We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Projects are divided into different phases using the Agile methodology. Agile Transformation modifies business operations and conduct, which helps promote change. This change intends to replace current operation models with a better strategy. The agile technique combines continuous planning, proper execution, and regular reviews. It also necessitates continual cooperation with stakeholders and continuous improvement at each level.
According to the State of Agile Report, 89% of participants responded that high-performing Agile teams have leadership empowerment, a clear-cut culture, and tools centred on people. Switching to agile can be challenging because it requires adjustments to organisational structure, technology, and operating procedures. These adjustments may be difficult, but they will benefit the company in the long run. Agile Transformation is the process of adopting and implementing agile methodologies across an organisation. Explore the benefits & challenges in this blog.
Table of Contents
1) Explaining the term: Agile Transformation
2) Important Stages of Agile Transformation
3) Roadmap of Agile Transformation
4) Advantages of Agile Transformation
5) Challenges faced while implementing Agile Transformation
6) Agile Transformation vs. Agile adoption
7) Conclusion
Explaining the term: Agile Transformation
Converting an organisation to an Agile method of working is known as Agile Transformation. For a firm to follow the Agile method, every employee in every division must adopt the values and guiding principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto. This entails a readiness to be more adaptable and responsive, to work well with others, and to speak honestly. Agility-focused businesses aim to be well-organised and effective in general.
Factors such as cooperation, communication, methods, and assessment will be based on the Agile Software Development concept. A thorough analysis and cross-organisational collaboration are necessary for such a transformation. Cross-functional teams make incremental progress and adjust to client comments and corporate requirements. Faster value delivery, lower defect rates, speedier development timeframes, and better client experiences are the ultimate objectives of the Agile Transformation approach.
Agile Frameworks such as Kanban and Scrum are often implemented by developers as pilot projects which shows the beginning of achieving the transformation. Other organisations might use agile more generally if these teams have seen the transformation successful. However, it must be noted that executive leadership must first embrace Agile Transformation across the organisation rather than making the technology team focus on it initially if a meaningful change needs to be implemented.
Important Stages of Agile Transformation

One needs to be aware of some essential stages while implementing Agile Transformation and setting out on a journey of Agile. The stages are discussed below:
Thinking the Agile way and recognising the different roles and responsibilities
The first stage involves training each team, influencing them to embrace change, and adopting an Agile mindset. This results in improved communication among team members motivating them to work together towards a common objective. This is needed because the organisation's current structures should be addressed in a full-swing Agile Transformation where collaboration and communication are its cornerstones.
Conducting Agile training
The second stage in the journey of Agile Transformation should be to conduct training on Agile. An Agile trainer's responsibility is to see that everyone understands the fundamentals of Agile Development and effectively applies the guiding principles. The cultural revolution puts automation tasks front and centre by removing the barriers between development and operations. Therefore, it is crucial to hire Agile coaches to assist in raising understanding of the various Agile frameworks and practises.
Creating Agile Transformation Roadmap
The next stage is to create an Agile Transformation strategy that will assist you in establishing the objectives and goals and the associated checkpoints along the way. Such roadmaps help one to achieve a successful transition. Some of the points that must be focussed on while creating a roadmap are creating a vision and goal for a particular Agile Transformation management.
Secondly, knowing the length of an Agile Transformation and preparing detailed timetables. Finally, the biggest barrier that the organisation needs to overcome is changing how teams have worked for years and including cross-functional arrangements in which everyone collaborates to achieve a common objective.
Changing to product mindset over project mindset
Organisations typically work with the project mindset, switching to the next project after delivering a functionally developed program to the end-user or the customer. However, Agile does not support this idea and believes that Project Management should be different. The Agile team maintains and delivers value over the course of developing a program according to a product mindset. Therefore, the crucial component of fully embracing the Agile Transformation is choosing a product mindset over a project mindset.
Evaluate, learn and verify the status of Agile
In this stage of the Agile Transformation journey, there should be a focus on testing the Agile phases. Some include sprint tests, daily scrum meetings, sprint retrospective meetings, setting up product backlogs, and limiting Work in Process (WIP). Through these phases, obstacles and other weaknesses are determined, and the Agile Transformation approach is revised to address them. Factors like no ongoing interaction with the end users, no precise requirements, lack of feedback, etc., show that real Agile is not implemented and is just by name only.

Roadmap of Agile Transformation
A roadmap provides a structured approach to achieving a goal. Transforming a complex organisation can only be accessible with appropriate assistance; this section will look at a practical roadmap for Agile Transformation.
Stage one: Getting started
Beginning the Transformation involves setting business goals for the organisation, and setting the end goals at the beginning enables many controllable factors in defining the course ahead. Keeping the end goal in perspective, tasks such as forming a team, defining process flows, establishing command and developing strategies for performance assessment can be implemented effectively.
Stage two: Implementation
Once the plans for the roadmap are established, the next stage involves implementing the developed methods. This stage consists of forming, training and evaluating the teams. Once the team gets to work, their performance is analysed based on the desired outcome for achieving the end goal; these metrics are monitored regularly and communicated to the teams to improve efficiency.
Stage three: Maintaining efficiency
Once the teams gain momentum in implementing the plans, the next stage focuses on maintaining the overall plan's progress. This stage involves:
a) Constantly monitoring the process, adapting based on process requirements and creating training materials on the updated process.
b) Updating the methods and strategies based on process requirements.
c) Conducting assessments with teams to communicate the performance metrics and to identify any hurdles.
Following a structured approach in terms of a roadmap ensures progress and enables teams to overcome any difficulties in a planned manner, assisting in achieving end goals effectively.
Learn more about the Agile Roles, Progressions and Lifecycle journeys by signing up for our Agile Overview course now!
Advantages of Agile Transformation
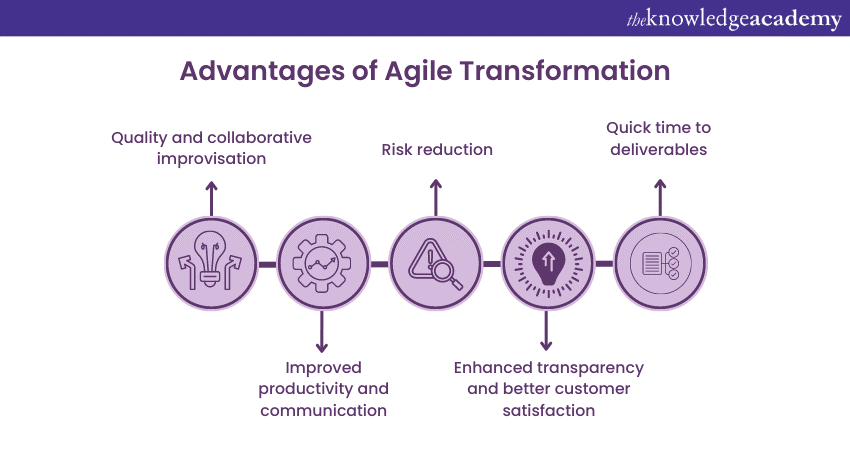
We will discuss some of the advantages below if organisations implement Agile Transformation:
Quality and collaborative improvisation
Agile Transformation employs a repetitive approach, meaning that procedures are refined with each iteration. Along with the larger cross-functional product team, there is a possibility of often communicating with the product management team. The members are encouraged to self-organise and develop their approaches to problems and methods of operation. The project team members know the project's scope, timeline and preference for completion since an engineering representative regularly attends product team meetings. One of the fundamental tenets of Agile is the continual emphasis on quality assurance and improvement, which promotes the production of superior goods.
Improved productivity and communication
In order to make sure everyone is aligned and working towards the same goals, Agile teams typically hold daily meetings in the form of in-house engagements and ongoing dialogues. These meetings serve valuable to them. There is a possibility of delivering new functionality more quickly by segmenting a work into sprints. Effective communication between development and testing teams results in awareness of how the workflows and processes increase productivity and prevent project-running faults. They avoid potential misunderstandings and accomplish their goals by speaking with one another frequently.
Risk reduction
Agile Transformation can swiftly fix bugs and react to client input in real time by adapting and repeating throughout the product development cycle. Project Developers constantly evaluate their work across each iteration, giving them increased project visibility and the ability to identify possible roadblocks immediately. The project has a better chance of acceptance if these minor concerns are dealt with before they become more serious. Additionally, Agile can incorporate changes without completely breaking the product development cycle.
Enhanced transparency and better customer satisfaction
Product management's priorities are accessible and well-documented. Agile teams communicate with their clients and demonstrate that they respect their feedback by including them in the development process. The team uses an agile development tool to visualise work in progress and keep the status of accountability, dependencies, and time frame. Because tools are integrated throughout the business, observing how cross-functional work affects the overall project or product is possible. These customised outputs will probably enhance user experience generally and increase client retention.
Quick time to deliverables
Sprints are brief events conducted repeatedly by Agile teams that last, on average, two weeks, and each one ends with some delivery. Project managers can more easily assess team performance and allocate resources according to these fixed durations. The team can remove general distractions and narrow their focus on a single goal by segmenting the project into smaller timeframes.
Additionally, the estimation process is made simpler by the fact that costs for shorter time periods may be predicted more accurately than for long-term projects. This also helps in greater flexibility in product distribution due to a quicker time to market due to the possibility of adjusting to the requirements and hastening the delivery of your product.
Gain an awareness of the basics of Agile Project Management and Agile Lifecycles by signing up for our Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®) course now!
Challenges faced while implementing Agile Transformation
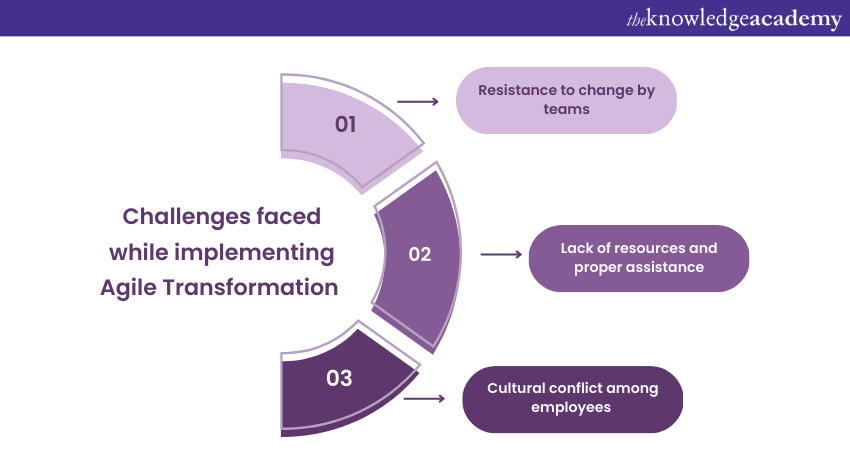
There are always obstacles in the way of a successful Agile Transformation. We discuss some challenges organisations will face in the Agile Transformation process.
Resistance to change by teams
One of the biggest challenges is not showing any interest to change. It is necessary to coach the organisation's staff to be fully accountable for their work and develop their skills. However, there are sections of employees who may be difficult to persuade to completely change how they operate if no drawbacks are visible to them to their conventional approaches. In such cases, more efforts need to be poured in to persuade the team members to adopt Agile Transformation by majorly highlighting its advantages. By fully owning the product, the approval process may be shortened, and individual productivity can be boosted.
Lack of resources and proper assistance
A business must invest in new technologies to implement Agile Transformation. The use of Agile methodology necessitates modifications to the fundamental management techniques that the staff may access. Teams may find it tedious to execute fast without these adjustments to vital management processes, which could affect innovation and lengthen the time to market. Therefore, businesses must spend a lot of time preparing for the move and educating their staff. It can take years to convert an organisation to be more agile.
Cultural conflict among employees
The next challenge is that employees might want to adopt Agile Transformation but could struggle to adapt to an unconventional style of working. For this, the working team must change from the bottom up, and the leaders must modify their behaviour and mindset since these things have a tremendous impact on the organisation's culture. It will take a new set of concepts, procedures, team responsibilities, and other things to switch from a traditional methodology to an agile one. These efforts could fizzle out before the advantages are felt, and the Agile change is finished if there isn't complete investment by the executive and no proper leadership.
Don't miss out on the key Agile interview questions that can set you apart. Explore them now!
Agile Transformation vs. Agile adoption
It is common to need clarification on Agile Transformation and Agile adoption. Let us briefly look at Agile Transformation and Agile adoption to understand how they differ from each other:
Agile adoption is when a single team adapts to an Agile project management methodology such as Kanban or Scrum. Agile adoption is a relatively short-term management methodology compared to Agile transformation. Agile adoption is implemented temporarily for projects as it does not include significant structural changes and does not require detailed project planning.
On the contrary, Agile transformation is a long-term process and requires detailed planning of the process. It can take years to functionally implement Agile Transformation, as the change sets in slowly and involves the entire organisation, from engineering teams to leadership teams. Agile Transformation involves complex plans, and project managers must have in-depth knowledge of Agile principles.
Conclusion
After reading this blog, you will now be able to know the concept and the purpose of Agile Transformation and understand the vital areas of implementing Agile. You will also appreciate the benefits and know the challenges while implementing Agile in your organisation. An agile transition needs a lot of time, support from employees and resources to be successful, and the will to remain with it through the tough times. However, some businesses are ready to implement an Agile Transformation because it can fundamentally change how they manage projects, respond to client requests, and expand their business.
Get to learn about the construction of the Agile Lifecycle and an understanding of the Agile Practices by signing up for our Certified Professional In Agile Project Management (CPAPM) course now!






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


