We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Project Management can sometimes seem like a complex puzzle, but understanding Project Execution is the base of putting everything together. Imagine that you are an engineer, and you are about to start constructing a beautiful house. You must remember to work on four key aspects if you want to make your project successful. They are: a clear and well-decided plan, getting the right people on the team and carrying out effective communication with other team members. Execution is one of the project life cycle phases where all the project deliverables are produced by the project team, and the project outcomes are delivered too. It is the most critical stage that comprises the control over the resources, risks, changes, quality, and communication issues.
Thus, it is crucial for organisations to learn about how to execute projects and achieve success. Read this blog to understand what Project Execution is, why you need it and common challenges faced while executing projects.
Table of Contents
1) What is Project Execution?
2) Why do you need Project Execution?
3) What happens during the Execution phase?
4) Common challenges during Project Execution
5) How to create a Project Execution Plan?
6) Conclusion
What is Project Execution?
There are five process groups within the project life cycle. Each phase holds specific objectives and outcomes. After the project's initial stage, where the project purpose and scope are defined, the planning phase provides the road map for project objectives. Once Project Planning is over, Project Execution commences.
Project Execution, the third phase, is the most important one as it makes it possible to transform plans into action. This part of the project involves creating deliverables and presenting them to customers and stakeholders. It is usually the longest phase, lasting for endless periods of time. It requires flawless precision and management.
The Project Managers are responsible for overseeing different Project Execution stages, such as resource allocation, cost management, schedule adherence, quality control, and risk mitigation. To ensure everything stays on track, a Project Audit is often conducted to assess the effectiveness of these stages and resolve any challenges that may arise.

Why do you need Project Execution?
Project Execution is a fundamental and indispensable phase in Project Management for several critical reasons:
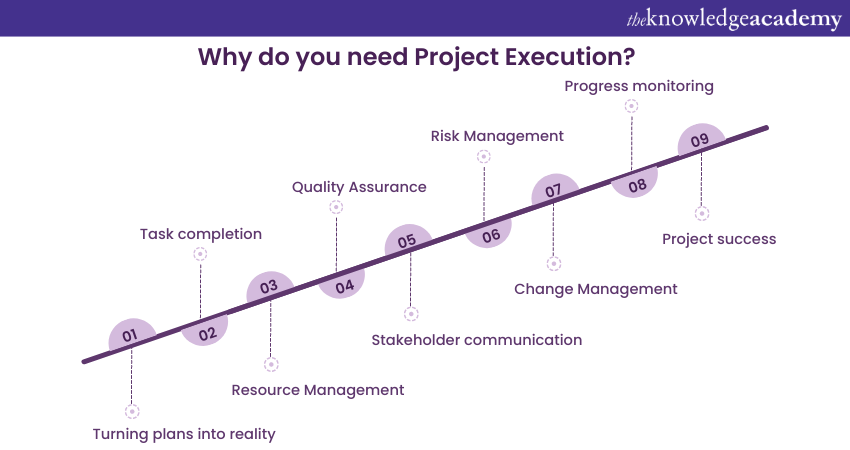
a) Turning plans into reality: Project Execution is the phase where project plans, meticulously created during the planning phase, are put into action. Without Execution, these plans remain theoretical, and the project's objectives are never realised.
b) Resource Management: Execution involves the allocation and management of resources, including people, materials, equipment, and finances. Proper Project Resource Management ensures that the project progresses efficiently and effectively.
c) Task completion: Tasks are organised, kept track of, and reviewed during the Execution phase. It helps in delivering the project with its intended and completed tasks during the process of its operation and on time.
d) Quality assurance: This is the stage where quality standards are confirmed or corrected. Quality assurance procedures are used to keep the defects at bay and ensure that the quality of the deliverables remains good enough, which is a key aspect of meeting the project goals and pleasing the stakeholders.
e) Stakeholder communication: Efficient communication with stakeholders, including how team members, sponsors, and clients get involved, is an aspect that is taken into consideration with every step. This also means that everybody is well informed about the process and confronts any misunderstanding, and these are on one page.
f) Risk Management: In the Project Execution, monitoring and managing the potential risks and issues using a hands-on approach is critical. In cases when an emergency situation takes place, a team should be ready to address an issue and make sure that no obstacles drive the project out of track.
g) Change Management: Project plans do not stand still and are set on this. In Execution, the deliverables are assessed to keep alterations from affecting the implementation scope, time schedule, and resources. This is done by accommodating or rejecting them on the basis of their impact.
h) Progress monitoring: Execution allows real-time tracking, which is one of the many vital requirements for the 50 shades of eyewear to accomplish the project on time. It facilitates corrective actions on time to keep the project directives of who, what, and how within restrictions.
i) Project success: The ultimate purpose of Project Execution is to bring the project to a successful conclusion, meet its objectives, and deliver value to stakeholders. Without Execution, a project plan remains an unrealised vision.
Unlock your path to success with our Introduction To Management Certification Course and become a Project Management pro!
What happens during the Execution phase?
During the project's Execution phase, you'll arrange tasks based on your project type and how your organisation likes to work. Let’s explore some of them below:
a) Carry out the project plan
b) Supervise the team's tasks
c) Suggest changes if needed
d) Keep in touch with everyone involved
e) Do activities to strengthen the team
f) Cheer when we reach goals and keep the team inspired
g) Check on progress regularly
h) Write down any changes to the plan
Common challenges during Project Execution
A Project Execution that goes smoothly without a hitch does not exist, even if it is built on a perfect project plan. Here are a few common challenges and how to deal with them:
Scope Creep: This happens when you modify a project after the project gets started. Furthermore, the changes are beyond what was agreed on during the initial phase. Therefore, planning is very important, and you should follow the initial plan you have set for yourself.
Quality Control: Making sure things are done right is crucial during Execution. Regular check-ins and working in small steps (sprints) can help maintain quality.
Change Requests: Sometimes, clients want changes as the project progresses. Using forms to track and approve these changes helps keep everything organised and ensures everyone agrees on what's happening.
What Is a Project Execution Plan?
A Project Execution Plan outlines how a project's Execution phase will be handled. It's like a project plan but focuses solely on Execution, unlike project plans that cover the entire project cycle.
Having an Execution plan ensures everyone knows their roles, fixes any resource problems, and addresses final details before starting. It's crucial for clarity, resource management, and final preparations before Project Execution.
How to create a Project Execution Plan?
Creating a Project Execution Plan is a critical step in the Project Management Process. This Project Plan is like a compass that outlines the Project Execution phase. It aligns the project to proceed in an organised and timely manner. The key steps involved in creating a Project Execution Plan are given below.
a) Review the project Charter: Open the Project Charter as a first step. Then, outline what the project is about, the need to do it, the project goals, its scope, stakeholders, and the constraints that the project is subject to in the document. Consider this document as a starting point for your Project Execution Plan.
b) Define project objectives: You should be clear about the goals and deliverables your project is expected to bring. These goals should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART) to ensure the necessary direction.
c) Scope statement: Prepare a well-defined project scope statement that will outline the boundaries of what's included and what's not included. Make sure that this is in accordance with the project charter and what the client expects.
d) Identify stakeholders: Account for all project stakeholders, for instance, people involved in the team, sponsors, clients and any other ones in the project. Describe their corresponding duties, responsibilities as well as the format of the communication between the team members on the plan.
e) Create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): Elaborate those major outcomes of the project into smaller, operable tasks and sub-tasks while conducting this project. WBS is the hierarchical framework component that aids in the simplification of the work to be achieved.
f) Schedule and timeline: Establish a project schedule which takes into account the starting and finishing dates for each task. Make this step to take the dependencies for among tasks into account and schedule each activity appropriately. Visual tools such as Gantt Charts are useful to avoid confusion and enable a clear perception of the timeline.
g) Resource allocation: Identify the necessary resources, as these may be in the form of human resources, equipment, materials, and financial aspects. Set resources for individual tasks and see that they are available in the proper moment while completing the task.
h) Quality Management: Define the quality standards that need to be met for each deliverable. Establish processes for Quality Assurance and control and specify who is responsible for these activities.
i) Risk Management: Identify the risks which may influence project during running which may cause either an obstacle or terminate step in project. Form an approach that helps the project team trace and evaluate risks and ensure that there are mitigations established for these risks at every stage of the project.
j) Communication plan: Be specific on how project information will be channelled in keeping the stakeholders informed. It also encompasses the timing and style of status messages, data-reporting strategies and a method of implementing a mechanism to address (and even resolve) issues and problems.
k) Change control: Develop a procedure for managing the changes to your system. The policy creates a frame for how additions, deletions, or amendments to the project scope, schedule, and resources will be addressed to the required level.
l) Monitoring and control: Create the outlines that would help in tracking and reporting project progress. Ensure adequate monitoring and measurement mechanism is put in place to evaluate the project in comparison with the plan. The KPIs can be used to measure the performance.
m) Closeout plan: Specify the closing phase in order to outline what has been completed, client acceptance, documentation withholding, and post-project assessments.
n) Legal and compliance requirements: If the project has legal or compliance obligations drawn up, then these should be taken into consideration in the plan.
o) Final approval: Limit the presentation of Project Execution Plan to a number of various key stakeholders, like the Project Sponsor, by endorsement and adoption.
Master the art of successful Program Management with a Programme Management (PgM) Fundamentals Course. Your path to excellence!
Conclusion
Effective Project Execution is the key element ensuring project success in Project Management. It is like turning a picture into reality that requires planning, effective resource management, quality control, and smooth communication. The eight core principles shared in this blog are the keys to navigating these complexities. By embracing them, you can confidently steer your projects from inception to a triumphant conclusion, consistently meeting objectives and delivering value to stakeholders.
Unlock your potential with our Project Management Masterclass and lead with confidence. Join now !
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key skills for Project Execution roles?

Critical skills in Project Execution roles include oral and written communication, leadership, time management, problem-solving, planning, and adaptability. These capabilities are responsible for the effectiveness of Project Management in that the activities are implemented, managed, and completed within the given schedule and budget.
What role does Project Execution play in securing leadership positions?

Project Execution showcases leadership's ability to deliver results, meet goals, and manage resources effectively. Success in executing projects demonstrates leadership competency, which is a key component of the Leadership Competency Framework, fostering trust and credibility and paving the way for advancement to leadership positions.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is the Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Project Management Courses, including Introduction to Project Management Certification and Project Management Masterclass. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Project Resource Management.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Project Management Skills, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your skills in Project Management, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to Project Management Course
Introduction to Project Management Course
Fri 9th May 2025
Fri 15th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


