We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In Risk Management, two prominent standards, ISO 27005 and ISO 31000, emerge as key players. While sharing the overarching goal of helping organisations navigate risks, these standards diverge in their scope, applicability, and focus. ISO 27005 is tailored to safeguard information security, while ISO 31000 offers a broader framework applicable to diverse risk types.
Understanding the difference between ISO 27005 and ISO 35000 is essential in Risk Management. In this blog, we explore the differences between ISO 27005 and ISO 31000 to help you choose the right Risk Management standard for your organisation.
Table of Contents
1) ISO 27005: Risk Management in information security
2) ISO 31000: Risk Management framework
3) ISO 27005 vs ISO 31000: A comparative analysis
a) ISO 27005
b) ISO 31000
4) Conclusion
ISO 27005: Risk Management in information security
ISO 27005 is a Risk Management standard that provides guidelines and principles for managing information security risks within an organisation. It helps organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks related to the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information assets. ISO 27005 is a part of the ISO 27000 series, which focuses on Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This standard places a strong emphasis on several key concepts and principles:
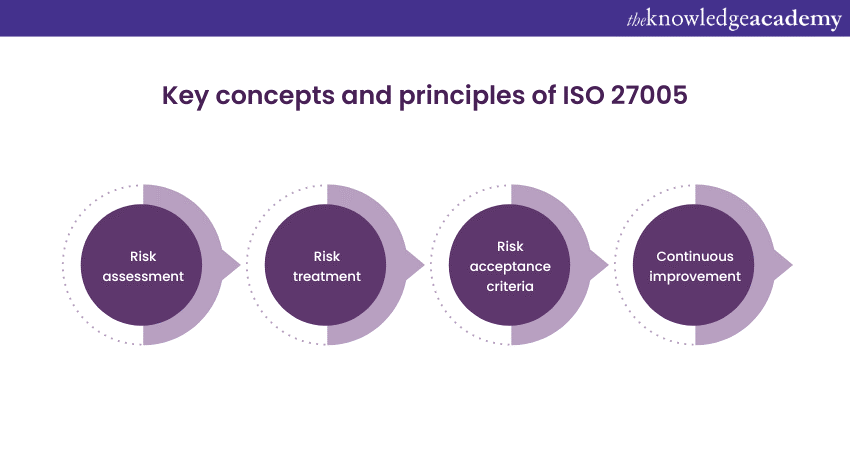
a) Risk assessment: ISO 27005 guides organisations in identifying and evaluating risks associated with their information assets, considering internal and external threats, vulnerabilities, and potential impacts.
b) Risk treatment: It provides methodologies for selecting and implementing appropriate risk treatment options, including risk mitigation, risk transfer, risk avoidance, or risk acceptance.
c) Risk acceptance criteria: ISO 27005 encourages organisations to establish clear criteria for accepting or rejecting risks, ensuring that Risk Management decisions align with business objectives and risk tolerance levels.
d) Continuous improvement: The standard highlights the significance of constant and adaptive Risk Management procedures that enable organisations to respond to emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Ready to elevate your organisation's information security Risk Management practices? Explore our ISO 27005 Training Course!
ISO 31000: Risk Management framework
ISO 31000, titled "Risk Management – Guidelines," is a versatile and globally recognised standard that provides a comprehensive framework for Risk Management across various industries and domains. Unlike ISO 27005, which focuses on information security, ISO 31000 is a generic framework that can be applied to manage risks of all types and is not limited to a specific context.
At its core, ISO 31000 is built upon fundamental principles, including integration into organisational governance, customisation to an organisation's context, and a continuous improvement approach. These principles ensure that Risk Management aligns with an organisation's strategic goals and evolves with changing circumstances.
ISO 31000's versatility applies to various financial, operational, strategic, compliance, and reputational risks. It provides a structured methodology for organisations to effectively identify, assess, treat, and monitor risks.
One of its key strengths is adaptability; organisations can tailor the ISO 31000 framework to suit their specific needs and objectives. This flexibility allows for incorporating industry-specific standards and practices, ensuring the Risk Management process remains relevant and aligned with the organisation's unique risk landscape.
ISO 27005 vs ISO 31000: A comparative analysis
ISO 27005 and ISO 31000 are two internationally recognised standards that address Risk Management, but they serve distinct purposes and have different scopes. This comparative analysis will dive deeper into the differences between these two standards, focusing on critical aspects such as scope, terminology, industry relevance, and certification.
ISO 27005
ISO 27005 standard is dedicated to information security Risk Management. It explicitly targets risks related to information assets' confidentiality, integrity, and availability. ISO 27005 is integral to the broader ISO 27000 series, encompassing various aspects of information security management. ISO 27005 utilises information security terminology, making it well-suited for organisations with a strong focus on cybersecurity. It seamlessly integrates with ISO 27001, the Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) standard.
ISO 27005 standard is highly relevant to organisations prioritising information security, such as IT companies, financial institutions, healthcare providers, and any entity that handles sensitive data.
ISO 31000
ISO 31000, on the other hand, is a generic Risk Management framework that applies to all types of risks organisations face, not limited to information security. It can manage financial, operational, strategic, compliance, and more chances. ISO 31000 provides a versatile Risk Management framework that can be customised to any organisation's unique context and needs, regardless of the risk nature. ISO 31000 has broader industry applicability. It caters to organisations across all sectors, from finance and healthcare to manufacturing and government, making it a flexible choice for comprehensive Risk Management.
Ready to establish a strong foundation in information security Risk Management? Join our ISO 27005 Foundation training!
Conclusion
In the domain of ISO standards, ISO 27005 and ISO 31000 stand as beacons for organisations seeking effective Risk Management. ISO 27005 zeroes in on the critical domain of information security, while ISO 31000 casts a broader net, encompassing chances of all shapes and sizes.
Going through a comparison between ISO 27005 vs ISO 31000 will help you to gain a clear understanding of both standards. Your choice ultimately depends on the nature of your organisation, the breadth of risks you face, and your strategic objectives. Armed with this comparative analysis, you can now decide to bolster your Risk Management practices and fortify your organisation against an ever-growing risk domain.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 ISO 27005 Foundation
ISO 27005 Foundation
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


