We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

From Strategic and Operational management to Financial and Human Resource Management, each type plays a crucial role in shaping organisational strategies, optimising operations, and fostering growth. Join us as we dive into the intricacies of these management types, exploring their significance, key components, and real-world applications.
Discover different Types of Business Management, including strategic, operational, and Human Resource Management. Learn how each type can impact your company's success.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding the significance of Business Management
2) Strategic Management
3) Operational Management
4) Financial Management
5) Human Resource Management
6) Marketing Management
7) Innovation and Change Management
8) Project Management
9) Environmental Management
10) Conclusion
Understanding the Significance of Business Management
Business Management goes beyond mere oversight; it encompasses a range of practices that guide organisations toward their objectives, ensure optimal resource utilisation, and foster an environment conducive to innovation and adaptability. At its core, Business Management provides direction and purpose to an organisation. It involves defining the vision, mission, and goals that guide all activities. Without a clear management framework, businesses can drift aimlessly, lacking a unifying purpose that aligns efforts across different departments and teams.
Resources, be they financial, human, or technological, are the lifeblood of any organisation. Business Management involves allocating these resources strategically to maximise efficiency and returns. A robust management approach identifies areas of resource wastage, reallocates assets based on priority, and ensures that resources are utilised optimally to achieve the desired outcomes. From routine operational choices to high-stakes strategic decisions, a structured management approach helps evaluate options and mitigate risks.
Through performance measurement, evaluation, and continuous improvement initiatives, management identifies areas of underperformance and devises strategies to enhance productivity and efficiency. This drive for excellence elevates the organisation's overall capabilities.
Embark on a transformative journey of leadership excellence with our Leadership Training
Strategic Management
Strategic Management is a comprehensive approach that involves formulating, executing, and overseeing an organisation's long-term goals and plans. It is the art of steering an organisation toward success by aligning its internal strengths and weaknesses with external opportunities and threats.
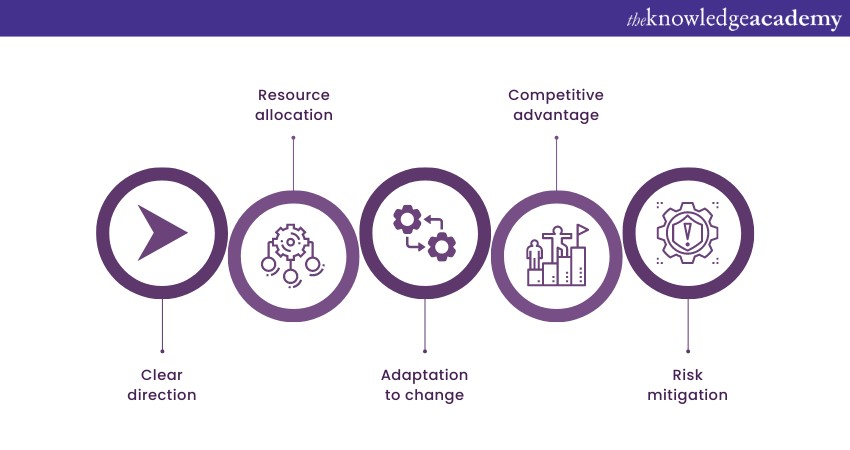
Strategic Management is like plotting a course on a vast, ever-changing sea. It requires a thorough understanding of the organisation's current state, its desired future, and the route to bridge the gap between the two. This process involves a blend of analysis, decision-making, and execution to create a roadmap that navigates the organisation toward its envisioned horizon.
Strategic Management serves as the compass that guides an organisation through turbulent waters. Several vital factors underscore its importance:
1) Clear direction: Strategic Management gives the organisation a clear sense of direction. It defines the purpose, mission, and vision that steer all activities and decisions.
2) Resource allocation: Through Strategic Management, resources are allocated judiciously to areas that promise the greatest Return on Investment (ROI). This prevents resource wastage and ensures efficient resource utilisation.
3) Adaptation to change: In a world characterised by rapid change, Strategic Management equips organisations to adapt and thrive. It anticipates shifts in the market, technology, and customer preferences, enabling the organisation to pivot when necessary.
4) Competitive advantage: A well-devised strategy can establish a competitive edge by leveraging the organisation's strengths against market demands. This can lead to differentiation and a stronger market position.
5) Risk mitigation: Strategic Management involves a thorough analysis of potential risks and the development of contingency plans. It minimises the impact of unforeseen challenges and allows for quicker recovery.
Operational Management
Operational Management is the art and science of optimising processes, resources, and activities to ensure efficient production, delivery of goods or services, and overall organisational performance. The invisible hand orchestrates the flow of tasks, people, and materials, ultimately shaping the organisation's ability to meet its objectives.
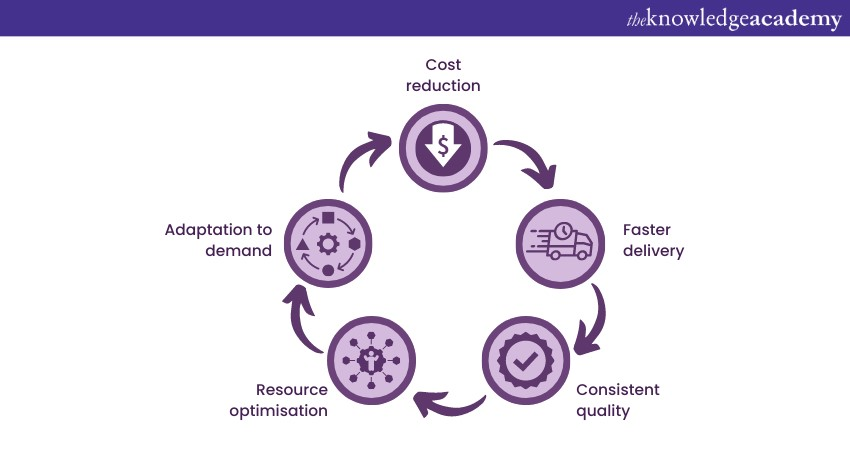
Operational Management plays a pivotal role in enhancing efficiency across the organisation. Here's how:
1) Cost reduction: By identifying inefficiencies and optimising processes, operational management helps reduce operating costs. This leads to improved profitability and competitiveness.
2) Faster delivery: Streamlined processes and efficient resource allocation lead to quicker production and delivery of goods or services, satisfying customer demands promptly.
3) Consistent quality: Operational Management consistently ensures that products or services meet quality standards, fostering customer trust and loyalty.
4) Resource optimisation: By effectively managing resources, Operational Management prevents wastage and ensures the optimal utilisation of assets.
5) Adaptation to demand: Operational Managers monitor market trends and demand patterns, adjusting production levels and resource allocation accordingly.
Embark on a transformative journey with our Business Administration Masterclass today!
Financial Management
Financial Management is the strategic process of planning, controlling, and optimising an organisation's financial resources to achieve its goals and objectives. The compass guides decision-making, allocates resources, and steers the ship of business towards profitable shores.
Financial Management plays a pivotal role in addressing several critical challenges:
1) Capital allocation: Financial Managers must allocate resources wisely to maximise returns and sustain growth while managing the organisation's financial structure.
2) Uncertainty management: Financial Managers assess and mitigate financial risks in a volatile market to ensure the organisation's stability.
3) Resource optimisation: Efficient Financial Management minimises waste and ensures optimal utilisation of resources.
4) Strategic decision-making: Financial insights guide expansions, acquisitions, and product development, ensuring alignment with the organisation's goals.
5) Stakeholder confidence: Transparent financial reporting builds stakeholder confidence, attracting investors and maintaining solid relationships with lenders and shareholders.
Human Resource Management
Human Resource Management (HRM) is about effectively managing an organisation's most asset: its people. From recruitment to development, HRM plays a pivotal role in creating a conducive work environment, nurturing employee potential, and aligning individual goals with organisational objectives.
HRM encompasses a spectrum of responsibilities that revolve around people and their well-being within the organisation. Some of its fundamental pillars include:
1) Recruitment and onboarding: HRM is responsible for sourcing, selecting, and onboarding new employees who align with the organisation's culture and values.
2) Employee development and training: HRM designs training programs, skill development initiatives, and career advancement opportunities to enhance employee capabilities.
3) Performance management: HRM establishes performance metrics, conducts evaluations, and provides feedback to ensure employees meet their potential and contribute effectively.
4) Employee engagement and well-being: HRM's purview falls under creating a positive work environment, fostering employee satisfaction, and addressing well-being concerns.
Marketing Management
Marketing Management is the art and science of planning, implementing, and controlling marketing strategies to effectively promote products or services, capture customer interest, and create lasting brand connections. It's the bridge that connects businesses with consumers, forging relationships and driving growth.
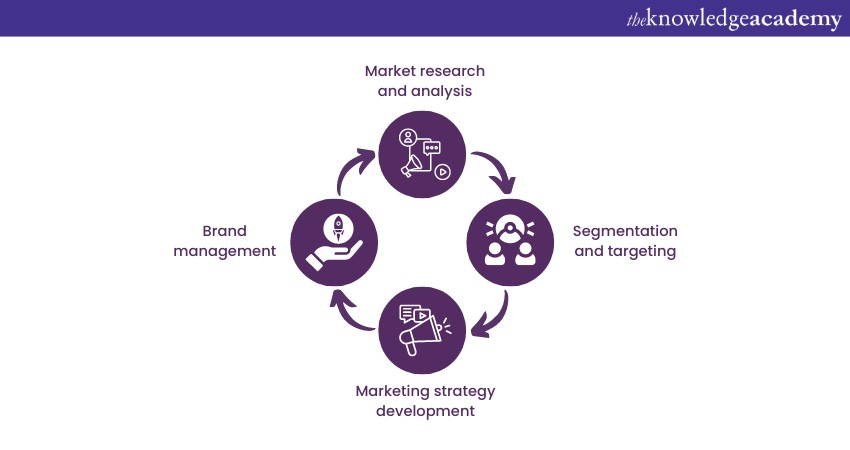
Marketing Management encompasses a range of activities aimed at attracting and retaining customers. Some of its fundamental pillars include:
1) Market research and analysis: Marketing Managers gather and analyse data about market trends, customer preferences, and competition to make informed decisions.
2) Segmentation and targeting: They divide the market into segments based on characteristics and needs, then target specific segments with tailored strategies.
3) Marketing strategy development: Marketing Managers formulate strategies that outline product positioning, pricing, distribution, and promotion.
4) Brand management: Cultivating and maintaining a solid brand identity is essential for conveying value and building brand loyalty.
Effective Marketing Management revolves around developing strategies that resonate with the audience:
1) Product positioning: Marketing Managers define how their products or services stand out, highlighting unique features and benefits.
2) Pricing strategies: They determine appropriate pricing models that reflect value while remaining competitive.
3) Promotion and communication: Marketing Managers create compelling messages and campaigns that reach the target audience through various channels.
4) Distribution channels: Decisions regarding how products reach consumers are critical to ensuring accessibility and convenience.
Innovation and Change Management
Innovation and Change Management involve:
1) Fostering a culture of creativity.
2) Introducing novel ideas.
3) Guiding organisations through transitions to ensure sustainable success.
Innovation involves generating and implementing new ideas, processes, or products that create value and improve efficiency. It is the spark that ignites progress and differentiation in the market.
1) Change Management: It is the structured approach to transitioning individuals, teams, and the organisation from the current state to a desired future state. It ensures that change is embraced and smoothly integrated. Change is met with resistance, but effective Change Management can overcome it:
2) Identifying the need for change: The first step is to recognise when change is necessary due to shifting market conditions, technological advancements, or other factors.
3) Creating a vision: Articulating a clear and compelling vision of the future state helps employees understand the purpose and benefits of the change.
4) Engaging stakeholders: Involving employees in the change process empowers them and creates a sense of ownership.
Project Management
Project Management is the systematic approach of planning, executing, and controlling tasks to achieve specific objectives within defined constraints. It's the art of harmonising people, resources, and processes to make sure that projects are concluded on time, within scope, and to stakeholders' satisfaction.
Project Management is not confined to a specific industry; it is a universal practice that guides projects from inception to completion. A project could be developing a new product, launching a marketing campaign, building a bridge, or implementing a software system. Effective Project Management remains the key to success regardless of the project's nature.
A significant portion of Project Management involves meticulous planning and scheduling:
1) Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Breaking down the project into smaller, manageable tasks makes assigning responsibilities and tracking progress easier.
2) Gantt charts: Visualising the project timeline and task dependencies through Gantt charts helps allocate resources efficiently.
3) Critical path analysis: Identifying the critical path—the sequence of tasks with no room for delay—ensures that project completion is not compromised.
Environmental Management
Environmental Management involves adopting strategies, policies, and practices that minimise negative environmental impacts while fostering business growth. It is the commitment to balance economic prosperity with ecological stewardship, ensuring a harmonious coexistence between business and the planet.
At the core of Environmental Management lies sustainability and corporate responsibility:
1) Reducing carbon footprint: Environmental Management aims to reduce carbon emissions by optimising energy use, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and improving energy efficiency.
2) Waste reduction: Minimising waste generation through efficient production processes and recycling initiatives is a hallmark of Environmental Management.
Environmental Management goes beyond regulatory compliance; it is about integrating ecological considerations into every facet of an organisation's operations:
1) Sustainable practices: Environmental Management encourages businesses to adopt practices that minimise resource consumption, waste generation, and pollution.
2) Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): Embracing environmental management showcases a commitment to social responsibility, enhancing a company's reputation and public.
Conclusion
Each Type of Business Management has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice of which approach to adopt depends on factors such as the organisation's size, industry, culture, and goals. What remains constant, however, is the essential role that Business Development domain plays in steering businesses toward success.
Attain knowledge of strategic planning, financial management, and operational excellence with our Business Management Training!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Business Analysis Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Leadership Skills Training
Leadership Skills Training
Fri 28th Feb 2025
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


