We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
The stock market can feel like a rollercoaster, constantly shifting between two major forces: the Bull and the Bear. But what exactly do these terms mean, and why should investors care? The "Bull vs Bear Market" debate isn’t just about numbers; it's a battle of moods, emotions, and market trends that shape the world of investing. Understanding these markets can give you the upper hand.
In this blog, we'll break down the key differences between the "Bull vs Bear Market" and explore how each impacts investor behaviour, and the economy.
Table of Contents
1) What is a Bull Market?
2) What is a Bear Market?
3) Difference Between Bull Market and Bear Market
4) How to Invest in Bull or Bear Markets?
5) Conclusion
What is a Bull Market?
A Bull Market is defined as a long-term trend where the stock prices are rising. This happens when the market appears stable, and investors are relatively optimistic about the economy.
In a Bull Market, several factors contribute to the optimism:
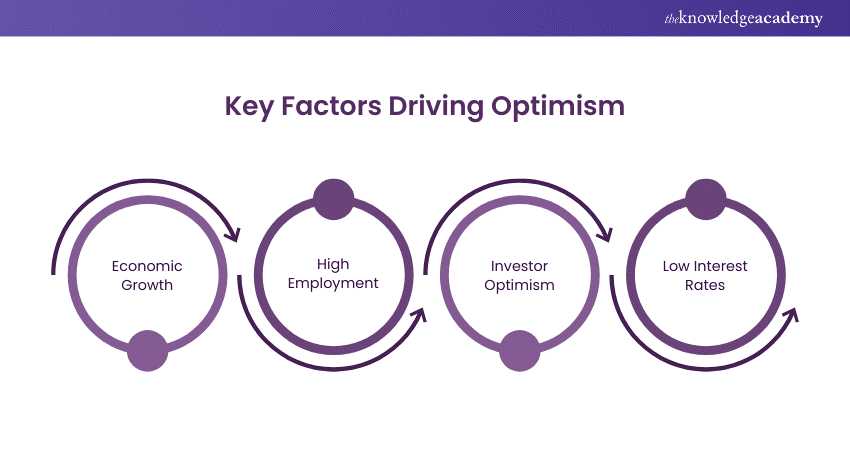
1) Economic Growth: The economy is expanding with increased GDP and high corporate profits.
2) High Employment: There is high employment, and the rates of unemployment are minimal, thereby increasing consumer spending.
3) Investor Optimism: It is owing to the fact that investors think that growth will pick up in the future, causing them to invest in stocks. This helps increase prices.
4) Low Interest Rates: The central banks may reduce the interest rates so that people borrow and invest, which then further facilitates this market.
What is a Bear Market?
A Bear Market is characterised by a decline of at least 20% in stock prices from recent peak levels. In most cases, the Bear Market follows a weakening economy where investor confidence levels are very low.

Here are the factors that contribute to Bear Markets:
1) Decreased Investor Confidence: If investors lose confidence in the market, they may sell their stocks, causing prices to fall further.
2) Negative News: Bad news about the economy, businesses, or geopolitical issues can scare investors, leading to more selling.
3) High Inflation: Rising prices can eat into consumer spending and corporate profits, resulting in lower stock prices.
4) Market Overvaluation: If stocks are priced too high compared to their actual value, a correction can occur when investors realise this.
In a Bear Market, negative emotions can also become self-reinforcing. The lower prices continue to fall, the more investors become fearful and sell their stock, setting off the next round of declines. Investor panics can create substantial problems, as the short-term trend of the market may remain downward for an extended period.
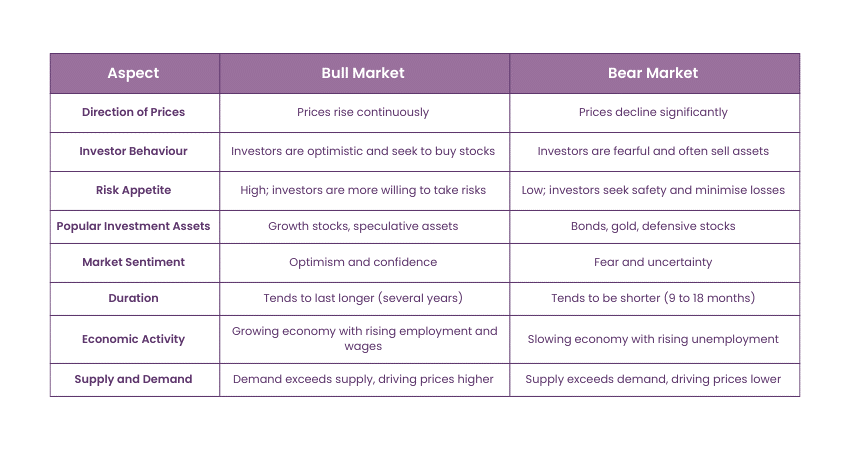
Difference Between Bull Market and Bear Market
Bull and Bear Markets differ mainly in the direction of movement, but this is just the tip of the iceberg. Here are the key differences:
1) Impact on Investor Behaviour
In a Bull Market, investors tend to take more risks. They find opportunities to buy stocks actively, believing that the stock price will never decline and hence boost returns. Confidence in the market triggers even more speculative investment and directs the focus toward growth stocks, which are assumed to produce great future earnings.
On the other side, during a Bear Market, fear and uncertainty dominate investor psychology. The risk appetite declines and investors are bound to liquidate their positions so as not to incur losses in such markets. Safe-haven assets like bonds, gold, and defensive stocks that have stable prices tend to attract the investors.
2) Duration of Bull and Bear Markets

A Bull Market, characterised by rising prices and investor confidence, can last for several months to several years, often fuelled by economic growth and positive market sentiment.
In contrast, Bear Markets, marked by declining prices and investor pessimism, typically last shorter, averaging around 9 to 18 months. However, extreme cases can extend beyond this average, influenced by factors like economic recessions or significant geopolitical events, making the timing of market cycles unpredictable.
3) The Role of Investor Psychology
The markets are primarily influenced in a Bull as well as a Bear Market by investor psychology. In a Bull Market, the overall mood is optimism. People believe that the market will continue to rise, leading prices to reach unnatural levels due to over-exuberance. Eventually, this situation bursts like a balloon, resulting in a market correction.
On the other hand, Bear Markets are largely driven by fear. With every price decline, panic selling increases. Investors will make panicked decisions to sell on the way down, even accelerating the accelerating spiral. Fear can spread rapidly even to fundamentally strong assets.
4) Shifts in Economic Activity
There's a good possibility that a Bull Market reflects an improving economy. When companies expand and profits increase, so does the demand for labour, wages inflate, and consumer spending expands. High spending leads to higher revenues for corporations, further churning the demand for rising markets.
Conversely, in a Bear Market, the opposite is seen. Economic activities slow down because consumer spending goes down with unemployment and unprofitable businesses. Therefore, companies might resort to lay-offs or hiring freezes, worsening the economic recession.
Master the stock market with our Stock Trading Course and become a Trader- Register now!
5) Supply and Demand Dynamics for Securities
The supply and demand relationship lies at the centre of any Bull or Bear Market. In the case of a Bull Market, demand runs out ahead of supply due to a surplus of willing buyers over the number of sell orders in the market. Such high demand tends to push prices upwards and continues the Bull Market.
Contrasting this is a Bear Market. It is a situation where supply exceeds demand because more investors want to sell their holdings which thus results in declining prices. The oversupply of securities drives down the value further, and thus the prices may not rally easily without a drastic change in the mindset of the market.
How to Invest in Bull or Bear Markets?
Investing in Bull and Bear Markets requires different strategies to maximise returns or minimise losses.
In a Bull Market:
1) Focus on Growth Stocks: As prices rise, growth stocks tend to perform well. Look for companies that are expanding rapidly.
2) Buy and Hold Strategy: In a rising market, buying stocks and holding onto them can yield substantial long-term returns.
3) Take Advantage of Optimism: Investor confidence is high, so taking calculated risks on speculative investments may pay off.
In a Bear Market:
1) Seek Safe-haven Assets: Gold, bonds, and defensive stocks like utilities are less volatile and may provide better returns during market downturns.
2) Diversify Your Portfolio: A well-diversified portfolio can help spread risk and cushion the blow of falling prices.
3) Consider Dollar-cost Averaging: By investing a fixed amount regularly, you can lower your average cost per share during a Bear Market.
4) Short Selling: Some investors engage in short selling, betting on the decline of stock prices to profit in a Bear Market. However, this is a riskier strategy and requires careful planning.
Ready to trade like a pro? Discover the skills to invest smarter and trade confidently. Join our Investment and Trading Training today!
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Bull vs Bear Market is crucial for any investor. While Bull Markets bring prosperity and optimism, Bear Markets challenge investors with fear and uncertainty. Knowing how to navigate these market conditions can help you make informed investment decisions. Markets will always fluctuate, but with the right approach, you can remain a confident investor in any market environment.
Master the skills to profit in the Cryptocurrency market our Cryptocurrency Trading Training - Join now!
Frequently Asked Questions

A Bullish market in stock sign indicates increasing prices, while a Bearish market signifies a fall in stock prices. Analysts also analyse certain indicators such as moving average, trading volume, and even investor sentiment.

The 3-day Rule says one should wait for three days since the price had gone a long way down, then buy. This is just to give time to the market to stabilise and avoiding buying too early since it might go down instead.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Investment and Trading Courses, including the Cryptocurrency Trading Training, Day Trading Course, and Stock Trading Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Types of Investments.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Investment and Trading, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Trading Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Stock Trading Course
Stock Trading Course
Thu 20th Feb 2025
Thu 24th Apr 2025
Thu 19th Jun 2025
Thu 21st Aug 2025
Thu 16th Oct 2025
Thu 18th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


