We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In the world of networking and Internet technology, terms like Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) are often thrown around. While both play crucial roles in the smooth operation of networks, they serve distinct purposes; hence, learning the Difference Between DNS and DHCP is vital in this age.
According to Statista, the market for Network Infrastructure is expected to reach a worth of 162.83 billion GBP by 2023. DNS and DHCP are vital parts of this infrastructure; thus, shedding light on what sets them apart and how they contribute to the functionality of networks is extremely important. Both were developed to simplify how we use networks and the Internet. In this blog, we will take you through the Difference Between DNS and DHCP.
Table of Contents
1) What is DNS?
2) What is DHCP?
3) What is the Difference Between DNS and DHCP?
4) DNS vs DHCP: Which one suits your needs?
5) Conclusion
What is DNS?
Let's start with DNS, the backbone of the Internet which acts as a directory service that helps translate human-readable domain names (like www.example.com) into IP addresses (such as 192.168.1.1). In simpler terms, DNS serves as the Internet's phonebook, mapping user-friendly domain names to the numeric addresses that computers and servers use to identify each other on the network.
In the world of networking and Internet technology, terms like Domain Name System (DNS) and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) are often thrown around. While both play crucial roles in the smooth operation of networks, they serve distinct purposes; hence, learning the Difference Between DNS and DHCP is vital in this age.
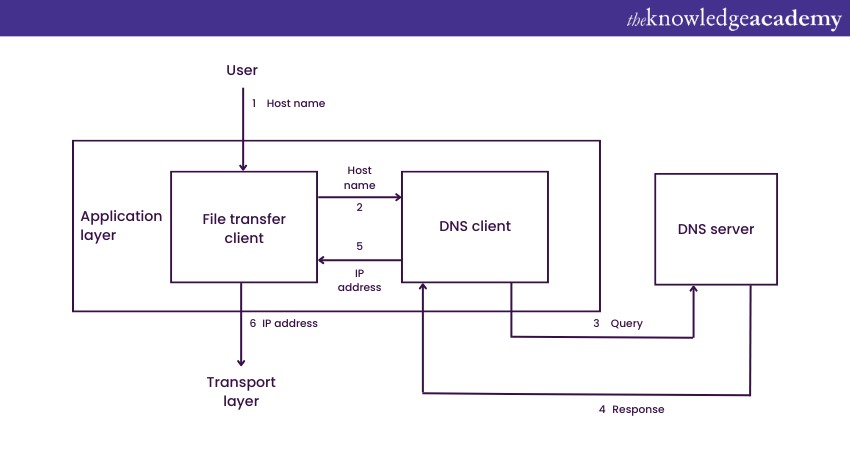
DNS is critical for the smooth functioning of the Internet. Without it, we would need to remember and use numerical IP addresses to access websites, which would be impractical and confusing. DNS simplifies our online experience by allowing us to use user-friendly domain names while ensuring that our requests are directed to the correct destination servers across the global Internet, though it remains vulnerable to threats like DNS Hijacking.
Interested in creating new IT strategies? Try our courses in IT Support and Solution Training!
What is DHCP?
On the other hand, DHCP, or Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, is a network management protocol. It provides automatic IP address allocation and other network configuration settings to devices within a network. DHCP ensures that every device connected to a network can obtain an IP address and other essential parameters without manual intervention.
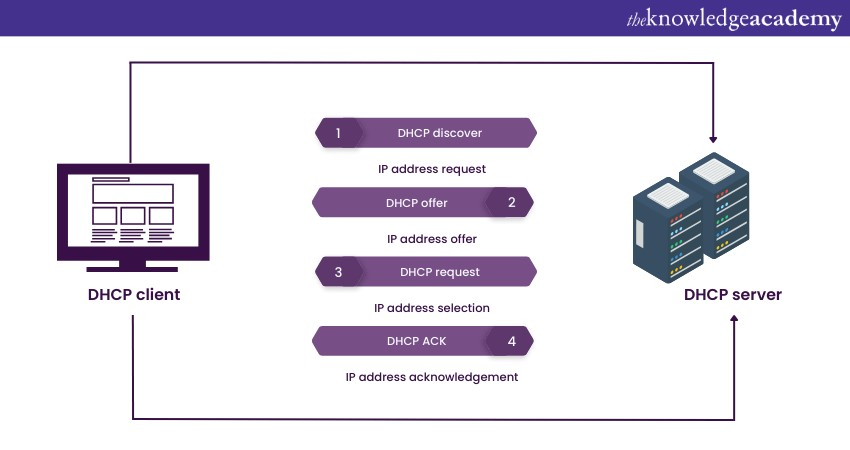
DHCP is a fundamental component of network administration because it simplifies the process of adding, moving, or removing devices on a network. Without it, network administrators would need to manually configure IP addresses for every device, which would be time-consuming and error-prone, especially in large networks.
DHCP streamlines the process, ensuring that devices can seamlessly connect to the network and obtain the necessary network configuration settings, making it an essential tool for efficient and user-friendly network management.
Interested in mastering the Domain Name System? Try our BIND DNS Administration Training!
What is the Difference Between DNS and DHCP?
Now that you have a basic understanding of DNS and DHCP, understanding the differences between these critical components of networking should be easier for you. Some of these differences are as follows:
Functionality
Functionality in networking refers to the specific tasks and capabilities that a network component or protocol performs. Here are some DNS and DHCP differences based on their respective functionalities:
1) DNS: DNS primarily deals with the resolution of domain names to IP addresses. It translates user-friendly domain names into numeric IP addresses, making the process of accessing websites much more easier and services on the Internet. Essentially, it makes Internet resources more accessible by allowing users to use domain names instead of memorising complex IP addresses.
2) DHCP: DHCP focuses on automating the allocation of network resources, primarily IP addresses and related configuration settings. When a device joins a network, DHCP dynamically assigns it an IP address, ensuring that devices can connect and communicate without requiring manual configuration.
Purpose
The purpose of a networking component or protocol defines its main objective and role within the network. The differences between the purpose of DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: The main purpose of DNS is to provide a user-friendly way to access resources on the Internet. It allows users to access various websites and online services using domain names, which are easier to remember than numeric IP addresses.
2) DHCP: DHCP's primary purpose is network management and resource allocation. It assigns IP addresses to devices, manages IP address leases, and configures network settings such as subnet masks, default gateways, and DNS servers.
Operation
Operation in networking describes how a component or protocol functions in practice. The differences between the operation of DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: DNS operates at the application layer of the OSI model, translating domain names into IP addresses when requested by applications or devices, which is a key function of DNS in Application Layer. It does not assign IP addresses but simply resolves domain names to IP addresses.
2) DHCP: DHCP operates at the network layer of the OSI model, providing IP address allocation and configuration services to devices during the network initialisation process. It actively assigns IP addresses and manages their usage.
Don’t know how to connect device? Worry not, our Introduction to Networking Training is what you need!
Communication flow
Communication flow in networking refers to how data and requests are exchanged between components or devices. The differences between the communication flow of DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: In DNS, the client sends a domain name query to a DNS server, requesting the corresponding IP address. The server allows the client to establish a connection with the desired resource by responding to the IP address.
2) DHCP: DHCP operates in a more proactive manner. When a connective device joins a new network, it receives a request to a DHCP server. It seeks an available IP address and other network configuration parameters. The server responds with the requested information.
Statefulness
Statefulness in networking indicates whether a protocol or component maintains information over time. The differences between statefulness of DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: DNS is stateless, meaning it doesn't maintain any information about previously resolved domain names. Each DNS query is independent, and the server responds based on its current knowledge.
2) DHCP: DHCP is stateful, as it keeps track of IP address leases and network configurations. This ensures that IP addresses are not allocated to multiple devices simultaneously and that network settings are consistent.
Resource type
Resource type in networking refers to the specific types of data or parameters managed by a protocol or component. The differences between recourse type usage of DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: DNS primarily deals with domain name records (A records, CNAME records, etc.) and their associated IP addresses. It resolves domain names to IP addresses and vice versa.
2) DHCP: DHCP deals with IP address leases, subnet masks, default gateways, DNS server addresses, and other network configuration parameters. It allocates and manages these resources for devices on the network.
Scalability
Scalability in networking reflects the ability of a component or protocol to adapt to different network sizes and demands. The differences between DHCP and DNS are as follows:
1) DNS: DNS servers are typically organised hierarchically, with a small number of root servers at the top and a larger number of distributed servers beneath them. This hierarchical structure allows DNS to scale effectively.
2) DHCP: DHCP servers are usually deployed within a local network or subnet. Scalability depends on the network's size and the number of devices requiring IP addresses. Larger networks may require multiple servers for redundancy and load balancing.
Does the privacy of Virtual Private Network fascinate you? Learn all about it with our VPN Training!
DNS vs DHCP: Which is better in two?
It's important to note that DNS and DHCP serve entirely different purposes in a network, and their "better" or "worse" comparison isn't meaningful in a direct sense. Instead, their value depends on the specific needs and objectives of the network:
Strengths of DNS
Domain Name System has the following strengths:
1) Enhances user-friendliness: DNS simplifies Internet navigation by translating domain names into IP addresses, making it easier for users to access websites and services. This makes it much easier for users to access websites and services, as remembering and typing in IP addresses would be impractical for most people.
2) Critical for web browsing: DNS is a cornerstone of the Internet's infrastructure. It plays a major role in the functioning of web browsing. Without it, users would need to remember and enter IP addresses for every website they want to visit, which is both inconvenient and inefficient.
Prepare effectively with DNS Interview Questions and Answers. Stand out in your next interview by mastering key concepts and examples!
Limitations of DNS
Domain Name System has the following limitations:
1) Vulnerability to attacks: DNS is vulnerable to various types of threats, including DNS Attacks such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning. These attacks can lead to security risks by redirecting users to malicious websites or intercepting their traffic. Network administrators must implement security measures to mitigate these risks.
2) Limited to domain name resolution: DNS is primarily designed for domain name resolution, translating domain names into IP addresses and vice versa. It does not handle IP address assignment or network configuration tasks. This means that while it simplifies accessing resources, it doesn't manage the allocation of IP addresses within a network.
Strengths of DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol has the following strengths:
1) Efficient network management: DHCP excels in network management by automating the allocation of IP addresses and network configuration settings. It reduces the need for manual configuration, which minimises errors and saves time for network administrators.
2) Scalability: DHCP is highly scalable and can efficiently handle IP address assignment in both small and large networks. It allows for the seamless addition of new devices without significant administrative overhead.
Limitations of DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol has the following limitations:
1) Dependency on DHCP server: DHCP's functioning depends on the availability and proper configuration of its servers. If a server fails or is misconfigured, it can disrupt network connectivity, making it essential to maintain reliable server infrastructure.
2) Requires careful configuration: Proper configuration of DHCP settings is crucial to avoid IP address conflicts or network misconfigurations. Carelessness in configuration can lead to network issues, including device connectivity problems.
Conclusion
In brief, learning the Difference between DNS and DHCP is integral to mastering the fundamentals of networking and ensuring efficient network operation. As technology evolves, staying updated on the development of these terminologies is crucial. These protocols, with their unique roles, facilitate Internet access and device connectivity, enhancing digital efficiency for all, from network administrators to tech enthusiasts.
Interested in open-source web server software? Why not try our NGINX Training!
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BIND DNS Administration Training
BIND DNS Administration Training
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


