We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on +44 1344 203 999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Imagine a world where money isn’t controlled by banks or governments, but by the very people who use it. Sounds like something out of a sci-fi movie, right? Well, that world is here, and it’s called Bitcoin. But have you ever stopped to think about how it all works behind the scenes? It’s not just a matter of transferring digital coins from one person to another—there’s an intricate process happening in the background that keeps the whole system running smoothly. So, what exactly is Bitcoin mining, and why is it so crucial to the ecosystem? Let’s take a deep dive and uncover how this fascinating process powers the future of money!
Table of Contents
1) What is Bitcoin Mining?
2) Why Does Bitcoin Need Mining?
3) How Does Bitcoin Mining Work?
4) Methods of Bitcoin Mining
5) What is Proof of Work in Bitcoin?
6) Why to do Bitcoin Mining?
7) Time Taken to Mine One Bitcoin
8) Requirements for Bitcoin Mining
9) Cost of Bitcoin Mining
10) Risks of Bitcoin Mining
11) Taxes on Bitcoin Mining
12) Bitcoin Mining Rewards Over the Last Decade
13) Avoiding Bitcoin Mining Scams
14) Why are Bitcoin Miners needed?
15) Conclusion
What is Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining is like a digital treasure hunt in which the prize is Bitcoins. Miners use high end powerful computers to solve complex mathematical puzzles. This process, called 'hashing,' is part of Proof of Work (PoW) and requires a lot of energy, putting a significant strain on computer parts like graphic cards.
In hashing, miners make numerous quick guesses to find the right answer to a puzzle. As more miners join, the puzzles become harder, requiring even more computing power. This ensures that transactions are verified and the network remains secure, rewarding successful miners with Bitcoins.
However, Bitcoin mining consumes a large amount of energy, raising concerns about its environmental impact. This has led to discussions on developing greener and more efficient methods to sustain Bitcoin mining.
As miners continue their quest for Bitcoins, the future remains uncertain. Will innovations make mining more sustainable, or will the demand for digital currency keep pushing the limits of technology and energy use? Only time will tell.
Why Does Bitcoin Need Mining?
If you're using Bitcoin for trading or purchases, you may not think much about mining. However, it's important to understand its role in Bitcoin’s decentralised system. Unlike traditional systems, Bitcoin doesn’t have a central authority or a ledger of balances. Instead, users maintain copies of the transaction history.
Mining is how users agree on the validity of transactions. Every 10 minutes, the network compiles enough transactions into a new "block," securing it with cryptography. The user who successfully adds this block to the Blockchain is rewarded with new Bitcoin.
Key Points:
a) Decentralisation: No central authority; users maintain the ledger.
b) Blockchain: Transactions are grouped into secure "blocks."
c) Mining: Miners verify transactions and add blocks.
d) Reward: Miners earn Bitcoin for their work.
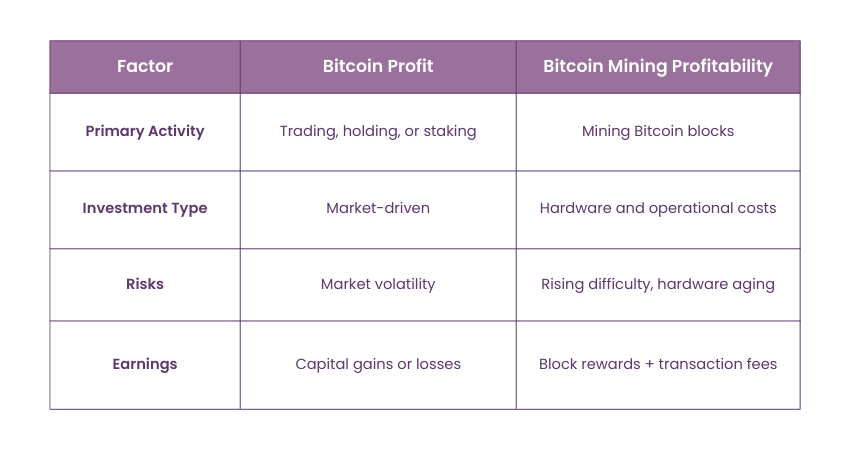
Bitcoin Profit and Bitcoin Mining Profitability
Bitcoin profit is all about deriving benefits on the basis of price difference with limited or zero involvement in the procedure of crafting the digital currency, Bitcoin mining profitability is straight associated with the actual process of creation of the digital asset. Bitcoin profit means the profit achieved from buying BTC, holding it or investing it in staking.
On the other hand, the profitability of the process of Bitcoin mining depends on the feasibility of carrying out mining activities to determine the truth of transactions and their integration into the block chain. These are mining difficulty, cost of electricity, efficiency of the hardware used, and current price of the Bitcoin.
They both need management planning and continuous evaluation in order to ensure the highest yield since they depend on the market environment, technologies, and other aspects such as regulatory policies.
How Does Bitcoin Mining Works
Mining is the main feature of Bitcoin’s functionality: it generates new coins, as well as checks the prospective transaction and adds it to the Blockchain. It is a process of using processors that are designed for mathematical computation in order to secure the Blockchain that underlies the Bitcoin system. Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how Bitcoin mining works:
a) Transaction Collection: Every time Bitcoin users make a transaction; the transaction is announced to the network by the users. Miners get the transactions done and put them in a block so that it will be unique.
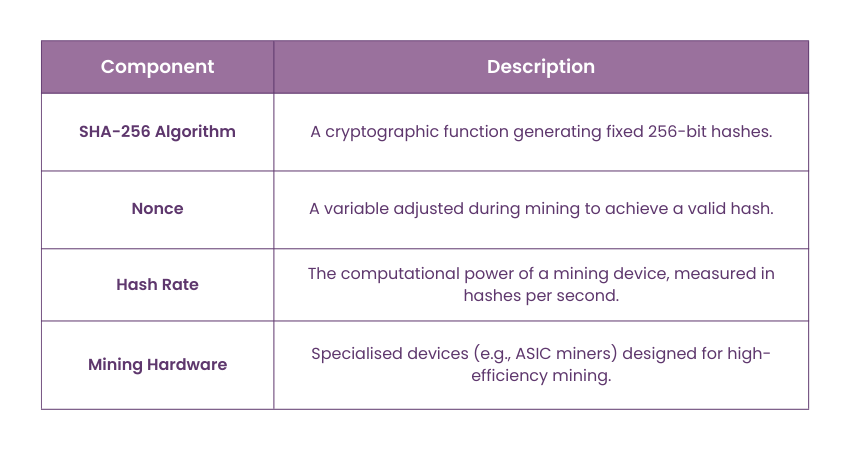
b) Solving Cryptographic Puzzles: Miners can solve an algorithm, which is creating a hash, an alphanumeric solution, that is accomplished by the rules set forth in the Bitcoin protocol. This process is called “proof of work”. Mining is computationally exhaustive, making mining resources demanding.
c) Adding Blocks to the Blockchain: The first miner whose terminal has computed the hash appears to the other members of the network and proclaims it has solved the puzzle. Others must validate the solution, and when approved, the group of transactions is incorporated into the Blockchain. It is a permanently stored record, thus optimising its security and transparency level.
d) Mining Rewards: To mine a block successfully, the miner earns bitcoins and the transactions fees as of 2024 the block reward was 6.25 bitcoins per block. These rewards make other miners agree to play a part in sustaining the network.
e) Difficulty Adjustment: In an endeavor to keep a standard block production time of about 10 minutes, the Bitcoin network usually adjusts the level of difficulty every 2016 block or about two weeks. If mining is becoming faster ye to better hardware or more miners, then the difficulty rises and vice versa.
Here are some key components of working of Bitcoin Mining:
Methods of Bitcoin Mining
Here, we have discussed some of the several methods available to Bitcoin Miners to mine BTC:
a) Application-specific Integrated Circuits (ASIC) Mining - These computers have been designed to serve only one purpose: To mine Cryptocurrency like Bitcoin. It is a highly effective means of mining cryptocurrencies.
b) Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) Mining - This mining method serves more purpose than ASIC. This method is helpful because a GPU can serve as a lower model of entry in the Cryptocurrency mining world. These are more affordable than the ASICs and can also support standard hardware.
c) Central Processing Unit (CPU) Mining - A CPU is the main part of any computer system. The method of CPU mining allows miners to use the idle power of their systems to mine Cryptocurrency. In the beginning, Bitcoins were mined using CPU power only.
d) Mining Pools - This is another method of mining where several miners join their resources to form a pool and mine the Cryptocurrencies. As many miners work together, finding a new block increases. Once the new block is found, these miners share the profit, and thus, collectively, they also increase their earnings.
e) Solo Mining - It is the exact opposite of Mining pools. Here, only one person is involved in the mining process. The single individual bears all the costs and profits of mining alone.
f) Cloud Mining - In this method, the miner outsources their computational work to a cloud mining farm. The miner or the user pays someone else to mine on their behalf. Starting the mining process becomes easier with cloud mining because the miner does not have to procure or arrange specialised hardware for mining.
What is Proof of Work in Bitcoin?
Proof of Work (PoW) is a system used to validate the transactions made and add new blocks to Bitcoin's blockchain. It ensures decentralisation by eliminating the need for government or bank intervention.
In PoW, the miners are required to solve complex mathematical puzzles to generate a hash that matches a target hash. The first miner to achieve this gets to add a new block to their blockchain and earn a Bitcoin as a reward. This process secures the network, prevents double spending, and keeps a record of all transactions.
Bitcoin introduced PoW, which is known for its high security but is criticised for its inefficiency and environmental impact. The PoW model, using the SHA-256 hashing algorithm, requires significant computational power, ensuring that only legitimate transactions are validated and respectivly recorded on the blockchain.
Preparing for a Job Interview? Check out our Blockchain Interview Questions!
Why to do Bitcoin Mining?
Bitcoin mining serves multiple crucial roles in the cryptocurrency ecosystem beyond just being a source of income for miners.
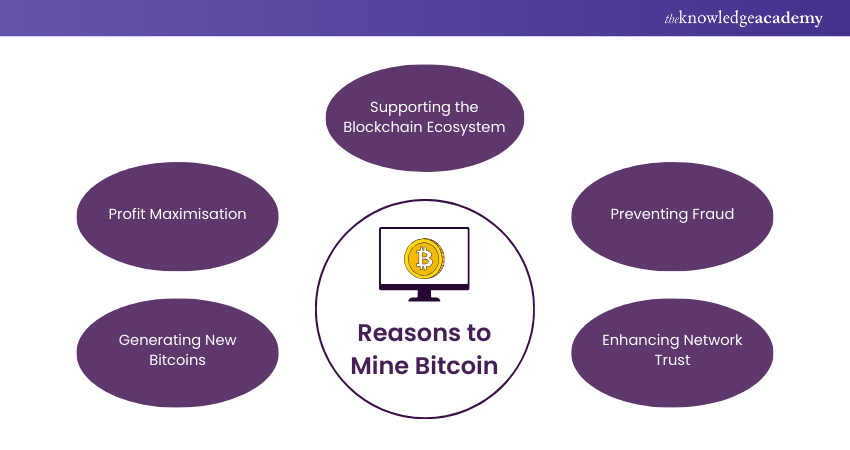
a) Generating New Bitcoins
The primary way to generate new Bitcoins is through mining. When Bitcoin was launched, it was initially circulated through the Genesis block, created by Satoshi Nakamoto. Since then, every Bitcoin has been generated and released through the mining process. Without miners, the Bitcoin network would exist but would be unusable because no new currency would be minted.
b) Maximising Profit
Mining Bitcoins can be highly profitable, especially given the high market value of Bitcoin today. Purchasing Bitcoin can be expensive, so miners can maximise their earnings by generating new Bitcoins through mining. With fewer than two million Bitcoins left to be mined out of the 21 million cap, their value is expected to increase, making mining potentially even more lucrative.
c) Supporting the Blockchain Ecosystem
Mining is important for maintaining and securing the Bitcoin network. Miners validate transactions, preventing fraud by ensuring that each Bitcoin is only spent once. This process involves solving complex puzzles, which help to confirm and record the transactions on the main blockchain. As their reward for their work, miners receive Bitcoins, incentivising them to continue supporting the network.
d) Preventing Fraud
Without miners, the Bitcoin network would be highly susceptible to fraud. Fraudsters could potentially spend the same Bitcoin more than once if transactions were not validated. The mining process reduces this risk, enhancing the confidence and trust of both miners and users in the Bitcoin blockchain.
e) Enhancing Network Trust
Miners play a critical role in building trust within the Bitcoin ecosystem by validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. This trust is fundamental for the continued adoption and stability of Bitcoin as a form of digital currency.
With our Blockchain Training Course, you will learn technologies behind Cryptography, Bitcoin, Ethereum, and others.
Time Taken to Mine One Bitcoin
The creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, designed the system to mine a new block every 10 minutes. To keep this pace, the difficulty of solving the puzzles adjusts based on the number of miners: more miners mean higher difficulty and vice versa.
Factors Affecting Mining Time
The following are the factors affecting mining time:
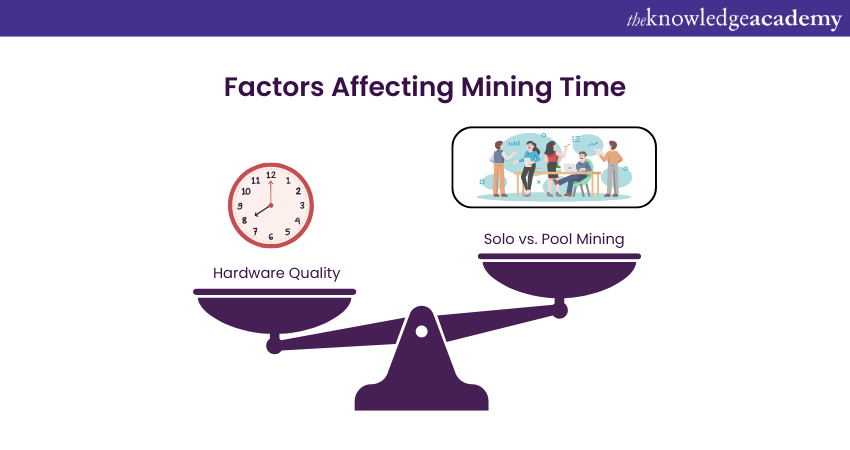
Hardware Quality: Advanced mining equipment can solve puzzles faster, earning Bitcoins more quickly.
Solo vs. Pool Mining: Solo mining takes more time since you work alone. Joining a mining pool speeds up the process as miners combine resources for better equipment and share the workload.
Requirements for Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining is a complex process, as it requires technical knowledge and access to various hardware and software. It involves three main components:

a) Cryptocurrency Wallet:
1) A miner needs a cryptocurrency wallet to store the keys for tokens or coins obtained from mining.
2) Wallets have unique addresses for sending, receiving, and securely storing tokens.
3) Options include online wallets and 'cold storage' wallets (offline). Each has its pros and cons.
b) Mining Software:
1) Mining software, usually free and available for different Operating Systems (OS), is essential for the mining process.
2) The miner must choose compatible software to avoid issues that could affect mining efficiency.
c) Mining Hardware:
1) Miners select hardware based on their needs and budget. Options range from personal computers (slow) to specialised, high-performance equipment (expensive and sometimes imported).
2) The right hardware simplifies and enhances the mining process.
Want to learn how to use a managed Blockchain Network quickly? Join our Amazon Managed Blockchain Training course today!
Cost of Bitcoin Mining
a) Mining Cost: The expense of mining a single Bitcoin varies significantly based on the energy rate per kilowatt-hour (kWh) and the efficiency of the mining hardware. For instance, at a rate of 4.7 cents per kWh, mining one Bitcoin costs roughly $5,170, whereas at 10 cents per kWh, it totals around $11,000. The substantial energy consumption required for mining is exemplified by an ASIC miner consuming about 3,032 watts to mine one Bitcoin, equating to a cost of roughly $10,200 at 5 cents per kWh.
b) Hash Rate Growth: With a greater number of miners joining, the hash rate increases, making Bitcoin mining more challenging and costly. This trend can lead to decreased profitability for individual miners. To mitigate the risk of not solving the cryptographic puzzle and enhance the chances of earning a reward, many miners opt to join mining pools. However, this also means that the reward is divided among the pool members.
c) Cost Components: Capital expenses (CapEx) such as purchasing and maintaining mining hardware significantly contribute to the overall mining cost. For example, the cost of an ASIC miner can be around $4,600, making the effective price per Bitcoin approximately $14,300. Operational expenses (OpEx) like electricity costs, cooling, and other overheads further add to the total cost. For instance, the electricity cost per Bitcoin can amount to around $10,200, resulting in a total production cost per Bitcoin of approximately $26,500.
d) Profitability Challenge: The profitability of mining Bitcoin is influenced by factors such as production costs, Bitcoin's price, and the network hash rate. It can be challenging for small-scale miners to optimize production costs enough for mining to be highly profitable.
Join Blockchain Training Courses to learn the basics of Bitcoins and Blockchain Technology!
Risks of Bitcoin Mining
Bitcoin mining can be financially rewarding, but it comes with several risks from financial, organisational, and environmental perspectives. Key risks include:
a) High Operational Costs:
i) Electricity: Mining consumes significant power, and high electricity rates can make it unprofitable.
ii) Hardware: ASIC miners are expensive to buy and operate, with limited lifespans due to wear and technological advancements.
b) Market Volatility: Bitcoin’s price fluctuates frequently, and low prices can make mining unprofitable if costs outweigh the Bitcoin value.
c) Mining Difficulty and Competition: Difficulty adjusts every two weeks, and as more miners join, competition increases, reducing individual success rates.
d) Environmental Impact: Mining requires significant energy, often from non-renewable sources, contributing to a large carbon footprint and potential for increased regulation.
e) Centralisation Risks: Pool mining centralises power, potentially conflicting with Bitcoin’s decentralised ethos.
f) Regulatory Uncertainty: Governments may impose regulations or taxes that could make mining less profitable or even illegal.
Taxes on Bitcoin Mining
It is important to consider the impact of taxes on Bitcoin mining. With the recent surge in cryptocurrency prices, tax authorities, including HMRC (Her Majesty's Revenue and Customs), have become more focused on regulating owners and traders of cryptocurrencies. Below are the key tax considerations for Bitcoin miners in the UK.
Are You Operating a Business?
If you are conducting Bitcoin mining as a business, you may be able to offset certain tax expenses. The value of the bitcoins you mine would be treated as sales income. However, if mining is more of a hobby, you may not be able to claim expenses associated with it.
Mined Bitcoin as Income
The fair market value of the Bitcoin or other cryptocurrencies you mine will be considered taxable income in the year you receive them. This is treated as ordinary income, and you will need to report it on your tax return.
Capital Gains
If you sell the bitcoins you mined for a higher price than what you originally paid (or mined them at), the profit will be subject to capital gains tax, similar to other forms of investment like stocks and bonds.
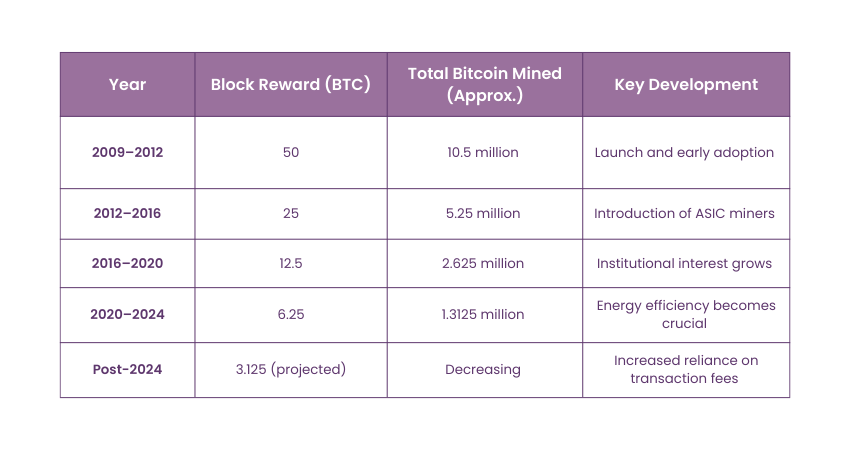
Bitcoin Mining Rewards Over the Last Decade
The nature of Bitcoin Mining rewards has shifted severally since the creation of bitcoin in 2009. The rewards are intended to defuse through time by a mechanism known as the halving, which takes place roughly every four years (after 210,000 blocks).
Halving events decrease the block reward by 50 % so, therefore total supply of bitcoins is capped at 21 million to ensure scarcity. Here's an overview of mining rewards over the last decade:
1) 2009–2012: The Early Days:
Block Reward: 50 BTC per block.
Total Mined: Early miners mainly ornamentation could mine Bitcoin using ordinary Central Processing Units and Graphics Processing Units.
Impact: Frequent emission of Bitcoin, which encourages use and guarantee of the Blockchain.
2) 2012–2016: First Halving:
Block Reward: Cut down to 25 BTC per block by the end of November in 2012.
Mining Evolution: To improve the efficiency of the mining process ASICs were introduced employing which has proved to be costly.
Economic Impact: Halving also made Bitcoin known to be a deflationary currency and the worth of mined Bitcoin also rose.
3) 2016–2020: Second Halving:
Block Reward: Cut down to 12.5 BTC per block in July 2016.
Network Growth: They increased during the last bull run and institutional adoption of Bitcoin.
Profitability: Higher coin rewards compensated for the lowered profits, making mining for optimum efficiency possible with Bitcoins.
4) 2020–2024: Third Halving:
Block Reward: Decidedly cut to 6.25 BTC per block in May 2020.
Market Impact: This halving occurred in a period of a bull market causing the price of Bitcoin to skyrocket to record levels.
Mining Trends: Mining pools were the primary force, and energy consumption was now important.
5) Future: Post-2024 and Beyond:
Next Halving: Projected for mid-2024, decreasing of the rewards to 3.125 BTC per block.
Implications: The experts are expecting that miners are going to extract their income from the transaction fees as block rewards are decreasing over time.
Some summaries of halving events:
Avoiding Bitcoin Mining Scams
What does it mean? Nothing new under the sun, naturally; as with anything that involves money, Bitcoins and Bitcoin mining are not immune to attracting bad parties. In case you decide to embark on it, you will probably want to be cautious of mining scams before you decide on the software, tools, or networks. Here are some the more common scams:
a) Cloud Mining Platforms: These are websites that claim to rent mining power to customers. It’s not that all these services are scams, but always ensure you read some reviews, talk to people, and generally ensure you are doing enough research before choosing a particular service.
b) Fake Wallets: Cryptocurrency wallets are the place where your private keys are stored. However, thieves can take time to replicate these wallets with the intention of taking your keys. Where you get your wallet from is important.
c) Fake Exchanges: There are numerous cases when people receive emails and messages from fake exchanges in which they are pressured or can be deceived into depositing money.
Why are Bitcoin Miners Needed?
Bitcoin mining goes beyond creating new Bitcoins; it validates cryptocurrency transactions and maintains their records. Miners play a crucial role in preventing double-spending, which is akin to counterfeiting. Satoshi Nakamoto designed the Proof of Work (PoW) system to ensure that each Bitcoin is only spent once.
Miners validate their transactions and add them to the Blockchain in blocks. This prevents cybercriminals from reusing already spent Bitcoins, as each transaction is checked against a public ledger. This validation process helps with maintaining the integrity of the Bitcoin network.
Moreover, Bitcoin miners collectively secure the network. More miners mean increased security, reducing the risk of fraud. A secure network attracts more users, encouraging the widespread use of Bitcoin for various transactions.
Earnings of a Bitcoin Miner
Bitcoin mining rewards are halved every four years or 210,000 blocks. When Bitcoin launched in 2009, the reward was 50 BTC per block. This was later reduced to 25 BTC in 2012, 12.5 BTC in 2016, and currently stands at 6.25 BTC since the 2020 halving. In 2024, the reward will further decrease to 3.125 BTC. Despite these reductions, the value of Bitcoin fluctuates daily.
Currently, earning 6.25 BTC per block still represents significant income, given that one Bitcoin is valued at approximately £75,358. However, Bitcoin's value is highly volatile and can change rapidly. Many experts predict a dramatic increase in Bitcoin's value in the near future, potentially boosting miners' earnings and making the mining process even more profitable.
Conclusion
With the rising popularity of Cryptocurrencies and Bitcoin in particular knowing how Bitcoin Mining works can be a great benefit. This blog explains the concept and process of Mining Bitcoins in great details. It additionally provides insight into the different methods, requirements and costs involved in Bitcoin Mining. So, wait no longer gear up your systems and start your journey of this unique online treasure hunt.
Gain in-depth knowledge of Cryptocurrency and how to trade with the Trading and Investing Training course.
Frequently Asked Questions

The legality of mining bitcoins differs from one country to another. It is legal in most areas of the world, such as, the United States, United Kingdom, and the European Union but prohibited in others such as China for energy issues or legislation. Citizens have to be careful all the time because the laws governing the use may change quickly.

21million Bitcoins can be mined in total and following this computation, about 2.1 million bitcoins are still available for mining. As seen above, the remaining supply is to be gradually released through block rewards though the amount decreases after every four years resulting in halvings until approximately 2140.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Advanced Technology Courses, including the Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course, Ethereum Developer Course, and Cryptocurrency Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Types of Blockchain.
Our Advanced Technology Blogs cover a range of topics related to Bitcoin, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Crypto skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course
Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Course
Thu 27th Feb 2025
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 26th Jun 2025
Thu 28th Aug 2025
Thu 23rd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


