We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +971 8000311193 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Concerned about the safety and well-being of those in your care? Safeguarding is paramount in today's world. Understanding the Principles of Safeguarding is essential for creating a safe and supportive environment.
This blog delves into the core principles that guide safeguarding practices. Discover how the Principles of Safeguarding empower individuals, prevent harm, and build strong communities. Whether you're a professional caregiver or simply a concerned citizen, this blog will equip you with the knowledge to make a positive impact.
Table of Contents
1) What is Safeguarding?
2) What are the Six Safeguarding Principles?
3) Why Were the Principles of Safeguarding established?
4) What are the Four Rs in Safeguarding?
5) Balancing Confidentiality with Safeguarding
6) Appointing a Safeguarding Officer
7) What Does ICB Stand for in Safeguarding?
8) What is the Difference Between Child Protection and Safeguarding?
9) Conclusion
What is Safeguarding?
Safeguarding is a comprehensive approach aimed at ensuring the well-being, safety, and protection of vulnerable individuals, particularly children and adults at risk of harm or abuse. It involves proactive measures to prevent and respond to potential threats, encompassing physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. Critical aspects of safeguarding include:
1) Creating a secure environment.
2) Implementing policies and procedures.
3) Conducting risk assessments.
4) Promoting awareness and education.
Safeguarding extends to various contexts, including healthcare, education, social services, and community settings. neglect, reporting concerns, and collaborating to provide support and intervention. Understanding the 5 Rs of Safeguarding helps guide these professionals in their responsibilities, ensuring that safeguarding efforts are effective and comprehensive. Ultimately, safeguarding seeks to empower individuals, Ultimately, safeguarding seeks to empower individuals, promote their rights, and create a protective network that ensures everyone can live free from harm and exploitation.
Discover the importance of safeguarding and learn how to protect people and data effectively.
Who Needs Safeguarding?
Everyone, from the young to the elderly, desires to live a safe and secure life within society. However, individuals at high risk or already facing abuse require the intervention and care of appropriate authorities. Children, being more vulnerable and less able to express their emotions, rely on their guardians for safety. In addition to children, those in need of protection include:
a) Elderly individuals who cannot care for themselves
b) Children with special needs
c) People with disabilities and disorders
d) Individuals unable to make decisions independently
e) Those with long-term illnesses

What are the Six Safeguarding Principles?
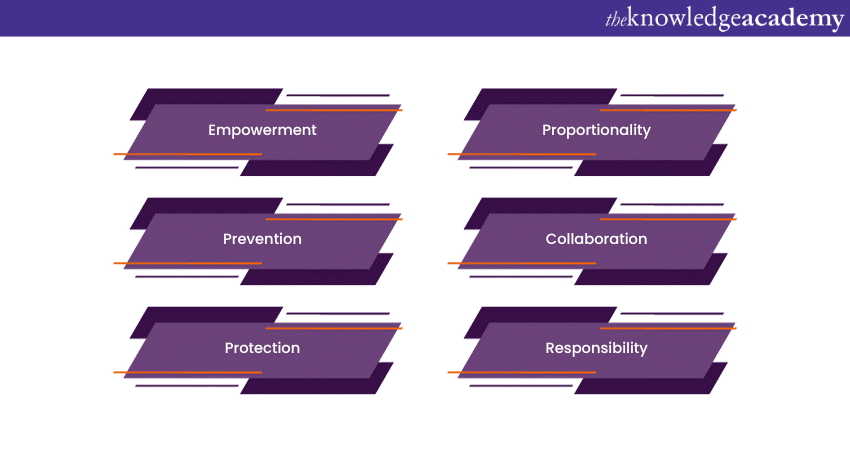
The six principles of safeguarding serve as fundamental guidelines to protect vulnerable adults, emphasising the core values of ensuring their health, well-being, and human rights. These principles form the cornerstone of effective safeguarding practices, aiming to prevent harm, abuse, and neglect in the lives of children and vulnerable adults.
1) Empowerment
Empowerment is a transformative concept that symbolises enabling individuals or communities to gain control over their lives, make choices, and assert their rights. At its core, empowerment seeks to enhance autonomy, self-determination, and confidence, fostering a sense of agency among people. This multifaceted approach involves providing individuals with the tools, resources, and information necessary to make informed decisions and shape their destinies.
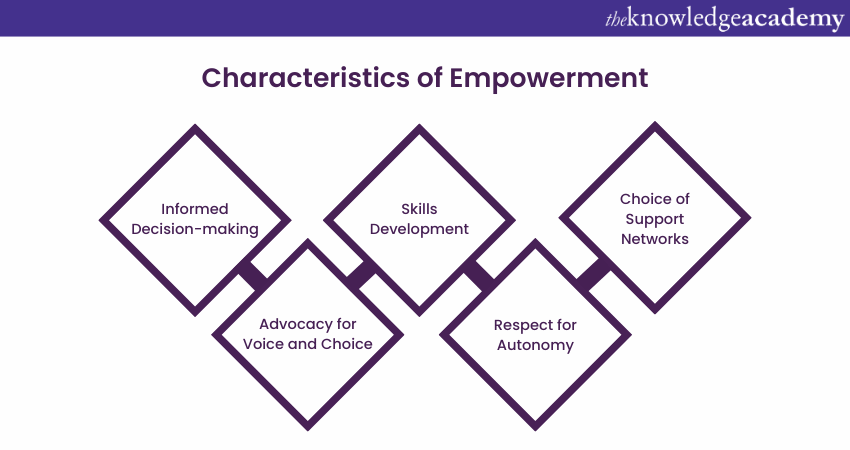
In social work and community development, empowerment often goes beyond the mere distribution of resources. It encompasses fostering a mindset of resilience, instilling self-belief, and dismantling systemic barriers that limit opportunities. Empowered individuals are equipped to navigate challenges and encouraged to participate actively in decision-making that affects their lives.
Empowerment is a dynamic process that recognises the diversity of experiences and backgrounds. It involves acknowledging and respecting individual strengths, perspectives, and cultural nuances. By promoting inclusivity and recognising the inherent worth of each person, empowerment becomes a catalyst for positive change, contributing to the creation of more equitable and just societies. In essence, empowerment is not just about giving power; it's about creating a supportive environment that enables individuals to discover and leverage their power for personal and collective growth.
Explore safeguarding examples to ensure safety and compliance in your workplace or organization.
2) Prevention
Prevention, as a critical principle in safeguarding, is a proactive approach to identifying and addressing potential risks to the well-being of vulnerable adults and children before harm occurs. This principle underlines the significance of early intervention and strategic measures to create a protective environment.
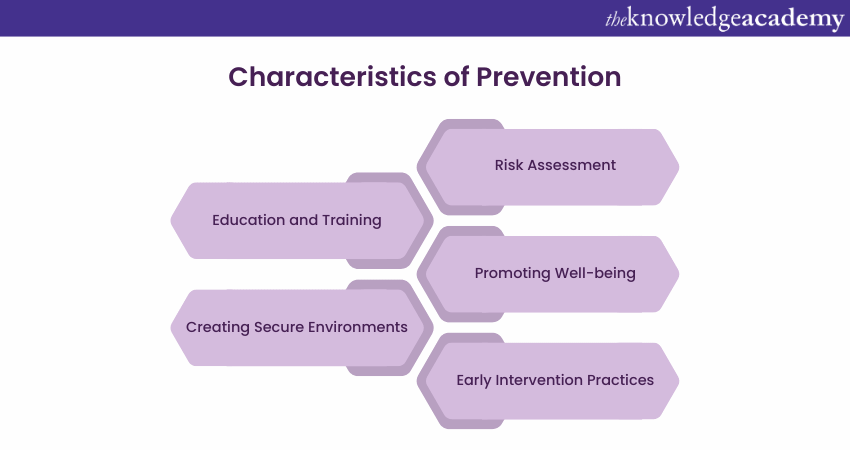
In safeguarding, prevention involves thorough risk assessments and considering factors that could contribute to abuse, neglect, or harm. This may include evaluating living conditions, caregiver dynamics, or potential external threats. The goal is to implement targeted strategies that reduce or eliminate identified risks, creating a safety net for those at risk.
Preventative measures may encompass educational programs to raise awareness, training for caregivers and professionals, and community initiatives fostering a culture of vigilance. By understanding individuals' specific risks, safeguarding practitioners can tailor preventive interventions to suit their needs, incorporating safeguarding examples to guide their approach effectively.
Moreover, prevention in safeguarding acknowledges the importance of empowerment, enabling individuals to recognise and protect themselves from potential harm. This principle emphasises the creation of a supportive environment that fosters resilience and equips individuals with the tools to make informed choices, reducing vulnerability and enhancing overall well-being and, through prevention, safeguarding endeavours to build a robust foundation that actively works against the occurrence of harm or abuse.
Boost your confidence with key safeguarding interview questions and expert preparation tips.
3) Protection
Protection is paramount in safeguarding vulnerable adults, encompassing a range of measures to ensure their safety, well-being, and freedom from harm or abuse. This principle emphasises the obligation to take decisive and effective action when individuals are identified as being at risk. Protection involves creating a secure environment and implementing strategies to prevent, respond to, and address potential threats.
One crucial aspect of protection is the timely and appropriate intervention in situations where harm may occur. This can include removing individuals from immediate danger, providing support services, or involving relevant authorities to address concerns. Protection also concerns advocating for the rights of vulnerable adults, ensuring they are treated with dignity and respect.
Protection also extends to creating systems and structures that proactively identify risks and vulnerabilities, allowing for preventative measures. It involves empowering individuals to report concerns and fostering a culture where disclosures are taken seriously and addressed promptly. Collaboration and partnership between various agencies, professionals, and the community are integral to adequate protection, as they enable a comprehensive and coordinated approach to safeguarding vulnerable adults. The principle of protection embodies a commitment to taking all necessary steps to secure the well-being and rights of those at risk.
Elevate your team's safety knowledge with our Health and Safety Courses – sign up now and ensure a secure workplace for all.
4) Proportionality
Proportionality, as a key principle in safeguarding, underscores the importance of tailoring interventions and responses to individuals' specific needs and risks. It emphasises a balanced approach, avoiding excessive or inadequate measures and ensuring that actions taken are commensurate with the level of risk and vulnerability.
In safeguarding contexts, proportionality guides professionals in assessing the severity of potential harm and determining the appropriate level of intervention. This principle recognises that individuals have diverse needs, and responses should be nuanced to respect their autonomy and rights. For example, in adult safeguarding cases, proportionality might involve carefully considering the most minor restrictive measures when addressing risks to an individual's well-being.
Moreover, proportionality encourages collaboration and information-sharing among relevant stakeholders, ensuring that interventions are well-informed and collectively agreed upon. It safeguards against unnecessary restrictions on an individual's freedoms while focusing on their safety and protection.
Proportionality promotes a thoughtful and individualised approach to safeguarding, reflecting vulnerable adults' diverse circumstances and requirements and acknowledging that safeguarding measures should be proportionate to the risks involved.
Understand the 5 Rs of Safeguarding to build a safer and more secure environment.
5) Collaboration
Collaboration is a pivotal principle in safeguarding, emphasising the necessity of joint efforts among various agencies, professionals, and the wider community to ensure the protection and well-being of vulnerable adults. This principle recognises safeguarding is a collective responsibility beyond individual roles or organisations.
Effective collaboration involves open communication, information sharing, and coordinated action. Agencies and professionals must work together to pool resources, expertise, and insights, creating a comprehensive support network for those at risk. This collaborative approach ensures that all relevant parties contribute to a holistic understanding of an individual's situation, enabling more informed and effective interventions.
Furthermore, collaboration extends beyond formal structures to encompass the broader community. Engaging with local communities helps build awareness, resilience, and a shared commitment to safeguarding. By fostering a culture of collaboration, individuals and organisations can respond promptly and effectively to safeguarding concerns, addressing the complex challenges associated with protecting vulnerable adults. Ultimately, the principle of collaboration underscores the interconnected nature of safeguarding efforts, emphasising the power of unified action in creating safer environments for those at risk of harm or abuse.
6) Responsibility
The safeguarding principle of responsibility is crucial in ensuring the well-being and protection of vulnerable adults. This principle places a significant emphasis on holding individuals and organisations accountable for their actions and decisions, with a commitment to preventing harm and promoting a safety culture.

Responsibility involves recognising and acknowledging individuals' and organisations' duty of care towards vulnerable adults. This includes professionals, caregivers, and institutions understanding their role in safeguarding, actively working to prevent harm, and responding appropriately to concerns or incidents. It underscores the importance of creating an environment where everyone feels responsible for the safety and welfare of vulnerable adults.
In practice, the principle of responsibility involves clear communication of roles and expectations, training and education on safeguarding protocols, and establishing robust reporting mechanisms. Professionals and organisations must proactively identify and address risks, intervene when necessary, and continuously evaluate and improve safeguarding practices.
Ultimately, the principle of responsibility fosters a collective commitment to prioritising the best interests of vulnerable adults, promoting a sense of duty and accountability across the spectrum of care and support.
Enhance your leadership skills with our Health and Safety Training for Managers and Supervisors — sign up now!
Why Were the Principles of Safeguarding Established?
The establishment of the Principles of Safeguarding stems from recognising the imperative to protect vulnerable adults and children from harm, abuse, and neglect. These principles were developed as a response to society's profound responsibility to ensure the well-being, dignity, and human rights of its most vulnerable members. The need for such principles became evident when individuals, particularly those with limited capacity to protect themselves, faced exploitation or harm.
The principles serve as a comprehensive framework to guide professionals, organisations, and communities in creating a protective environment. The impetus behind their creation lies in a commitment to fostering a culture prioritising vulnerable individuals' safety and welfare. By outlining core values such as empowerment, prevention, proportionality, protection, partnership, and accountability, the principles offer a cohesive approach to safeguarding that addresses the multifaceted nature of potential risks.
In essence, the establishment of these principles reflects a collective dedication to creating a society where everyone, regardless of age or vulnerability, can live free from the threat of harm, supported by a framework that places their well-being at the forefront of decision-making and intervention.
What are the Four Rs in Safeguarding?
Understanding the Four Rs of safeguarding is crucial for identifying and acting in dangerous situations to protect vulnerable individuals. Let’s delve into each of these essential steps.
1) Recognise
The first step in safeguarding is recognising the risk of abuse, which can manifest as physical, mental, or emotional harm. Without identifying these risks, progressing to the next steps is impossible. Vigilance and awareness are key to this initial phase.
2) Record
Once a risk is recognised, it is vital to meticulously record all details. Important questions to answer include:
a) When did the incident occur?
b) How did it happen?
c) Who was involved?
d) What were the circumstances?
e) Who reported the incident?
f) How can it be effectively documented?
Thorough documentation is essential for clarity and accountability.
3) Report
After identifying and recording the risk, the next crucial step is to report it to the appropriate authorities. This action is necessary to ensure that immediate and effective measures are taken to protect the victims and prevent further abuse. Proper reporting channels must be followed to ensure a swift response.
4) Refer
The final and often overlooked step is referring the case to the relevant authorities. This involves contacting the police, safeguarding teams, or local adult social care services. By referring the case, you ensure that specialised teams take the necessary steps to prevent further injustices and provide ongoing protection and support to the vulnerable individuals involved.
Master Your Safeguarding Interview – Download our essential guide on Safeguarding Interview Questions now!
Balancing Confidentiality with Safeguarding
Balancing confidentiality with safeguarding is a delicate act. While it's crucial to respect an individual's privacy, there are times when sharing information is necessary to protect someone from harm. Healthcare professionals must navigate the Principles of Safeguarding alongside the Caldicott principles, which guide the handling of patient information.
For more details on specific circumstances, refer to the Care Act of 2014.
How Do Safeguarding Principles Apply?
1) Protection and Accountability: Professionals are required to report any suspected abuse or neglect, even if it means breaching confidentiality.
2) Empowerment and Proportionality: Decisions must be in the best interest of the individual and involve them in the decision-making process as much as possible. This includes explaining why and where the information will be shared, in line with the individual's mental capacity, as required by the Data Protection Act of 2018.
This approach ensures that safeguarding measures are both effective and respectful of individual rights.
Appointing a Safeguarding Officer
Every organisation working with children or vulnerable adults should have a designated safeguarding lead, often referred to as a safeguarding officer. This role is crucial for ensuring that the six Principles of Safeguarding are upheld within the organisation.
Key Responsibilities of a Safeguarding Officer:
1) Primary Contact: Serve as the main point of contact for any safeguarding concerns.
2) Policy Development: Create and implement safeguarding policies.
3) Staff Training: Ensure staff are trained to recognise signs of abuse and neglect.
4) Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of any incidents and referrals to local authorities or the police.
5) Local Authority Liaison: Act as the organisation's point of contact with local authorities.
While everyone in the organisation should be aware of safeguarding principles, the safeguarding officer is the champion, ensuring that these principles are applied in daily operations.
What Does ICB Stand for in Safeguarding?
ICB stands for Integrated Care Board, which plays a crucial role in safeguarding by overseeing healthcare services to ensure they meet safety standards. ICBs work with local authorities and agencies to promote the welfare of children and vulnerable adults, addressing risks and ensuring effective, coordinated care and intervention.
What is the Difference Between Child Protection and Safeguarding?
Child protection refers to specific measures and actions taken to safeguard children who are at risk of or experiencing harm, abuse, or neglect. It involves identifying vulnerable children, responding to concerns, and taking steps to ensure their immediate safety and well-being. Child protection is often reactive, addressing situations where a child’s safety is compromised or harm has already occurred. It focuses on intervention and support to mitigate risks and protect the child from further harm.
Safeguarding, on the other hand, is a broader concept that encompasses all efforts to promote children’s welfare and prevent harm before it occurs. It includes creating safe environments, implementing policies to protect children’s rights, and ensuring they are supported to grow and thrive in a secure setting. Safeguarding is proactive, aiming to prevent risks and foster a culture where children’s safety and well-being are prioritised at all levels. While child protection is a critical component of safeguarding, safeguarding goes beyond protection to include prevention and advocacy for every child’s holistic development.
Enhance your safeguarding expertise with our comprehensive Safeguarding Officer Training — safeguarding the vulnerable, one step at a time.
Conclusion
Hopefully, this blog helped you understand the six basic Principles of Safeguarding and their role in protecting and empowering vulnerable individuals and communities both at the workplace and in society in general. Applying these principles effectively requires strong Social Work Skills, which can become the guiding light for all the steps you take towards a more equitable society.
Enhance your leadership skills with our Health and Safety Training for Managers and Supervisors — sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 5 P's of Safeguarding?

The 5 P's of safeguarding are Prevention, Protection, Partnership, Proportionality, and Accountability (People-centred approach). These principles guide actions to prevent harm, protect individuals, collaborate effectively, ensure responses are proportionate, and uphold accountability in safeguarding.
What Does SAB Stand for in Care?

SAB stands for Safeguarding Adults Board. It is a multi-agency body responsible for ensuring the safety and well-being of adults at risk. SABs coordinate efforts, develop safeguarding strategies, and review cases to improve practices and prevent harm within the care sector.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Health & Safety in the Workplace Courses, including the First Aid at Work Course, Manual Handling at Work Course and the Health and Safety in the Workplace Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Health and Safety.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Safeguarding, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Safeguarding skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Health & Safety Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Safeguarding Officer Training
Safeguarding Officer Training
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


