We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition, or in short, SCADA systems, have revolutionised industrial operations by offering a comprehensive platform for monitoring and managing various processes. However, like any technology, the Advantages and Disadvantages of SCADA must be carefully considered. In this blog, we'll delve into both sides of the coin to understand the characteristics of SCADA implementation.
Table of Contents
1) Advantages of SCADA
2) Disadvantages of SCADA
3) Conclusion
Advantages of SCADA
SCADA emerges as a powerhouse in industrial control systems, offering extensive data storage, broad sensor connectivity, and real-time simulation capabilities. This section unveils the commendable aspects that make SCADA a cornerstone in modern industrial operations.
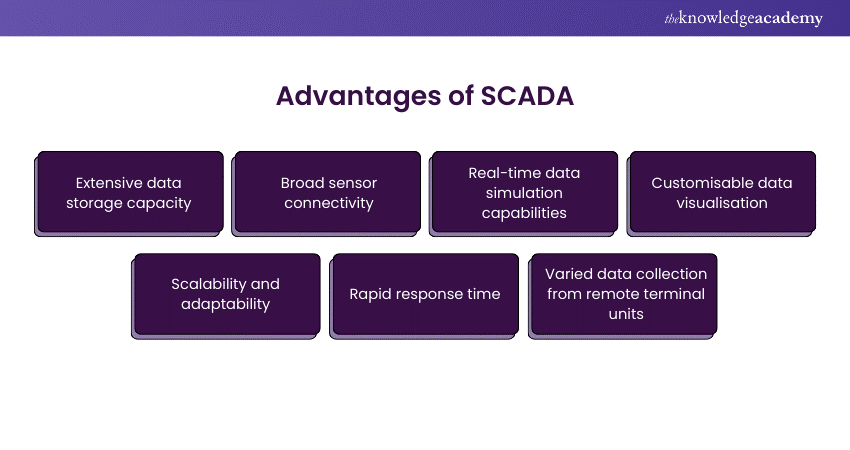
1) Extensive data storage capacity
One of the main advantages of SCADA systems is their ability to store robust amounts of data generated from industrial processes. This extensive storage capacity enables organisations to analyse historical data trends, identify patterns, and make informed decisions to optimise operations and improve efficiency.
2) Broad sensor connectivity
SCADA systems offer compatibility with a wide range of sensors and devices, allowing seamless integration into diverse industrial environments. This broad connectivity ensures that critical sensor data can be efficiently collected and monitored in real-time, enhancing overall system visibility and control.
3) Real-time data simulation capabilities
Another critical advantage of SCADA is its real-time data simulation capabilities, which enable operators to model different scenarios and analyse the significant impact of changes before implementation. This proactive approach helps minimise risks, optimise processes, and ensure smoother operations.
4) Customisable data visualisation
SCADA systems provide customisable data visualisation tools that allow users to tailor information display according to their specific requirements. Whether it's through charts, graphs, or dashboards, operators can visualise data to facilitate quick decision-making and enhance situational awareness.
5) Scalability and adaptability
SCADA systems are highly scalable, making them suitable for small-scale operations and large industrial complexes. Additionally, their adaptability allows for seamless integration with existing infrastructure and the incorporation of new technologies, ensuring long-term viability and flexibility.
6) Rapid response time
With its real-time monitoring capabilities, SCADA facilitates rapid response to critical events or emergencies. By providing instant alerts and notifications, operators can take prompt action to mitigate risks, minimise downtime, and prevent potential disruptions to operations.
7) Varied data collection from remote terminal units
SCADA systems enable diverse data collection from remote terminal units (RTUs) across different geographical locations. This capability is particularly beneficial for industries with distributed assets, as it allows centralised monitoring and control, improving efficiency and reducing maintenance costs.
Disadvantages of SCADA
While SCADA empowers industries with advanced control and monitoring, it has challenges. This section delves into the complexities associated with installing SCADA systems.
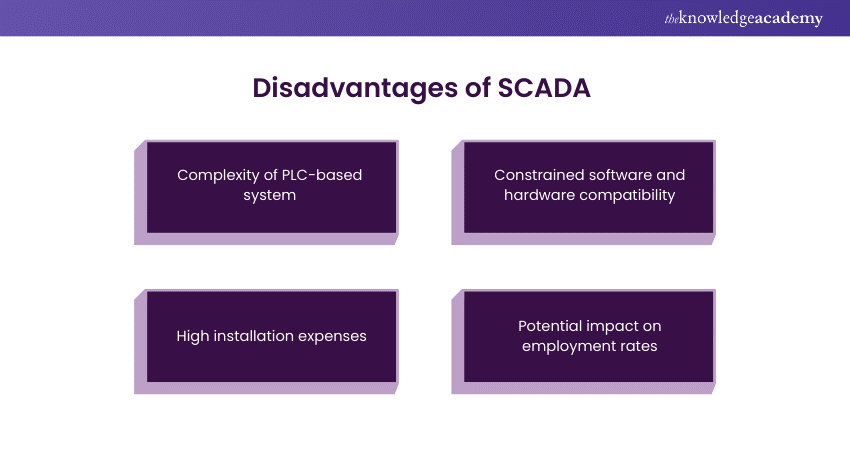
1) Complexity of PLC-based system
One of the major drawbacks of SCADA systems is the complexity associated with programmable logic controller (PLC)-based architectures. Configuring and programming PLCs require specialised skills and expertise, leading to higher training and maintenance costs for personnel.
2) Constrained software and hardware compatibility
SCADA systems often face software and hardware compatibility issues, especially when integrating with legacy systems or third-party devices. This constraint can limit the flexibility and interoperability of the system, potentially hindering its effectiveness in certain environments.
3) High installation expenses
The initial installation cost of SCADA systems can be huge, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises with limited budgets. This expense includes the hardware and software components and the associated infrastructure upgrades and installation services.
4) Potential impact on employment rates
The automation capabilities of SCADA systems can potentially impact employment rates, particularly in industries where manual labour is prevalent. While automation can lead to an increase in productivity and efficiency, it also results in job displacement or the need to retrain the existing workforce to operate and maintain the SCADA infrastructure.
Improve your Facilitation skills with our Facilitation Skills Training – Sign up today!
Conclusion
While SCADA systems offer advantages in data storage, connectivity, visualisation, scalability, and response time, they also present challenges such as complexity, compatibility issues, high costs, and potential workforce implications. Therefore, organisations must carefully weigh the Advantages and Disadvantages of SCADA implementation. By doing so, they can leverage SCADA technology to streamline operations, enhance productivity, and maintain a competitive edge in today's dynamic industrial landscape.
Learn more about the intricacies of SCADA with our SCADA Training – Join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

In today's complex industrial landscape, SCADA is crucial for streamlined operations, real-time monitoring, and rapid response. Its extensive data capabilities, connectivity, and adaptability make it a vital tool for enhancing efficiency and maintaining a competitive edge.

In the Internet of Things (IoT), SCADA serves as a critical component for centralised monitoring and control of interconnected devices and sensors. It enables seamless data collection, analysis, and management, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of IoT systems.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Industry Training including Basic Barista Training, SCADA Training, and Import and Export Masterclass. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Product Lifecycle.
Our Business Skills Blogs covers a range of topics related to online Businesses, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 SCADA Training
SCADA Training
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


