We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Animation is a complex and fascinating art form that has evolved over the years. However, choosing the right Animation for a project can be challenging, and a lack of understanding can lead to poor decision-making. This can result in a suboptimal final product that fails to meet the desired objectives. Understanding the difference between 2D and 3D Animation can help you make an informed decision on which style to use for your project. In this blog, you will learn about the difference Between 2D and 3D Animation. Moreover, you will also learn how to choose the right Animation style.
Table of Contents
1) What is 2D Animation?
2) What is 3D Animation?
3) Differences between 2D and 3D Animation
4) 2D Animation and 3D Animation: Which one is better?
5) Conclusion
What is 2D Animation?
2D Animation is the oldest and most widely used form of Animation. It involves creating and manipulating flat drawings or images on a 2D plane, such as paper, canvas, or computer screen. It can be done by hand drawing, scanning, or using software tools.
The basic principle of 2D Animation is to create a series of images or frames that show the changes in the position, shape, size, or colour of the objects or characters. These frames are then played back at a certain speed, usually 24 frames per second, to create the illusion of movement. Some examples of 2D Animation are cartoons, anime, comics, and web Animations.
What is 3D Animation?
3D Animation is the newest and most advanced form of Animation. It involves creating and manipulating 3D models and environments on a computer. This Animation can be done using software tools such as Maya, Blender, or Cinema 4D.
The basic principle of 3D Animation is to create a virtual space where the models and environments can be placed, moved, rotated, scaled, or textured. These models and environments can also be lit, shaded, and rendered to create realistic or stylised effects.
The 3D Animation can then be viewed from any angle or perspective and can be exported as images, videos, or interactive applications. Some examples of 3D Animation are movies, video games, simulations, and virtual reality.
Differences between 2D and 3D Animation
2D and 3D Animation have many differences in terms of their animating procedure, frame rate, expense, relevance, texture, space, shapes, and types. Here are some of the main differences between 2D Animation vs 3D Animation:
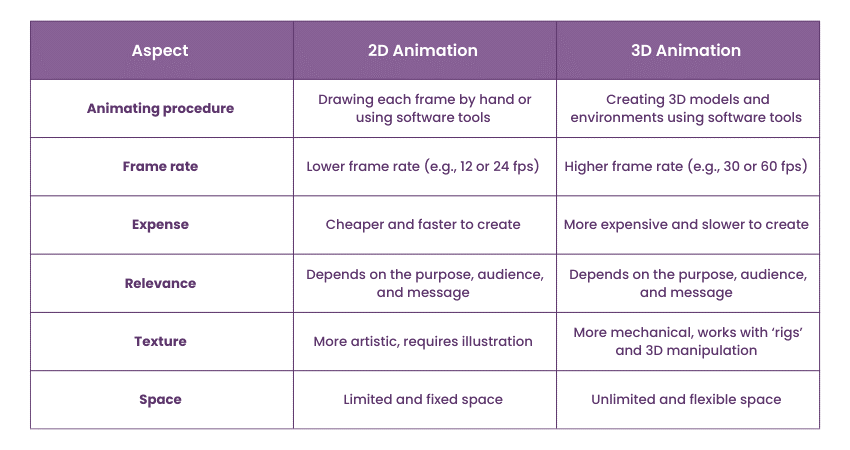
1) Animating procedure
2D Animation requires drawing each frame by hand or using software tools such as Adobe Animate, Toon Boom, or Photoshop. It also requires the use of techniques, such as keyframes, in-betweens, timing, and spacing, to create smooth and consistent Animation. 2D Animation requires a lot of artistic and creative skills, such as drawing, colouring, and designing.
3D Animation requires creating 3D models and environments using software tools such as Maya, Blender, or Cinema 4D. Developing strong 3D Animation Skills is essential for mastering techniques such as rigging, skinning, morphing, and motion capture to create realistic and expressive animation. Additionally, 3D Animation demands a solid foundation in technical and mathematical skills, including modelling, texturing, lighting, and rendering.
2) Frame rate
The frame rate of 2D and 3D Animation is different in terms of the number of frames per second (fps) used to create the Animation. 2D Animation usually uses a lower frame rate, such as 12 or 24 fps, to create the Animation. This is because drawing each frame by hand or using software tools can be time-consuming and labour-intensive.
2D Animation can also use a technique called “on twos”, which means that each frame is shown twice to reduce the number of frames needed. 2D Animation can create a more stylised and expressive Animation with a lower frame rate.
3D Animation usually uses a higher frame rate, such as 30 or 60 fps, to create the Animation. This is because creating 3D models and environments using software tools can be faster and easier.
3D Animation can also use a technique called “interpolation”. This means that the software can automatically generate the frames between the keyframes to increase the number of frames needed. Moreover, 3D Animation can create a more realistic and smooth Animation with a higher frame rate.
3) Expense
2D Animation can be cheaper and faster to create, depending on the complexity and quality of the Animation. 2D Animation can be done by using simple and affordable tools, such as paper, pencils, or software tools. This type of Animation can also be done by a smaller team or even a single person, depending on the scope and scale of the project. 2D Animation can be suitable for projects with a low budget and a short deadline.
3D Animation can be more expensive and slower to create, depending on the complexity and quality of the Animation. 3D Animation requires the use of sophisticated and expensive tools, such as software tools, hardware, or motion capture devices. It can also require a larger team or even a studio, depending on the scope and scale of the project. 3D Animation can be suitable for projects with a high budget and a long deadline.
4) Relevance
Both 2D and 3D Animation can be relevant for different types of projects and genres. For example, 2D Animation can be more suitable for comedy, satire, or fantasy, while 3D Animation can be more suitable for action, adventure, or realism. However, this is not a strict rule, as there are many examples of 2D and 3D Animation that cross genres and styles.
5) Texture
Texture in Animation refers to the surface quality of an object, which can be seen and felt. In 3D Animation, textures are applied to 3D objects to create a realistic look and feel. Textures can range from simple repeating patterns to unique images created for a specific 3D model, and they can potentially transform simple shapes and scenes into photorealistic, evocative characters and environments.
The main difference between 2D and 3D Animation is that 2D is more artistic, and 3D is more mechanical. In 2D Animation, every frame needs to be drawn, which requires a large amount of illustration. On the other hand, 3D Animation works with ‘rigs’, where a 3D model is essentially given a skeleton that can be manipulated.
Hone your expertise in 3D modelling with our Blender 3D Modeling for Unity Training – sign up now!
6) Space
The space of 2D and 3D Animation refers to the dimension and perspective of the Animation, which are key characteristics of animation. 2D Animation has a limited and fixed space, while 3D Animation offers an unlimited and flexible space. 2D Animation can only show one angle or view of the scene, whereas 3D Animation can display multiple angles or views, highlighting its diverse characteristics of animation. 2D Animation tends to create a simpler and clearer space, while 3D Animation can create a more complex and dynamic space, utilizing these distinct characteristics of animation.
7) Shapes
The shapes of 2D and 3D Animation refer to the forms and outlines of the Animation. 2D Animation has a linear and geometric shape, while 3D Animation has a curved and organic shape. 2D Animation can create a more abstract and symbolic shape, while 3D Animation can create a more realistic and natural shape.
8) Types
Both 3D and 2D Animation have subcategories and variations. Here are some of the most common types of 2D and 3D Animation:
2D Animation types:
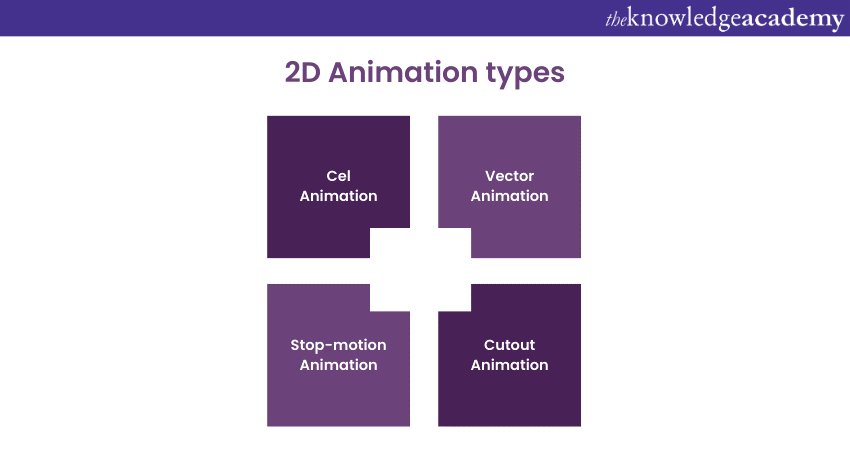
a) Cel Animation: Also known as traditional Animation, cel Animation involves drawing each frame by hand on a transparent sheet called a cel. The cells are then layered on top of each other to create the illusion of motion.
b) Vector Animation: Vector Animation uses mathematical equations to create images that can be scaled up or down without losing quality. This type of Animation is often used for logos and other simple graphics.
c) Cutout Animation: Cutout Animation involves moving flat, 2D characters and objects around on a background. This type of Animation is often used in television shows and commercials.
d) Stop-motion Animation: Stop-motion Animation involves taking photographs of objects or characters in small increments and then playing them back quickly to create the illusion of motion.
3D Animation types:
a) CGI Animation: Computer Generated Imagery (CGI) Animation involves creating 3D models on a computer and then animating them. This type of Animation is often used in movies and video games.
b) Motion capture Animation: Motion capture Animation involves recording the movements of real people or animals and then using that data to animate 3D models. This type of Animation is often used in movies and video games.
c) Claymation: Claymation involves creating characters and objects out of clay and then photographing them in small increments. This type of Animation is often used in movies and television shows.
d) Photorealistic Animation: Photorealistic Animation involves creating 3D models that look like real-life objects or people. This type of Animation is often used in movies and commercials.
Unleash your imagination with our Animation Masterclass – Sign up now!
2D Animation and 3D Animation: Which one is better?
There is no definitive answer to which type of Animation is better, as both 2D and 3D Animation have their own advantages and disadvantages. However, there are some factors that can help you decide which type of Animation to choose for your project, such as the following:

1) Target audience
The target audience is the group of people who watch and enjoy your Animation. You should consider the age, gender, culture, preferences, and expectations of your target audience when selecting the type of Animation.
For example, if your target audience is young children, you might want to use 2D Animation, as it can be more colourful, playful, and appealing to them. If your target audience is adults, you might want to use 3D Animation, as it can be more realistic, sophisticated, and impressive to them.
2) Software accessibility
Software accessibility is the availability and affordability of the software that you will use to create your Animation. You should consider the cost, compatibility, and functionality of the software when selecting the type of Animation.
For example, if you have a low budget, you might want to use 2D Animation, as it can be done with cheaper and simpler software. If you have a high budget, you might want to use 3D Animation, as it can be done with more expensive and advanced software.
3) Financial plan
The financial plan is the amount of money that you will spend and earn from your Animation. You should consider the production cost, marketing cost, and revenue potential of your Animation when selecting the type of Animation. For example, if you want to save money, you might want to use 2D Animation, as it can be done with fewer resources and less time. If you want to make money, you might want to use 3D Animation, as it can attract more viewers and sponsors.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand the differences between 2D and 3D Animation. They have their own pros and cons. The choice between these Animation types depends on various factors, such as the purpose, audience, and budget of your project. Additionally, using the right 2D Animation Software can enhance workflow efficiency and creativity for those opting for 2D animation. You should weigh the benefits and drawbacks of each type of Animation and choose the one that best suits your needs and goals.
Ignite your artistic potential with our Animation and Design Training – sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
Upcoming Office Applications Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 2D Animation Course
2D Animation Course
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


