We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Agile and Waterfall are two very popular Project Management methodologies that organisations use. Both methods increase the project success rate, but the debate between Agile and always persisted. it is because the fundamental structure of Agile vs. Waterfall is different, as Agile is an iterative process while Waterfall is a sequential process.Thus, choosing the appropriate Project Management Methodology is critical for a project’s success. According to a recent PMI survey, 71 per cent of projects were successful with high-agile organisations using the Waterfall Method and 68 per cent using the Agile Method.
So, read this blog on Agile vs. Waterfall, here you will learn their key differences to help you clear all your doubts and choose the best one.
Table of Contents
1) What is an Agile Model?
2) What is a Waterfall Model?
3) Six fundamental differences between the Agile and Waterfall model
4) Agile principles
5) Pros and Cons of Waterfall
6) Pros and Cons of Waterfall
7) Agile vs Waterfall: What to choose?
8) Conclusion
What is an Agile Model?
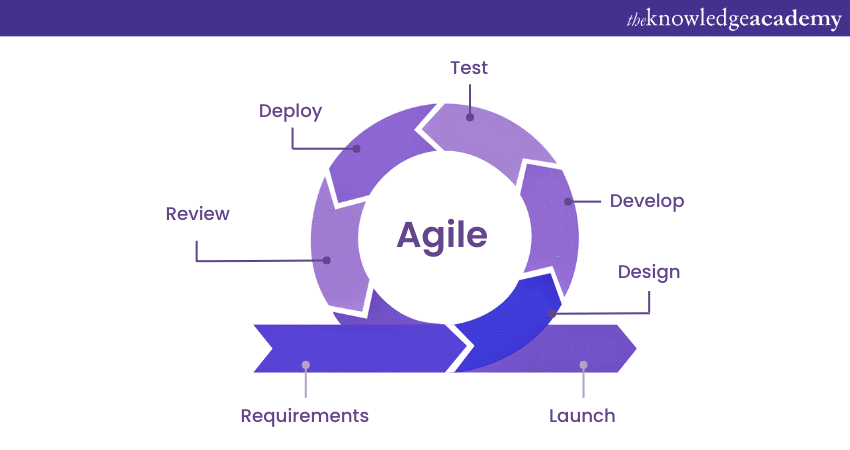
The Agile Method is a model for Software Development that allows for continuous interaction between development and testing throughout the entire process. One of the key features of this model is that it encourages significant interaction among developers, testers, customers, and Project Managers.
In the Agile Method, the project is divided into small incremental sprints. These sprints are typically one to three weeks long, and the method primarily focuses on collaboration, feedback, and rapid releases. However, it may not be ideal for smaller projects as it is based on dividing a large project into smaller ones, and the cost of development for smaller projects is higher compared to other models.
Learn the basics of Agile project management with our Agile Project Management Foundation (AgilePM®) training course.
What is a Waterfall Model?

The Waterfall Method is a model where the Software Development process is divided into phases such as requirements gathering, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. This method follows a simple linear execution process.
In the case of the Waterfall Model, clear requirements are crucial from the beginning, as it is a linear process. For example, testing can only occur after development, which may increase the chances of identifying errors in later phases of the project.
Six Fundamental differences between Agile and Waterfall model
There are fundamental differences between these two methods, and both have their pros and cons. These differences are not inherently good or bad but rather depend on factors such as project size, complexity, and requirements.
Structure
The fundamental structure of Agile vs. Waterfall is different. This is because Agile is an iterative process while Waterfall is a sequential process. Agile is broken down into smaller manageable pieces called “sprints”, which grow in increments, This reduces the risk of incomplete projects.
On the other hand, Waterfall is a sequential process where the entire project is divided into several stages or phases. It follows a linear path where one task is completed before moving on to the next.
Work prioritisation
The Agile Method is carried out with a single goal in mind: “Provide value to the customer”. The customer is the top priority in this method, and it strives to satisfy their needs through continuous delivery. Any shift in priorities is based on customer feedback. Essentially, the highest priority in this method is given to the customer.
On the other hand, in the Waterfall method, the priority is the scope of the project that is set before the project starts. Any change from the customer or shifts in priority cannot be easily accommodated, which increases the chances of project failure.
Planning
The Waterfall Model follows a traditional route for project management, relying on fixed project scope and deadlines to drive project completion. In contrast, the Agile model is flexible and adaptive, accommodating changing in project needs.
The Waterfall Method can be helpful in projects with a fixed scope and no room for changes. However, in many projects, changes can arise that may disrupt the initial project plan. Agile, on the other hand, accounts for this and takes a flexible approach.
Teams
Agile teams are highly adaptable, accommodating changes and responding to them during every iteration. Agile teams are typically self-organised, open to feedback, and take accountability and ownership of their work. However, while they are flexible, they may face challenges in dealing with uncertainty, which can potentially cause issues or delays in the project.
In contrast, Waterfall teams tend to be rigid in their approach, often focusing only on their specific tasks. Waterfall teams typically demonstrate less collaboration and have limited synchronisation with other team members.
Scope
Agile teams focus on frequent delivery of work and rely on timely feedback, making them more flexible when it comes to changes in project scope. On the other hand, in the Waterfall Method, the project scope is fixed before the project starts and cannot be changed mid-project. However, once the project scope is set and there are no provisions for changes, the Waterfall Method is used for planning, designing, and other tasks can be completed more easily and quickly.
Customer Involvement
One of the key features of the Agile Method is its significant interaction among the development team, testers, customers, and Project Managers. Customers, in particular, are given the highest priority in Agile, and it relies on their availability and continuous feedback.
On the other hand, the Waterfall Method sets the entire scope of the project based on the customer's requirements before the project starts, and that cannot be changed during the project. The customer's involvement is typically limited to the end of the project cycle, where feedback is taken for the next cycle of the project.
Discover the key differences between Agile Coach & Scrum Master roles! Unlock your team's potential. Learn more now!
Agile principles
The Agile methodology comprises various key principles which organisations can abide by for their business implementations. These principles are as follows:
a) The Agile project is segregated into many incremental steps. These steps include feedback intervals on a regular basis.
b) The project requirement is broken down into smaller parts. These parts are prioritised by their importance.
c) Agile principles also promote and foster a collaborative mindset with the customer.
d) Adjustments occur regularly during the project’s timeline to ensure the fulfillment of the customers’ needs.
e) Planning is integrated with execution, which enables the team to respond effectively to evolving requirements,
Elements to consider when moving to Agile
The shift to Agile can be a challenge for an organisation, when their teams are rooted in traditional Project Management approaches. However, their movement to adopting Agile practices may demand many process changes, especially in the case of DevOps approaches. The DevOps approach involves the collaborative efforts of the development and operations teams for the development and maintenance of software. Moreover, a team and project stakeholders should embrace two crucial concepts when shifting to Agile:
The Product Owner must focus on the value optimisation of the team’s output. The team is dependent on the product owner to prioritise the important tasks.
The development team must only work on the tasks that they are capable of completing. The Product Owner must remember not to push the team or get them to commit to arbitrary deadlines. More importantly, the development team accepts tasks from the business program’s backlog as they can accept fresh work.
Want to boost your team’s efficiency? Register for our Agile for Teams Course now to learn more!
Roadmaps
A team’s product roadmap contains the outline of how their solution develops with time. An Agile development roadmap offers organisations with crucial context that helps their teams reach both incremental and project-based goals.
Additionally, the roadmaps comprise of initiatives with large functions and contain the timelines that communicate the availability of a feature. Now as the work progresses and teams learn more, the roadmap changes to reflect the new information in subtle ways.
Furthermore, the team must ensure that they keep their focus on current conditions impacting the project and long-term goals for effectively working with the project’s stakeholders. These measures ensure that they respond to an adaptive and competitive landscape.
Moreover, the roadmap contains many initiatives that break down into a collection of requirements. These Agile requirements are lightweight descriptions of the necessary functionality as opposed to the 100-page documents that are associated with traditional projects.
More importantly, while all members of the team develop a mutual understanding through conversation and collaboration, the Agile requirements remain lean. The requirements are then explored in complete detail when the implementation is about to begin. These measures are followed by the maintenance of a backlog that helps set the team’s Agile priorities. This backlog comprises of new features, bugs, enhancements, technical or architectural tasks.
Pros and Cons of Agile
The following are some advantages and drawbacks of Agile:
Advantages of Agile
The various advantages of Agile are described as follows:
Advantages of Agile
The various advantages of Agile are described as follows
1) Agile is centered around “delivering value to the customer”, and the customer is involved throughout the process. Customer involvement increases the chances of project success.
2) Agile teams are self-aware and quickly adapt to customer feedback and changes, resulting in exceptional results.
3) Agile offers great flexibility and is suitable for projects where the project scope isn't fixed. When a customer requires an initial product with basic functions and wants to add new functions in iterations, the Agile Method is well-suited. Through continuous involvement of the customer and periodic feedback, such a project is more likely to succeed.
4) Agile enables close collaboration through daily stand-ups, frequent meetings, and a collaborative approach to problem-solving. This encourages communication, feedback, and shared understanding, among team members, stakeholders, and customers, resulting in a better final product.
5) The structure of agile allows for deliverables to be executed quickly, helping to bring the product to market faster.
6) Agile focuses on delivering improved products rather than the perfect ones. With continuous improvement and customer feedback, the product improves with every iteration. This allows the team to focus on production without stopping to fix major issues or change the process.
Drawbacks of Agile
The various drawbacks of Agile are described as follows:
1) While Agile is known for its flexibility, it can lead to uncertainty in project timelines and budgets. Because Agile is iterative and incremental, predicting the final cost and timeline of a project can be difficult.
2) Agile is heavily reliant on collaboration and communication among team members, stakeholders, and customers. It also requires the development team to be exceptionally well-synced in their approach and final goal. When there are gaps in communication and collaboration, the final product can be affected.
3) Agile allows for changes in requirements, which, if not managed properly, can lead to scope creep. Constant monitoring and supervision are necessary to avoid unnecessary changes to the project scope, which can affect deadlines and budgets.
4) Agile involves active participation from team members, including daily stand-ups, regular meetings, and continuous feedback loops. This can be time-consuming, especially in large projects or when team members are dispersed across multiple locations or time zones.
5) Agile is based on self-organising and cross-functional teams that function effectively with a certain level of expertise and experience. Building and sustaining such high-skilled teams can be difficult, and organisations must invest in training and development to ensure that team members have the necessary skills.
Pros and Cons of Waterfall
Here are the advantages and drawbacks of Waterfall model:
Advantages of Waterfall
The various advantages of Waterfall model are described as follows:
1) The Waterfall approach typically involves extensive upfront planning, documentation, and requirement definition. This results in a clear understanding of the project scope, deliverables, and expectations, which can aid in project management and stakeholder communication.
2) Waterfall follows a structured and linear approach, making it easier to predict project timelines, costs, and resources needed. This is beneficial for organisations that value predictability and must adhere to strict budgets and deadlines.
3) This method divides the development process into distinct phases, that assists teams in focusing on one phase at a time. This ensures each phase is completed before moving on to the next, providing structure and clarity.
4) Waterfall facilitates efficient resource management and allocation. It allows for upfront resource allocation, with teams being assigned to specific phases of the project.
5) Extensive documentation is required at each stage of Waterfall, which can be useful for auditing, compliance, and regulatory purposes. This is especially important in industries with stringent compliance standards, such as healthcare, finance, or construction.
6) The Waterfall Method is best suited for smaller projects with fixed deliverables and project scope, where there is no provision for changes. It enables projects to be completed at a lower cost and in less time.
Drawbacks of Waterfall
The various drawbacks of Waterfall are described as follows:
1) Waterfall follows a rigid sequential approach, which makes it difficult to accommodate changes in requirements or scope once a phase is completed. This, in turn, makes it challenging to respond to changing client needs or market situations during the development phase.
2) Waterfall often entails less client engagement during the development process, as most decisions are made before the project starts. As a result, there may be a disconnect between customer feedback and customer expectations.
3) Because testing and validation typically occur near the end of the Waterfall process, there is a higher chance of identifying defects or issues in the later stages. This can result in rework and delays, increasing costs.
4) Waterfall may not be well-suited for projects with evolving or ambiguous needs. It is because the changes in requirements can disrupt the entire sequential process, affecting the project timeline and budget.
5) It may result in longer development cycles because each phase must be completed before moving on to the next. This can lead to a longer time-to-market, which may be inconvenient for organisations that need to react quickly to market changes.

Agile vs Waterfall: What to choose?
The decision to use Agile or Waterfall Methodology is influenced by several factors, including the nature of the project, organisational structure, team dynamics, and stakeholder preferences. Here are some general guidelines to consider when deciding between them:
These are the various aspects that help to decide when to use Agile:
1) The project scope and requirements are not fully defined or may change over time.
2) The project requires continuous improvements and adjustments based on changing circumstances or customer needs.
3) The project requires close collaboration among team members, stakeholders, and customers.
4) There is a priority to reach the market faster.
These are the various aspects that help to decide when to use Waterfall:
1) The project has a very strict timeline and budget.
2) The requirements for the project are well-defined and will remain consistent.
3) The project is relatively smaller and needs to be completed quickly.
4) The project needs to follow strict compliance and regulatory rules.
5) The project requires a team that has a clear top-to-bottom hierarchy.
Conclusion
The choice between Agile vs Waterfall as the two methodologies is determined by the needs and characteristics of the project. Understanding the difference between Agile and Waterfall Methodologies, as well as their strengths and weaknesses, will enable Project Managers and teams to select the best methodology for their projects. Regardless of the approach taken, effective project management and clear communication are critical to project success.
Want to become a certified professional in Agile Project Management? Certified Professional In Agile Project Management (CPAPM) training course can help you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Project Management Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM®)
Agile Project Management Foundation & Practitioner (AgilePM®)
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 13th Jan 2025
Sat 18th Jan 2025, Sun 19th Jan 2025
Mon 20th Jan 2025
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 3rd Feb 2025
Mon 10th Feb 2025
Mon 17th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 3rd Mar 2025
Mon 10th Mar 2025
Mon 17th Mar 2025
Sat 22nd Mar 2025, Sun 23rd Mar 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 31st Mar 2025
Mon 7th Apr 2025
Mon 14th Apr 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Mon 28th Apr 2025
Tue 6th May 2025
Mon 12th May 2025
Sat 17th May 2025, Sun 18th May 2025
Mon 19th May 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 2nd Jun 2025
Mon 9th Jun 2025
Mon 16th Jun 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 30th Jun 2025
Mon 7th Jul 2025
Mon 14th Jul 2025
Sat 19th Jul 2025, Sun 20th Jul 2025
Mon 21st Jul 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 4th Aug 2025
Mon 11th Aug 2025
Mon 18th Aug 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 1st Sep 2025
Mon 8th Sep 2025
Mon 15th Sep 2025
Sat 20th Sep 2025, Sun 21st Sep 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 29th Sep 2025
Mon 6th Oct 2025
Mon 13th Oct 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 3rd Nov 2025
Mon 10th Nov 2025
Sat 15th Nov 2025, Sun 16th Nov 2025
Mon 17th Nov 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025
Mon 8th Dec 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


