams are a flexible and standard set of graphical tools used to model software systems with Business Processes. They apply various types of diagrams in their approach, like the use case diagrams, class diagram, activity diagram, and sequence diagrams in their approach, with each having clear modelling reasons. Use case diagrams explain the functionality of the system, operations, and the way users get involved with the system.
UML Class Diagrams detail the structure and relationships between the classes. Activity diagrams explain the workflow of the process. Interaction diagrams have the order of interaction between the components of a system. UML diagrams help communicate and collaborate with the project stakeholders in such a way that the need for the system, design specifications, and details of implementation is well understood by them.
Dive into the Detailed Case Study of Business Analysis
5) Business Process Modelling Notation (BPMN)
This is the de facto standard graphical notation for drawing Business Processes in a workflow, as it provides easy-to-understand flow diagrams to all participants. BPMN provides a rich set of symbols and rules that precisely specify process flows, events, tasks, and gateways representing procedures of an organisation. Consequently, BPMN helps organisations to document, analyse, and optimise their Business Processes effectively.
BPMN diagrams fill the communication gap between process design and implementation; hence, all stakeholders from any given level within an organisation can easily understand and appreciate any given process, appraise, and improve performance. BPMN in this sense is of help, whereby it offers common language and visual framework used in process modelling to help the organisation align, bring about transparency, and collaboration of their business execution in achieving operational excellence and success.
6) Functional Flow Block Diagrams (FFBDs)
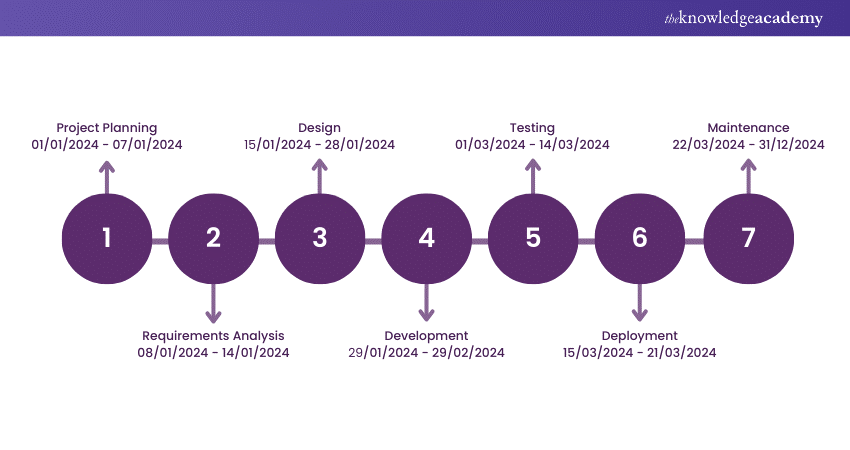
FFBDs provide a structured, time-sequenced graphical depiction of system functions, tracing activities from higher-level processes down to detailed functions. These diagrams organise system functionalities and interdependencies, aiding in system design, requirement analysis, and verification. FFBDs excel in breaking down complex systems into manageable parts, identifying functional dependencies, and establishing a clear system function hierarchy.
Based on the same example used for Gantt Charts, here is an FFBD for the same:
Transform your career and unlock new opportunities with our Business Analysis Courses – Register today!
7) Integrated Definition for Function Modelling (IDEF)
The Integrated Definition for Function Modelling (IDEF) family represents functions, processes, and data within systems. IDEF0, widely used among the IDEF methods, develops structured activity or process models. It uses a systematic approach for defining, analysing, and documenting system functions. IDEF0 diagrams, with their hierarchical box-and-arrow structure, clarify the flow of activities and information, enhancing communication, collaboration, and decision-making across various domains.
8) Petri Nets
Business Processes can be modelled using Petri Nets, showing tasks and their dependencies in terms of circles and bars. Petri Nets are a special way of modelling that extends flowcharts, which just show sequence. The places and transitions represent tasks and the dependencies. The work items being processed are represented as "tokens" flowing through the net. An action of transition is executed only when the input places contain sufficient tokens to leave through the net. Such a graphical and mathematical description enables the analysis of potential bottlenecks and the determination of places in which the process could be improved.
9) Role Activity Diagrams (RADs)
Role Activity Diagrams (RADs) graphically delineate roles and their associated activities within Business Processes, highlighting how different roles interconnect to achieve process goals. These diagrams offer a framework for analysing role behaviour, identifying responsibilities, and designing role-based workflows, thereby aiding in understanding process dynamics and optimising role-based Modelling.
10) Coloured Petri Nets (CPNs)
Coloured Petri Nets (CPNs) by differentiating tokens with colours (values), provide a versatile Modelling tool for complex systems. Tokens convey detailed information, enabling precise behaviour Modelling across diverse, interrelated components like distributed systems and workflow processes. This rich formalism captures system dynamics and interactions, facilitating accurate and rigorous complex system modelling.
Continuing the same Software Development example, here is a sample Coloured Petri Net for the above:
11) Object-Oriented Methods
Object-Oriented Methods model systems around objects, encapsulating data and behaviour. This approach supports modular design, code reusability, and scalability, fostering a structured, maintainable architecture. Applied to Business Process Modelling, it represents entities, activities, or resources, making Modelling intuitive and flexible for stakeholders to optimise workflows.
12) Role Interaction Diagrams (RIDs)
Role Interaction Diagrams (RIDs) illuminate the interactions within a process, outlining communication and coordination among role players. By depicting role relationships and collaboration mechanisms, these diagrams elucidate the dynamics of role-based interactions, aiding organisations in understanding information flow, decision authority, and accountability structures, thus promoting effective stakeholder collaboration.
Explore the Key Roles and Responsibilities of a Business Analyst Today!
Conclusion
By harnessing the power of Business Process Modelling Techniques, you can transform your business from a tangled web to a well-oiled machine. Armed with the knowledge in this guide, you're ready to unveil inefficiencies, optimise workflows, and propel your organisation towards peak performance. So, take charge and transform your business processes today!
Enhance your skills and drive business success with the BCS Practitioner Certificate in Modelling Business Processes – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the benefits of using Business Process Modelling Techniques?

BPMT offers a wide range of advantages, including improved process visibility, identification of bottlenecks, enhanced communication and collaboration, and streamlined operations leading to increased efficiency and cost savings.
Which Business Process Modelling Technique is right for my business?

There's no one-size-fits-all approach! This guide explores various techniques like BPMN, flowcharts, and Petri nets, highlighting their strengths and ideal applications. By understanding your specific needs and process complexity, you can choose the most effective method for mapping your workflows.
How can I implement Business Process Modelling Techniques in my organisation?

This guide doesn't just explain BPMT, it also offers practical steps for getting started. We'll provide tips on selecting the right tools, involving stakeholders, and effectively implementing your chosen technique to maximise its impact on your organisation.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related Courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Business Analysis Courses, including the Instagram Marketing Course, Search Engine Optimisation (SEO) Course, and Google Analytics Certification. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Business Process Modelling Tools.
Our Business Analysis Blogs cover a range of topics related to Digital Marketing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Digital Marketing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BCS Practitioner Certificate in Modelling Business Processes Training
BCS Practitioner Certificate in Modelling Business Processes Training






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


