We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Agile Methodology is like a superhero toolkit for Project Management. It’s all about being quick on your feet and ready to tackle changes head-on. Imagine a team of project ninjas, delivering awesome work swiftly and adjusting their moves as new challenges pop up. It’s the secret sauce that helps teams work smarter, not harder, and get things done efficiently. Read this blog to explore What is Agile Methodology along with its benefits, and essential steps involved in Agile Project Management.
Table of Contents
1) What is Agile?
2) What is the Agile Manifesto?
3) Understanding What is Agile Methodology in Project Management
4) How can Agile Methodology be Implemented into Projects?
5) What is Agile Methodology in Software Development?
6) Core Principles of Agile Methodology
7) Steps in Agile Methodology
8) Benefits of Agile Methodology
9) What is Agile Methodology in Simple Words?
10) How to Explain Agile Methodology in an Interview?
11) Conclusion
What is Agile?
Agile is a working process that focuses on delivering value to customers in small and frequent increments rather than in one big launch. Agile teams collaborate closely and adapt to changing requirements and feedback. The Agile Model also refers to a set of frameworks and practices that are based on the values and principles of the Agile Manifesto, with Agile Training Becoming Popular to enhance its implementation. .Scrum, Kanban Board, and Extreme Programming (XP) are the most common Agile frameworks.
Agile teams use various techniques, such as Pair Programming, Test-driven Development, Standups, Sprints, and retrospectives, to improve their software quality and efficiency. Agile is not only a Software Development method but also a mindset that fosters innovation, learning, and customer satisfaction. In Agile Case Studies, we see how these techniques are effectively applied to real-world projects, driving continuous improvement and success. Recognising the Difference between Change Management and Agile Change Agent is key to successfully implementing Agile principles.
What is the Agile Manifesto?
The Agile Manifesto is a cumulative statement of values and guidelines for Software Development. It was developed by a collective of practitioners in 2001. Here are the core values from the Manifesto:
a) Individuals and interactions over processes and tools
b) Working software, not comprehensive documentation
c) Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
d) Reacting to change rather than following the plan
Learn more about What Is an Agile Coach and how they can enhance your team's efficiency.
What is Agile Methodology in Project Management?
Agile Methodology in Project Management is an iterative and flexible approach that focuses on continuous improvement, collaboration, and customer feedback. It breaks projects into small, manageable increments (sprints) to enhance adaptability and efficiency, ensuring faster delivery and responsiveness to changes throughout the project lifecycle.
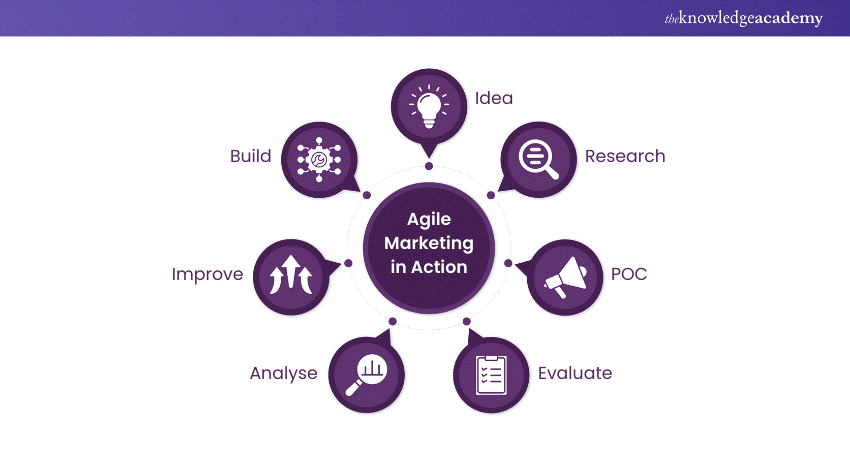
Agile Methodology promotes adaptability by dividing projects into smaller cycles, allowing teams to respond quickly to changing requirements. For example, in marketing, a team launching a new product campaign can use Agile to break the project into smaller tasks like market research, content creation, and ad testing.
The marketing team divides the campaign into sprints, focusing on tasks like research, content creation, and ad testing for efficiency. They launch a pilot ad, gather feedback, and refine messaging, visuals, or platforms in sprints, ensuring engagement, adaptability, and better Return On Investment (ROI).
Unlock your potential and drive your career forward with our SAFe Agile Certification!
How can Agile Methodology be Implemented into Projects?
If you want to transform your team’s workflows with Agile principles, follow these steps to implement an Agile Methodology that suits your needs:
Pick the right Agile framework
The first step is to choose an Agile framework that matches your team’s size, project requirements, and experience level.
Some of the most common Agile frameworks are:
a) Scrum: A Project Management approach based on principles
b) Kanban Board: A visual system for managing workflows and processes
c) Scrum Ban: A combination of Scrum and Kanban
d) XP: A product development method that focuses on customer satisfaction
e) APF: A flexible teamwork model that adapts to changing situations.
Learn how to prepare for Agile Projects with our Agile Project Management Practitioner (AgilePM®) Course. Sign up today!
Build Your Agile Team
An Agile team is not just any group of people working together. To succeed with Agile Methodologies, you need to have a team with clear roles and responsibilities and a culture of collaboration.
Here are some responsibilities of an Agile team:
a) Self-organisation: A key feature of an Agile team is the ability to self-organize. In Agile Project Management, the teams and team members are expected to take the initiative and structure themselves in a way that optimizes their performance. Becoming an Agile Change Agent plays a crucial role in guiding teams toward effective self-organization and continuous improvement.
b) Cross-functional Collaboration: Another essential aspect of an Agile team is the ability to collaborate across functions and departments. Agile teams must communicate effectively and work closely with various colleagues.
c) Iteration Planning: A specific skill required for Agile Project Management is iteration planning. This involves defining the scope of each sprint according to the product backlog.
Plan the Project
Once you’ve chosen an Agile framework and formed your team, it’s time to plan your project.
Careful planning is one of the secrets to successful Agile Project Management. From the start, you must clearly define your project objectives and scope. This will help you avoid unforeseen challenges and allow you to divide your project into manageable sprints (if you’re using Scrum). To ;earn more, you can refer to out Agile Project Management Guide.
You may also create a product backlog during the planning phase, especially useful for Software Development projects. The product backlog allows you to assign different priority levels according to your tasks or assignments, ensuring that every team member knows what they should focus on at a time, which is key when Optimizing Your Agile Resume to demonstrate your ability to manage priorities and streamline project workflows.
Manage Stakeholder Expectations
Before you start your project, it’s important to check in with key stakeholders to incorporate their feedback.
Depending on their level of involvement, your project stakeholders may want to be updated regularly or at least receive periodic reports. Creating feedback loops reduces any uncertainty on the stakeholder side and allows you to stay open to change if necessary at any stage of the process.
Measure Success
Measuring project success is vital to making meaningful progress with your Agile Methodology. You need to pay attention to what worked and what didn’t during the Project Management process. This helps you learn valuable lessons to apply to future Agile projects. There are several ways to track progress and measure success with Agile projects effectively:
a) Daily Standups: Short meetings to discuss challenges and find solutions.
b) Sprint Reviews: Casual sessions to present work and solicit team feedback
c) Retrospectives: Evaluations of past work to inspire and influence future improvement.
You should also introduce Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) before starting any new major project, as getting specific will help you establish milestones and measure Progress.
Practice makes perfect! Dive into mock interviews to refine your responses to common Agile Interview Questions and gain confidence in your abilities.
What is Agile Methodology in Software Development?
Agile is a flexible and customer-centric approach to Software Development. It involves an iterative and adaptive process that aims to deliver high-quality software products that meet the customer’s needs and expectations. Agile teams are flexible, collaborative, and self-organised, which allows them to respond quickly to changes, deliver products faster, and work together effectively.
Agile Methodology improves software quality by enabling iterative testing. By incorporating customer feedback and conducting multiple iterations and tests, Agile teams can identify and fix any issues along the way and create the best possible software.
The Agile software development life cycle has six simple stages:
a) Concept: Define the project scope and priorities
b) Inception: Form the Agile team based on project requirements
c) Iteration: Develop code with customer feedback in mind
d) Release: Test the code and resolve any problems
e) Maintenance: Provide ongoing tech support to ensure the product works well
f) Retirement: The end of the product life cycle, which often leads to a new one
Explore PRINCE2 vs Agile to understand which methodology fits your organisation best.
Core Principles of Agile Methodology
The Agile Manifesto consists of four basic values and 12 principles that support development and software delivery. Agile Methodology in Software Testing utilizes these values to guide the development and delivery processes. The four principles of Agile Methodology are as follows:
1) Individuals and Interactions Over Processes and Tools
Agile values people and their interactions during the project. It values communication and collaboration among team members, end-users, and customers. The Agile Manifesto states that successful Software Development is possible with good team coordination and cooperation. Members who communicate effectively with one another and work towards a single objective can solve difficulties more efficiently.
2) Working Software Over Comprehensive Documentation
The Agile Manifesto emphasises the necessity of being customer-centric, which fosters rapid iterations and gradual delivery of actual value to clients. Rather than focusing on thorough documentation, this idea fosters regular iterations and incremental delivery of meaningful value to clients.
While documentation is essential, the functionality and quality of the software being created are significant indicators of progress. Teams should focus on processing and delivering functional software to clients.
3) Customer Collaboration Over Contract Negotiation
The Agile Methodology emphasises active customer interaction and collaboration. Regular feedback and open communication guarantee that customer expectations are satisfied and that the final product matches their vision. This principle emphasises the value of customer satisfaction and adaptation to changing needs. Historically, the contract was the most significant component of project development since it supplied specific details about the result. Instead, the emphasis should be on continuous product development. Therefore, it is critical to collaborate with the consumers to obtain ideal results.
Responding to Change Over Following a Plan
Agile Methodology accepts change by embracing constant planning and adaptation. Requirements and priorities are reviewed and updated regularly based on feedback, which allows for improved responsiveness to changing client needs.
Agile teams value flexibility and adaptability. They are receptive to feedback on new information, make necessary adjustments, and provide the most value to consumers. This is why, according to the Agile Manifesto, all software teams should be able to modify their work as needed.
Learn the Agile approach and philosophy with our Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM®) Course. Join today!
Steps in Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology allows teams to produce value rapidly, adapt to changing requirements, and promote continuous improvement. The following are the essential steps in Agile Methodology:
1) Project Initiation: Define goals, scope, and form a team
2) Product Backlog: Prioritise and break tasks into user stories
3) Sprint Planning: Select tasks, estimate effort, and create a backlog
4) Daily Stand-up: Quick progress updates
5) Sprint Review & Retrospective: Demonstrate work, gather feedback, improve
6) Repeat & Adapt: Refine, optimise, and continuously improve
Here is a detailed breakdown of each step to help you better understand Agile Methodology and its implementation:
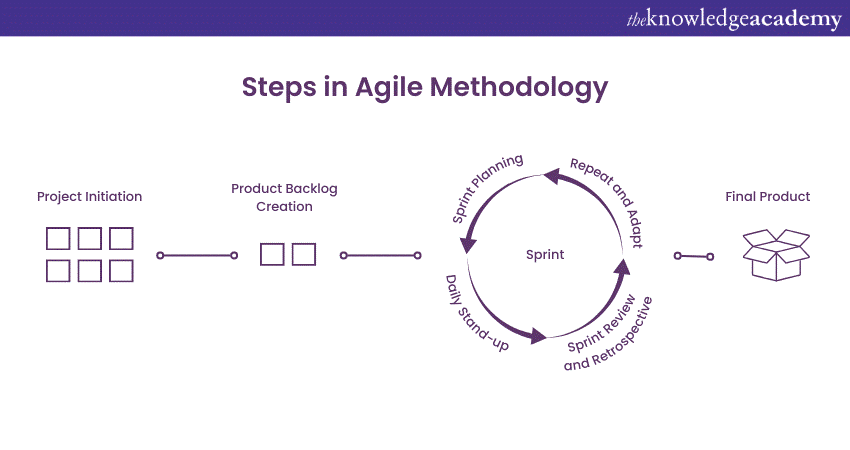
a) Project Initiation: Define the project goals, objectives, stakeholders, vision, and scope before forming an Agile team and identifying high-level requirements and constraints.
b) Product Backlog Creation: Work with stakeholders to define user stories, prioritise them based on business value and stakeholder demands, break them into manageable tasks, and keep a dynamic product backlog.
c) Sprint Planning: Choose a set of prioritised user stories for the sprint, describe the aim and deliverables by breaking user stories down into tasks and estimating effort, and construct a sprint backlog of activities to be performed.
d) Daily Stand-up: Team members should hold daily stand-up meetings to discuss what they accomplished the day before and what they will work on the following day. These discussions should last no more than 15 minutes and are not intended to be lengthy problem-solving sessions. To keep it brief, some teams hold them standing up.
e) Sprint Review and Retrospective: It is a critical step in the sprint process. A review shows the completed work to stakeholders, collects comments, conducts an accomplishment review, updates the product backlog, and reflects on the team's performance, processes, and practises. The purpose of a retrospective is to identify successes, areas for improvement, and potential solutions, as well as to discuss and prioritise changes and to build a Agile Culture of continuous learning.
f) Repeat and Adapt: Repeat the sprint cycles, refine and reprioritise the product backlog, analyse and adapt team procedures, tools, and practices for continuous improvement, welcome feedback, and cultivate a mindset of continuous learning and evolution.
Join our Agile Overview Training to acquire the knowledge of Agile to ensure a final solution that meets business needs.
Benefits of Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology provides several benefits that help to project success and performance. The following are some benefits of Agile Methodology:
1) Adaptability
Agile Methodology possesses many adaptable characteristics. Agile working in the Software Development endeavour helps teams quickly readjust strategies without any chaos in the project itself. Unlike the fall method of the traditional type, where stages are rigidly dependent on each other, Agile is more flexible, and strategy shifts will run smoothly. This is a plus point, especially in the rapidly developing area of software, showcasing the key Differences between Agile and Traditional Project Management.
2) Collaborative Teamwork
Emphasising communication within teams realises the importance of Agile principles. Although technological advances have broadened the use of remote work, personal interaction has remained relevant. Dispelling project separations strengthens the team's constructive aspects and reinforces the whole level of production.
3) Customer-centric Approach
The Software Development process combines the nuances of customer focus. In Agile methods, teamwork with clients is highly appreciated, and fast feedback from all users is possible. Valuing routinely caused by the major features and keeping a customer-focused concept will prove beneficial in the long run. Agile teams can quickly fulfil a similar role on another project when the needs are varied.
Join our Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®) Course today to learn effective Project Management.
4) Using Agile and Waterfall Methodologies
Some projects may require a combination of both Agile and Waterfall Methodologies. This hybrid approach can allow teams to use the Waterfall method for planning and design and the Agile method for development. This way, teams can have a clear and detailed plan upfront and deliver working software in short and frequent cycles. This can help teams balance both methodologies' benefits and cope with the challenges of complex and changing projects.
What is Agile Methodology in Simple Words?
Agile is a collaborative and adaptable approach to managing projects or software development. It divides work into smaller, manageable iterations or sprints, which can include larger tasks, also known as epics in Agile, enabling teams to deliver results incrementally. It values customer feedback, teamwork, and flexibility, ensuring quick responses to changes and continuous improvement.
How to Explain Agile Methodology in an Interview?
Agile is a Project Management method that delivers work in smaller, prioritised pieces rather than a single big delivery. It emphasises adaptability, collaboration, and customer-focused results. Frameworks like Scrum or Kanban guide teamwork, ensuring ongoing feedback, fast adjustments, and high-quality outcomes.
Conclusion
Agile Methodology has revolutionised Project Management and software development by promoting flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. With its core principles, structured steps, and numerous benefits, Agile enables teams to adapt quickly, enhance efficiency, and deliver high-quality outcomes. Implementing Agile ensures better project execution, making it a valuable approach in today’s work environment.
Learn about Lean-Agile leadership to improve organisational systems. Register now for the Certified Scaled Agile Framework Leading SAFe® 6.0 Training And Exam - join now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Four Principles of Agile?

The four principles of Agile are derived from the Agile Manifesto, which states that agile teams value:
a) Interactions over processes and tools
b) Software documentation
c) Customer collaboration over contract negotiation
d) Responding to change by following a plan
What is Meant by Sprint in Agile?

A sprint is a time-boxed period of 1-4 weeks during which a scrum team works to complete a set amount of work. Sprints are the core of Scrum, a popular agile framework. They allow teams to deliver working software frequently, adapt to changing requirements, and collaborate effectively.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Agile Training, including Agile Project Management Foundation, Agile Project Management Practitioner and Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Agile Roles and Responsibilities.
Our Project Management Blogs cover a range of topics related to Agile, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Project Management skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 AgilePM® Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM® v2)
AgilePM® Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM® v2)
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Sat 17th May 2025, Sun 18th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Sat 19th Jul 2025, Sun 20th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Sat 20th Sep 2025, Sun 21st Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Sat 15th Nov 2025, Sun 16th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


