We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Information is one of the most valuable assets of any organisation. It can gain a competitive advantage, improve customer satisfaction, and enhance operational efficiency. However, information also faces various threats, such as cyberattacks, data breaches, natural disasters, human errors, and sabotage. Therefore, protecting information from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, modification, or destruction is essential. That’s where the Information Security Management System (ISMS) comes in handy. But What is an Information Security Management System, and how does it work?
In this blog, we will provide a comprehensive answer to the question: What is an Information Security Management System, and what are its significance, components, and benefits? We will also discuss establishing, deploying, and maintaining an effective ISMS for your organisation. Whether you are a manager, an employee, a customer, or a supplier, you will find this blog helpful and informative.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is an Information Security Management System
2) What is the significance of an Information Security System?
3) How does ISMS work?
4) Establishing an Information Security Management System
5) What are the components of Information Security Management?
6) Advantages of implementing an Information Security Management System
7) Best Practices for Information Security Management Systems
8) Conclusion
Understanding What is an Information Security Management System
An Information Security Management System or ISMS is a set of procedures, policies, tools, and controls that manage the risks associated with information and ensure its security. An ISMS covers all aspects of Information Security, such as physical, technical, organisational, and human factors. An ISMS also defines the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders involved in Information Security, such as management, employees, customers, suppliers, and regulators. An ISMS is based on risk assessment, treatment, continuous improvement, and compliance principles.
What is the significance of an Information Security System?
An Information Security system is essential for several reasons:
a) It helps to safeguard an organisation's information assets from potential threats and vulnerabilities
b) It helps to meet the expectations and requirements of the customers, partners, and regulators regarding Information Security
c) It helps to enhance the reputation and trustworthiness of an organisation as a reliable and responsible entity
d) It helps to reduce the costs and consequences of Information Security incidents and breaches
e) It helps to enhance the productivity and performance of an organisation by ensuring the availability and quality of information
How does ISMS work?
An ISMS follows a systematic and structured approach to Information Security Management. The main steps involved in an ISMS are:

a) Plan: This step involves identifying the ISMS's scope, objectives, and context. It also necessitates conducting a risk assessment to determine the information assets, threats, vulnerabilities, and impacts. A risk treatment plan is developed based on the risk assessment to select and implement the appropriate security controls to mitigate the risks.
b) Do: This step involves executing the risk treatment plan and applying the security controls to the information assets. It also ensures the awareness and competence of the people involved in Information Security and provides the necessary resources and support.
c) Check: This step involves monitoring and measuring the ISMS's effectiveness and efficiency. It also involves conducting audits and reviews to evaluate the ISMS's compliance and performance against the established objectives and standards.
d) Act: This step involves taking corrective and preventive actions to address the gaps and weaknesses identified in the ISMS. It also involves updating and improving the ISMS based on the feedback and lessons learned.
Become a Certified Information Security Manager (CISM) and elevate your career in Cyber Security with our comprehensive training.
Establishing an Information Security Management System
Establishing an ISMS requires a strong commitment and support from an organisation's top management. It also requires the involvement and participation of all the relevant stakeholders, such as employees, customers, suppliers, and regulators. The main steps involved in establishing an ISMS are:
a) Define the scope and boundaries of the ISMS: This involves determining the information assets, processes, and activities that the ISMS covers, as well as the factors that impact it, both internal and external.
b) Obtain management support and approval: This involves obtaining the endorsement and authorisation from top management for the ISMS and assigning the roles and responsibilities for its implementation and maintenance.
c) Establish the ISMS policy and objectives: This involves developing and documenting the ISMS policy and objectives that reflect the vision, mission, and values of the organisation, as well as the expectations and requirements of the stakeholders.
d) Conduct the risk assessment and treatment: This involves identifying and analysing the associated risks and selecting and implementing the security controls to reduce the risks to an acceptable level.
e) Implement the security controls and procedures: This involves applying the security controls and procedures to the information assets and ensuring the awareness and competence of the people involved in Information Security.
f) Monitor and measure the ISMS performance and effectiveness: This involves collecting and analysing the data and information related to the ISMS, such as security incidents, audit results, customer feedback, and key performance indicators.
g) Review and improve the ISMS: This involves evaluating and verifying the ISMS against the established policy and objectives and identifying and implementing improvement opportunities.
What are the components of Information Security Management?
Information Security Management consists of five main components, namely:
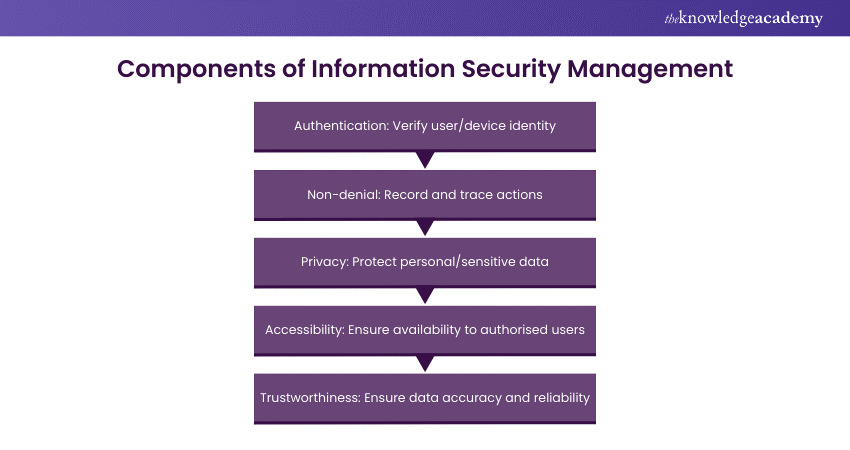
a) Authentication: This component ensures that the identity of the users and devices accessing the information assets is verified and validated. Authentication can be achieved using multiple methods, such as passwords, biometrics, tokens, certificates, and multifactor authentication.
b) Non-denial: This component ensures that the actions and transactions performed by the users and devices on the information assets are recorded and traceable. Non-denial can be achieved by using various techniques, such as digital signatures, timestamps, logs, and audit trails.
c) Privacy: This component ensures that the personal and sensitive information of the users and devices stays protected from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, modification, or deletion. Privacy can be achieved using various measures, such as encryption, anonymisation, pseudonymisation, and consent.
d) Accessibility: This component ensures that the information assets are available and accessible to the authorised users and devices when and where they need them. Accessibility can be achieved using various mechanisms, such as backup, recovery, redundancy, and load balancing.
e) Trustworthiness: This component ensures that the information assets are accurate, complete, consistent, and reliable. Various methods, such as validation, verification, quality assurance, and integrity checks, can achieve trustworthiness.
Level up your Cyber Security career with our top-notch CISM Training. Join now!
What factors are crucial for successfully deploying an ISMS?
Deploying an ISMS requires careful planning, execution, and evaluation. Some of the factors that are crucial for successfully deploying an ISMS are:
a) Alignment with the business strategy and objectives: The ISMS should be aligned with the organisation's vision, mission, and goals, as well as the expectations and requirements of the stakeholders. It should also support the organisation's core processes and activities, as well as its value proposition and competitive advantage.
b) Adoption of the best practices and standards: The ISMS should be based on the best practices and standards widely recognised and accepted in the industry and domain. It should also comply with the relevant laws and regulations that govern Information Security. One of the most popular and comprehensive standards for ISMS is ISO/IEC 27001, which provides a framework and a certification scheme for ISMS.
c) Integration with the existing systems and processes: The ISMS should be integrated with the organisation's existing systems and processes, such as the IT infrastructure, the business applications, the quality management system, and the risk management system. It should also leverage the organisation's existing resources and capabilities, such as the people, the technology, and the culture.
d) Communication and awareness: The ISMS should be communicated and promoted to all the relevant stakeholders, such as management, employees, customers, suppliers, and regulators. The ISMS should also raise awareness and understanding of the importance and benefits of Information Security, as well as the roles and responsibilities of the stakeholders in Information Security.
e) Training and education: The ISMS should provide the necessary training and education to the people involved in Information Security, such as the ISMS team, the security personnel, the users, and the auditors. The training and education should cover the knowledge, skills, and competencies required for Information Security, such as the ISMS policy and objectives, the security controls and procedures, the security incidents and responses, and the security audits and reviews.
f) Evaluation and improvement: The ISMS should be evaluated and improved regularly based on the feedback and data collected from the monitoring and measurement activities, such as the security incidents, the audit results, the customer feedback, and the key performance indicators. The evaluation and improvement should identify and address the gaps and weaknesses in the ISMS and the opportunities and strengths in the ISMS.
Enhance your Cyber Security expertise with our Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) Course and propel your career to new heights.
Advantages of implementing an Information Security Management System
Implementing an ISMS can bring various advantages to an organisation, such as:
a) Ensures continuity in business operations: An ISMS can help ensure the continuity and resilience of business operations by preventing or minimising the disruption and downtime caused by Information Security incidents and breaches. An ISMS can also help recover and restore information assets and services in a timely and efficient manner in case of an incident or a breach.
b) Fosters a positive company culture: An ISMS can help foster a positive and proactive company culture by promoting the values and principles of Information Security, such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It can also help enhance the morale and motivation of employees by providing them with a sense of security, responsibility, and accountability.
c) Responds effectively to evolving threats: An ISMS can help to respond effectively and efficiently to the changing and complex threats and challenges in the Information Security landscape, such as cyberattacks, data breaches, ransomware, phishing, and malware. It can also help to adapt and update security controls and procedures to cope with changing technologies, regulations, and customer expectations.
d) Improves customer satisfaction and loyalty: An ISMS can help to elevate customer satisfaction and loyalty by ensuring the security and quality of the information and services provided to the customers. An ISMS can also help to build and maintain the trust and confidence of customers by demonstrating the organisation's commitment and capability in information security.
e) Increases competitive advantage and market share: An ISMS can help increase an organisation's competitive advantage and market share by differentiating it from its competitors and creating a unique value proposition for customers. It can also help attract and retain new and existing customers, partners, and investors by showcasing the organisation's credibility and reputation in Information Security.
Elevate your expertise in Cyber Security architecture with our CISSP-ISSAP Training and Certification. Register today!
Best Practices for Information Security Management Systems
Implementing an ISMS is not a one-time set up and forget project. It is a continuous process that demands constant monitoring, evaluation, and improvement. Some of the best practices for Information Security Management Systems are:
a) Utilise data encryption: Data encryption is one of the most effective and widely used methods to protect the confidentiality and integrity of information. It involves transforming the information into an unreadable and unrecognisable form using a secret key or algorithm. Data encryption can be applied to information at rest, in transit, or use depending on the level of security required.
b) Ensure the security of devices: Devices, such as computers, laptops, smartphones, tablets, and USB drives, are often used to store, access, and transfer information. However, these devices are also vulnerable to theft, loss, damage, or unauthorised access. Therefore, it is important to ensure the security of the devices by using various measures, such as passwords, biometrics, encryption, antivirus, firewall, VPN, and remote wipe.
c) Comprehend business requirements: Information Security is not a one-size-fits-all solution but a tailored and customised solution that depends on the organisation's and stakeholders' specific needs and expectations. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend the business requirements, such as the scope, objectives, context, and risks of Information Security, as well as the standards, laws, and regulations that apply to it.
Become a Cyber Security leader with our Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) Training and safeguard your organisation against digital threats.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Information Security Management System (ISMS) serves as a cornerstone for safeguarding sensitive data, mitigating security risks, and ensuring organisational resilience. By adopting and adhering to ISMS best practices, organisations can uphold the integrity and confidentiality of their information assets, fortifying their defences against evolving threats.
Advance your career in Cyber Security Management with our Information Systems Security Management Training and acquire the skills to protect critical digital assets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Information Security and Cyber Security?

Information security focuses on protecting all types of data, including physical and digital assets, from unauthorised access, use, disclosure, alteration, or destruction. Cyber Security, on the other hand, specifically deals with safeguarding digital information and systems from cyber threats such as hacking, malware, and cyberattacks.
What are the common types of Information Security incidents and breaches?

Common types of Information Security incidents and breaches include data breaches (unauthorised access or disclosure of sensitive data), malware attacks (such as viruses or ransomware), phishing attacks (fraudulent attempts to obtain sensitive information), insider threats (misuse or unauthorised access by employees), and Denial-of-Service attacks.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various CISM Trainings, including the CISM Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into CISM Requirements.
Our IT Security and Data Protection Blogs cover a range of topics related to CISM, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your CISM Compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 CISM Certified Information Security Manager
CISM Certified Information Security Manager
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Sat 8th Mar 2025, Sun 9th Mar 2025
Sat 5th Apr 2025, Sun 6th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Sat 3rd May 2025, Sun 4th May 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Sat 7th Jun 2025, Sun 8th Jun 2025
Sat 5th Jul 2025, Sun 6th Jul 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Sat 2nd Aug 2025, Sun 3rd Aug 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Sat 6th Sep 2025, Sun 7th Sep 2025
Sat 4th Oct 2025, Sun 5th Oct 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Sat 8th Nov 2025, Sun 9th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Sat 6th Dec 2025, Sun 7th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


