We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Packet Sniffing involves intercepting data packets to gain insights into network activity, such as data source and destination, content, and protocols. This detailed analysis is essential for network troubleshooting, security monitoring, and performance optimising. This blog will give you everything you need to know about Packet Sniffing.
What is Packet Sniffing, and how does it work? Understanding this fundamental network analysis technique is crucial for efficient network management and cybersecurity in this digital age. This blog will further discuss Packet Sniffing, its types, tools and uses. Read further to gain a deeper understanding of this relevant topic.
Table of Contents
1) What is Packet Sniffing?
2) How does Packet Sniffing work?
3) Types of Packet Sniffers
4) Packet Sniffing tools
5) Uses of Packet Sniffing
6) Conclusion
What is Packet Sniffing?
Packet Sniffing is also known as network sniffing or protocol analysis. It is basically a method used to capture and inspect data packets as they pass over a computer network. These data packets contain essential information about network activity, making it a fundamental tool for various purposes, including
a) Network troubleshooting
b) Network optimisation
c) Cybersecurity
At its core, Packet Sniffing involves intercepting and analysing data packets. These packets are the building blocks of data transmission in networks, and they carry information about various things like:
a) Source of data
b) Destination of the data
c) Data's size
d) Data’s type
Packet Sniffing tools access the network's data link layer, where data packets are encapsulated before being sent across the network. Once the packet sniffer gains access to this layer, it can intercept these packets, making them available for analysis.

How does Packet Sniffing work?
Packet Sniffing is vital to cybersecurity, providing insight into network traffic and helping identify potential security threats. To understand how Packet Sniffing works in cybersecurity, let's learn its functionality and significance in safeguarding digital assets.
Data packet capture
Packet sniffers are deployed at strategic points within a network infrastructure. These sniffers capture data packets as they pass through the network. They can be positioned at key junctures, such as routers, switches, or firewalls, to intercept packets effectively.
Traffic analysis
Once the data packets are captured, the packet sniffer analyses their contents. This analysis involves examining the packet's header and payload. The header contains critical information about the packet's source and destination, as well as other routing and protocol data. The payload comprises the real data being conveyed.
Signature-based detection
One of the primary uses of Packet Sniffing in cybersecurity is signature-based detection. The packet sniffer compares packet contents against a database of known attack patterns or signatures in this approach. If it identifies a match, it raises an alert. This method effectively detects well-known threats like viruses, malware, and common attack vectors.
Anomaly-based detection
Packet Sniffing is also instrumental in anomaly-based detection. Here, the Sniffer looks for deviations from established network baselines. Unusual traffic patterns, sudden spikes in data volume, or unexpected behaviour can trigger alerts. These anomalies may signify potential security breaches.
Deep Packet Inspection
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is an advanced form of packet analysis used in cybersecurity. It involves scrutinising the content of packets at a granular level. DPI can identify specific applications or services being used within the network, which is valuable for spotting malicious or unauthorised activities.
Behaviour analysis
Cybersecurity professionals use Packet Sniffing to examine network behaviours. By monitoring data exchange patterns, they can identify unusual or suspicious activities. For example, a sudden surge in data leaving the network may indicate data exfiltration, a common sign of a cyberattack.
Real-time monitoring
Packet Sniffing tools provide real-time monitoring capabilities. This enables security teams to respond promptly to potential threats. Alerts are generated as soon as a suspicious packet is detected, allowing for immediate investigation and mitigation.
Boost your cyber security knowledge and protect your digital world. Sign up for our Cyber Security Awareness Course now!
Forensic analysis
In the event of a security incident, Packet Sniffing data is invaluable for forensic analysis. Cybersecurity experts can analyse captured packets to reconstruct the sequence of events leading to the breach, trace the attacker's actions, and identify vulnerabilities that need patching.
Mitigation and response
Based on the insights gained through Packet Sniffing, cybersecurity professionals can implement mitigation strategies and respond to threats effectively. For example, they may isolate compromised systems, block malicious traffic, or take other actions to contain and neutralise the threat.
Types of Packet Sniffers
Packet Sniffing comes in various types, each with its unique capabilities and use cases. These types of Packet Sniffing tools allow network administrators, cybersecurity professionals, and analysts to capture and analyse data packets for specific purposes. Various types are discussed below:
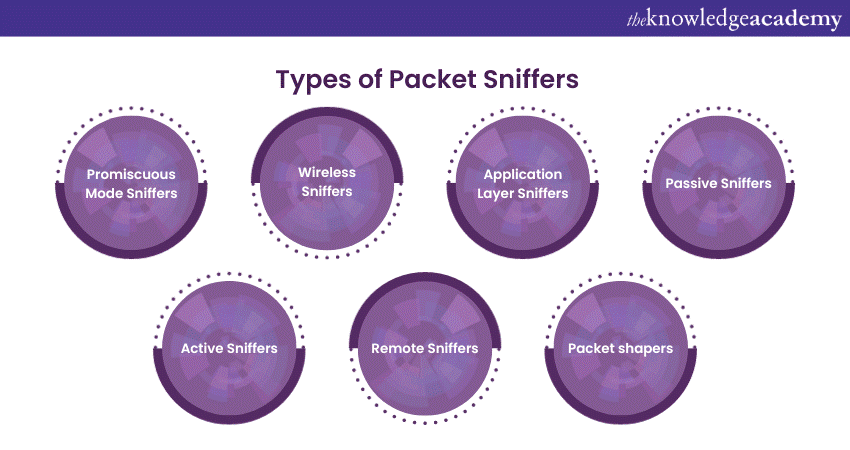
Promiscuous Mode Sniffers
Promiscuous mode sniffers capture all data packets on a network, whether they are meant for the Sniffer's device or not. They operate at the data link layer, providing a complete view of network traffic. These sniffers are vital for network troubleshooting and security, as they allow network administrators to
a) Diagnose issues
b) Monitor performance
c) Detect potential threats in real-time
Wireless Sniffers
Wireless sniffers are specialised tools designed for wireless networks, like Wi-Fi. They capture and analyse data packets transmitted over the airwaves. These sniffers help secure wireless networks by monitoring for unauthorised access and potential vulnerabilities. They also assist in optimising Wi-Fi performance and diagnosing issues related to wireless connectivity.
Application Layer Sniffers
Application layer sniffers focus on specific software applications or protocols, providing in-depth analysis of the data exchanged at the application level. These tools are invaluable for diagnosing problems within specific applications, such as email, web browsing, or database services. They allow administrators to pinpoint and resolve application-specific issues efficiently.
Passive Sniffers
Passive Sniffers are non-intrusive tools that observe and analyse network traffic without actively participating. They are excellent for monitoring network behaviour without causing disruptions. These sniffers are used in scenarios where collecting data without interfering with the network's regular operation is essential.
Active Sniffers
Active sniffers participate in network traffic, interacting with data packets and network devices. While more intrusive, they provide a more comprehensive view of network activities and are often used for security testing, network optimisation, and troubleshooting where active participation is required.
Remote Sniffers
Remote sniffers capture data packets from a location separate from the network they are monitoring. This remote access is invaluable for monitoring distributed networks or when physical presence at the network's location is not feasible. They ensure that data can be analysed from afar, making them highly practical for remote network management and analysis.
Packet shapers
Packet shapers are tools that manage and control the flow of network traffic, optimising it for performance. They can prioritise, deprioritise, or shape traffic to meet specific objectives, ensuring that critical data gets through smoothly while preventing less important data from overwhelming the network. These tools are crucial for maintaining consistent network performance and preventing congestion, making them valuable for traffic management and quality of service (QoS) implementations.
Packet Sniffing tools
These tools are indispensable for various network-related tasks, including network troubleshooting, security monitoring, and performance optimisation. Packet Sniffing tools come in different forms, each with its own set of features and capabilities.
Wireshark
Wireshark is a widely used open-source packet sniffer that provides a comprehensive interface for capturing and analysing packets. It supports various platforms and can decode a multitude of network protocols. Wireshark's versatility and user-friendly interface make it a favourite among network administrators and security professionals.
Secure your digital assets with a comprehensive Cyber Security Risk Management Course. Join today!
Tcpdump
Tcpdump is a command-line packet analyser available on Unix-like operating systems. It offers powerful packet-filtering capabilities and is often used with other network utilities to capture and inspect packets. Its command-line nature allows for scripting and automation of network monitoring tasks.
Snort
Snort is an intrusion detection system that can also be used for Packet Sniffing. It focuses on real-time traffic analysis and packet logging. Network administrators and security experts rely on Snort to identify and respond to network threats, making it a valuable tool for cybersecurity.
Tshark
Tshark is the command-line version of Wireshark, ideal for capturing and analysing packets on headless servers or when a graphical user interface is not available. It shares Wireshark's decoding capabilities and flexibility, making it suitable for automation and scripting.
Cain and Abel
Cain and Abel are comprehensive network tools that include packet sniffer. It's primarily used for password recovery and network monitoring. While it offers a wide range of features, it is worth noting that this tool is Windows-based and less commonly used in professional network management.
Ethereal
Ethereal is the predecessor of Wireshark and offers similar features for packet analysis. However, it is no longer actively maintained, and users are encouraged to use Wireshark instead.
Colasoft Capsa
Colasoft Capsa is a commercial packet sniffer that provides in-depth network analysis. It offers real-time and post-event analysis, as well as graphical representations of network traffic. Capsa is a valuable tool for network administrators and IT professionals seeking detailed network insights.
Eggplant Wireshark
Eggplant Wireshark is a Wireshark derivative designed to simplify and enhance network troubleshooting. It includes advanced features like remote packet capture and provides an improved user interface for more efficient analysis.
Nmap
While primarily known as a network scanning tool, Nmap can also capture and analyse packets. It's particularly useful for network discovery and security assessments.
SmartSniff
SmartSniff is a lightweight packet sniffer from NirSoft. It's designed for basic packet capture and analysis, making it a straightforward option for quick network monitoring tasks.
Explore our Cybersecurity courses to enhance your knowledge and skills in system and network security. Join our Introduction To System And Network Security Course now!
Uses of Packet Sniffing
Discussed below are various uses of Packet Sniffing.
a) Network troubleshooting: Packet Sniffing is invaluable for identifying and resolving network issues. It helps network administrators pinpoint problems like slow network performance, connectivity glitches, or improper configurations. By analysing packet data, administrators can quickly diagnose the root causes of these issues.
b) Security monitoring and intrusion detection: In cybersecurity, Packet Sniffing plays a vital role in monitoring network security. It enables the detection of suspicious or malicious activities. Security experts use packet sniffers to identify patterns associated with cyberattacks, such as unauthorised access, malware infections, or data breaches.
c) Performance Optimisation: Network performance can be enhanced through Packet Sniffing. By analysing traffic patterns and identifying bottlenecks, network administrators can optimise bandwidth usage, reduce latency, and ensure that critical applications receive the necessary resources for smooth operation.
d) Quality of Service (QoS) Management: Packet Sniffing tools help organisations manage QoS by prioritising certain types of traffic over others. This is critical for ensuring that applications requiring low latency, such as voice or video conferencing, receive the necessary network resources to function effectively.
e) Network traffic analysis: Packet Sniffing is used to gain a deep understanding of network traffic. This includes the types of applications in use, data transfer rates, and the source and destination of data packets. This data is invaluable for network planning and capacity management.
f) Forensic analysis: Packet Sniffing data is vital for forensic analysis in the aftermath of a security incident or network breach. It helps experts reconstruct the sequence of events, trace the attacker's actions, and understand how the breach occurred. This information is critical for improving security measures and preventing future incidents.
g) Application troubleshooting: Packet Sniffing can be applied to diagnose issues with specific applications or services. It allows administrators to understand how data is transmitted between clients and servers, helping to identify problems and improve the user experience.
h) Unauthorised access detection: Packet Sniffing helps identify unauthorised access attempts by monitoring login or authentication traffic. It can signal when login credentials are being transmitted insecurely or when multiple failed login attempts occur, indicating potential intrusion attempts.
Conclusion
As we have learned, Packet Sniffing is a critical network analysis technique that provides valuable insights into network traffic, aiding in troubleshooting, security monitoring, and performance optimisation. Its ability to capture and analyse data packets helps administrators and security experts identify issues, prevent cyber threats, and ensure network efficiency. It is, therefore, an indispensable tool in today’s cyber era.
Enhance your cybersecurity skills with our courses on Cyber Security Training. Join today!
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


