We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +32 35001305 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Cloud Networking is now crucial for businesses wanting to stay connected and efficient in the digital world. But what exactly is Cloud Networking? If you've ever wondered, "What is Cloud Networking," this blog is for you! Cloud Networking —a game-changer for managing and connecting network resources in the cloud. If you’ve ever wondered, “What is Cloud Networking?” This blog is your go-to guide!
From understanding the different types of Cloud Networks to exploring how they work, this blog guides you through everything you need to know. So, whether you’re a tech enthusiast or just curious, keep reading to discover how Cloud Networking works and its benefits.
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Cloud Networking?
2) Different Types of Cloud Networking
3) How Does Cloud Networking Work?
4) Benefits of Cloud Networking
5) Drawbacks of Cloud Networking
6) Cloud Networking vs Cloud Computing
7) Cloud Networking Services Use Cases
8) Conclusion
Understanding What is Cloud Networking?
Cloud Networking manages and connects computers, devices, and data through the internet instead of using traditional physical networks like routers and switches. In Cloud Networking, network resources, such as servers, storage, and software, are hosted in the cloud and can be accessed remotely.
This approach allows businesses to set up, manage, and scale their networks quickly without needing much physical hardware. It also provides flexibility, as users can access the network from anywhere with a network connection. Cloud Networking is used in services like file storage, online applications, and secure communication between different systems.
Different Types of Cloud Networking
The following are the different types of Cloud Networking:

1) Public Cloud Networking
Public Cloud Networking involves using network services offered by third-party cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud. These services are shared among multiple customers, making them cost-effective. Businesses can quickly access network resources without managing physical infrastructure.
2) Private Cloud Networking
Private Cloud Networking is when a business creates its own cloud environment, either on-site or hosted by a third party. This type of networking offers more control, security, and customisation, making it ideal for organisations with strict data privacy requirements.
3) Hybrid Cloud Networking
Hybrid Cloud Networking combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Businesses use this model to keep sensitive data in a private cloud while leveraging the flexibility and scalability of public clouds for less critical operations.
4) Multi-cloud Networking
In Multi-cloud Networking, a business uses services from multiple cloud providers. This approach helps avoid dependency on a single provider and allows businesses to choose the best cloud services for their specific needs.
5) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A VPC is a secure, isolated network within a public cloud environment. It gives businesses control over their virtual network resources, including IP addresses, subnets, and routing, while benefiting from the scalability of the public cloud.
How Does Cloud Networking Work?
Cloud Networking works by connecting devices, applications, and data through a network infrastructure hosted in the cloud. Here’s a simple breakdown of how it functions:
a) Virtualisation: Cloud Networking uses Virtualisation, which means that traditional physical hardware like servers, routers, and switches are replicated in the cloud as virtual devices. These virtual devices perform the same functions as their physical counterparts but are managed remotely.
b) Network Infrastructure Hosted in the Cloud: The core components of a network, such as firewalls, load balancers, and switches, are hosted in data centres provided by cloud service providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure. This infrastructure is scalable and can be accessed and managed from anywhere via the Internet.
c) Cloud Connectivity: It relies on connecting devices and users to the cloud environment over the internet. Depending on the setup, this can be done through public internet connections, private connections like Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), or dedicated leased lines for higher security and performance.
d) Network Management Through Software: Cloud Networking is often managed using software, which controls how data flows between devices, cloud applications, and cloud services. This management is done via dashboards that allow administrators to configure, monitor, and secure their Cloud Network in real-time.
e) Automatic Scaling and Flexibility: One of the advantages of Cloud Networking is its ability to scale up or down automatically based on the demand. As your business grows, additional network resources can be added instantly without the need for physical installations.
f) Data Security and Compliance: Security is a critical aspect of Cloud Networking. Cloud providers implement strong encryption, multi-factor authentication, and Compliance Tools to protect data while it moves across the network and ensure that it meets industry standards.
Learn the skills for troubleshooting with our Microservices Architecture Training – Join today!
Benefits of Cloud Networking
Here are the advantages of it:
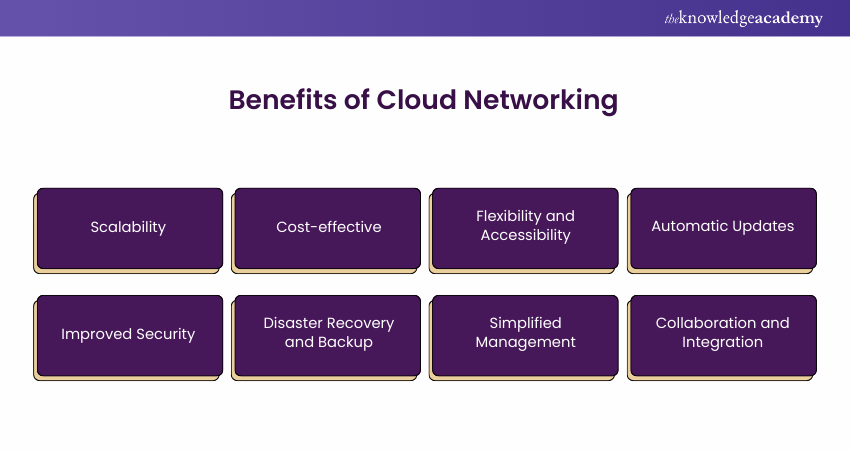
a) Scalability: Cloud Networking allows you to easily expand or reduce your network resources based on your needs. You can quickly add more storage, bandwidth, or computing power without needing new hardware.
b) Cost-effective: You only pay for the network resources you use, which can save money. There’s no need to invest in expensive physical equipment, and maintenance costs are lower since everything is managed in the cloud.
c) Flexibility and Accessibility: With Cloud Networking, you can access your network from anywhere with a network connection. This is great for remote work and allows businesses to operate globally without being tied to one location.
d) Automatic Updates: Cloud service providers handle software updates and security patches automatically. This ensures that your network is always up-to-date without needing manual intervention.
e) Improved Security: Cloud providers use advanced security measures like encryption and firewalls to protect your data. They also regularly update their systems to defend against new threats.
f) Disaster Recovery and Backup: It offers reliable backup and recovery options. In case of data loss or a disaster, you can easily recover your information from the cloud without significant downtime.
g) Simplified Management: Cloud Networking can be managed through user-friendly dashboards, making it easier to control your network, monitor performance, and make adjustments without needing specialised IT expertise.
h) Collaboration and Integration: Cloud Networking makes it easy for teams to collaborate by providing seamless access to shared resources and applications. It also integrates well with other cloud services, improving overall efficiency.
Drawbacks of Cloud Networking
The following are the drawbacks of Cloud Networking:
a) Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Cloud Networking relies heavily on a stable internet connection. Any disruptions can lead to downtime, affecting access to critical services and data.
b) Limited Control: Since the infrastructure is managed by cloud providers, you may have less control over certain aspects of the network. Customisation options can be limited compared to on-premise setups.
c) Data Security Concerns: Storing data in the cloud creates issues about data breaches and unauthorised access. Although providers offer robust security, sensitive data may still be at risk if not properly managed.
d) Ongoing Costs: While Cloud Networking is cost-effective initially, ongoing subscription fees can add up over time. For long-term use, these costs might exceed traditional network investments.
e) Compliance and Regulatory Challenges: Different regions have different regulations regarding data storage. Ensuring compliance with local regulations can be difficult when your data is stored across multiple locations globally.
Learn the basics of Cloud Computing with our Cloud Computing Training – Join today!
Cloud Networking vs Cloud Computing
Here are the key differences:
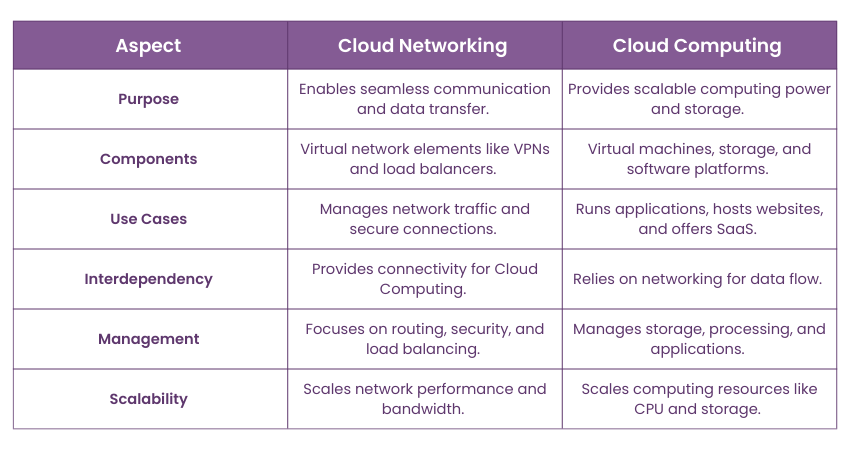
Purpose
The main goal of Cloud Networking is to enable smooth communication and data transfer between devices and applications in the cloud. On the other hand, Cloud Computing’s purpose is to provide scalable and flexible computing power, storage, and application hosting without relying on physical hardware.
Components
Cloud Networking involves virtualised network components like VPNs, load balancers, and IP addresses that connect cloud-based resources. In contrast, Cloud Computing includes virtual machines, storage solutions, and software platforms for running applications and processing data.
Use Cases
Cloud Networking is typically used for managing network traffic, ensuring secure connections, and connecting distributed applications. On the other hand, Cloud Computing is widely used to run applications, host websites, manage databases, and offer Software as a Service (SaaS).
Interdependency
Cloud Networking supports Cloud Computing by providing the necessary connectivity and infrastructure. In contrast, Cloud Computing relies on Cloud Networking for efficient data flow and communication between cloud services and users.
Management and Control
Cloud Networking involves configuring and managing network traffic, including routing, security, and load balancing across cloud environments. In contrast, Cloud Computing focuses on managing resources like storage, processing power, and applications, often with less emphasis on network configuration.
Scalability and Flexibility
Both Cloud Networking and Cloud Computing offer scalability, but they apply it differently. Cloud Networking allows you to scale network performance and bandwidth, while Cloud Computing enables scaling computing resources like CPU and storage based on demand.
Land your dream networking job – master key Networking Interview Questions!
Cloud Networking Services Use Cases
Let’s explore specific use cases to gain a deeper understanding of the potential of Cloud Networking.
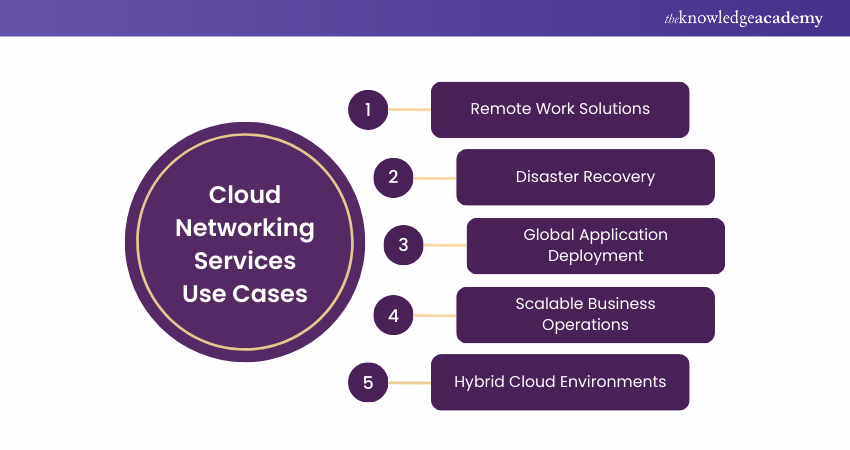
a) Remote Work Solutions: Cloud Networking enables businesses to securely connect remote employees to company resources. It allows them to work from anywhere without compromising security or performance.
b) Disaster Recovery: With Cloud Networking, businesses can easily back up data and systems in the cloud, ensuring quick recovery in case of system failures or disasters.
c) Global Application Deployment: Cloud Networking allows companies to deploy applications globally with consistent performance by connecting multiple data centres across different regions.
d) Scalable Business Operations: As businesses grow, Cloud Networking allows them to scale up their network resources effortlessly, ensuring smooth operations without hardware limitations.
e) Hybrid Cloud Environments: Many organisations use Cloud Networking to connect their on-premise infrastructure with public or private clouds, creating a hybrid environment for greater flexibility and control.
Advance your IT career with a comprehensive CompTIA Course. Develop key skills and get certified now!
Conclusion
Understanding "What is Cloud Networking?" is crucial for businesses in today’s digital era. It offers a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective way to manage and connect network resources in the cloud. As technology continues to evolve, adopting Cloud Networking can give your business the edge it needs to stay connected in the ever-changing digital landscape.
Elevate your job prospects with our OpenStack Administration Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an Example of a Cloud Network?

An example of a Cloud Network Is Amazon Web Services (AWS) Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). It allows businesses to create a secure, isolated network environment within the AWS cloud, connecting resources like servers and databases.
How to Build a Cloud Computing Infrastructure?

To build a Cloud Computing infrastructure, you first need to choose a cloud provider like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Then, set up virtual servers, storage, and networking resources and configure them to meet your business needs.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cloud Computing Courses, including Cloud Computing Training, Terraform Training and Microservices Architecture Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Essential Cloud Engineer Skills.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cloud Computing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


