We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, global regulatory bodies recognised the need to fortify the banking sector against unforeseen shocks. To address this, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision introduced Basel III, a comprehensive set of reforms aimed at enhancing the resilience of financial institutions. Among its core components are Basel III Buffers, which act as critical cushions to absorb losses during times of economic stress.
According to a report by The Financial Times around $10 trillion,00 more than a sixth of the global Gross Domestic Product in 2008 was lost during the financial crisis. The Basel III framework has become the bedrock since then to avoid such a calamity in the future. This blog delves into the significance of Basel III Buffers, their role in maintaining financial stability, and their impact on the banking landscape.
Table of Contents
1) What is Basel III?
2) Understanding the Basel III Buffers
3) Significance of Basel III Buffers
4) Impact on the banking Landscape
5) Conclusion
What is Basel III?
Basel III is a comprehensive framework of international banking regulations devised by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) to fortify the global financial system's stability. The primary objective of this framework is to curtail the potential damage inflicted on economies by banks that engage in excessive risk-taking. This regulatory framework emerged in response to the 2008 Global Financial Crisis, a period marked by severe economic downturns and the vulnerability of financial institutions.
The critical focus of this framework is to enhance the resilience of banks when faced with financial stress, fortifying their ability to weather economic shocks. Additionally, it places a premium on elevating transparency levels and disclosure practices within the banking sector. By addressing weaknesses identified in earlier accords like Basel I and Basel II, Implementing Basel III represents a crucial step in refining regulatory measures in the banking industry. This ongoing process underscores a commitment to fostering a more secure, transparent, and resilient global financial environment, mitigating the adverse impacts of future financial crises. It encapsulates a collective effort to learn from past challenges and fortify the foundations of international banking to ensure sustained stability.

Understanding Basel III Buffers
Basel III Buffers stands as a fundamental component of the comprehensive reforms introduced by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision after the 2008 financial crisis. Designed to fortify the resilience of the global banking system, these Buffers play a critical role in safeguarding financial institutions against unexpected shocks and economic downturns.
Capital conservation buffer: Building a safety net
At the core of Basel III Buffers is the Capital Conservation Buffer. Set at 2.5% of risk-weighted assets, this buffer acts as a vital safety net for banks. Its purpose is to ensure that banks maintain a minimum level of capital even during times of economic stress. If a bank's capital falls below the prescribed threshold, it triggers restrictions on distributing dividends and bonuses to shareholders and employees. By enforcing these limitations, the buffer compels banks to retain capital within the institution, enhancing their ability to absorb losses and maintain stability.
Countercyclical Capital Buffer: Navigating economic cycles
Complementing the Capital Conservation Buffer is the Countercyclical Capital Buffer. This buffer addresses the inherent cyclicality of credit and economic cycles. It requires banks to accumulate additional capital during periods of excessive credit growth and economic exuberance. By doing so, it helps mitigate the risk of lending bubbles and prevents the excessive expansion of credit that could lead to financial instability. The implementation of the Countercyclical Capital Buffer is determined by national regulatory authorities, allowing for flexibility in response to local economic conditions.
Systemically Important Banks (SIB) Buffer: Mitigating systemic risk
In recognition of the risks posed by systemically important banks, Basel III introduces the SIB Buffer. Globally significant banks are required to hold an extra layer of capital, proportional to their systemic importance. This buffer serves to prevent these institutions from becoming "too big to fail" and causing significant disruptions to the financial system in the event of their failure. By requiring SIBs to maintain higher capital reserves, the buffer mitigates the potential domino effect that their collapse could trigger.
Basel III Buffers represent a paradigm shift in the way regulators and financial institutions approach risk management. By mandating higher capital standards and Buffers, the framework establishes a more resilient financial ecosystem. These Buffers not only enhance the stability of individual banks but collectively fortify the entire banking sector against future economic uncertainties. As global financial institutions navigate a dynamic and interconnected landscape, the importance of Basel III Buffers in creating a resilient and robust banking system cannot be overstated.
Significance of Basel III Buffers
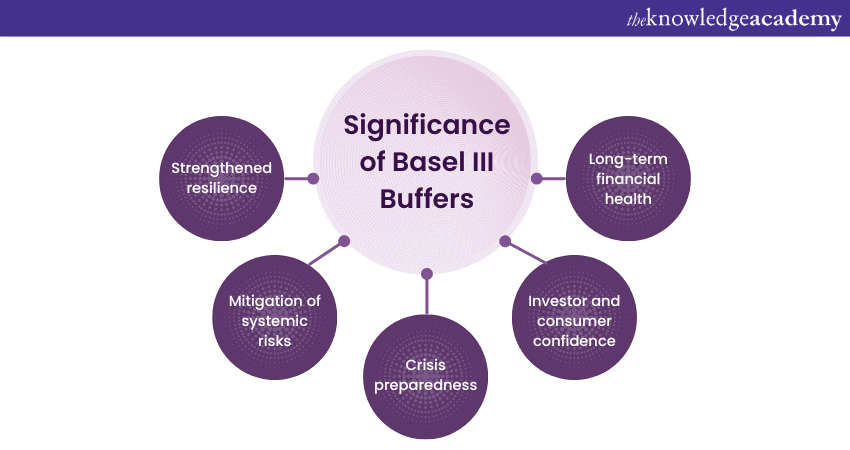
The introduction of Basel III Buffers marks a pivotal moment in the evolution of global banking regulations, fostering financial stability and resilience. These Buffers hold immense significance in safeguarding the financial system against shocks and mitigating systemic risks.
a) Strengthened resilience: These Buffers elevate the resilience of financial institutions, enabling them to endure economic downturns and market turbulence with greater fortitude. By mandating banks to maintain surplus capital beyond the minimum requirements, the Buffers create a robust cushion that can absorb losses, reducing the likelihood of insolvency.
b) Mitigation of systemic risks: The Buffers are instrumental in reducing the systemic risks that emanate from the interconnectedness of financial institutions. Adequate capital reserves discourage excessive risk-taking, ensuring that banks are equipped to manage unexpected losses without triggering a domino effect of failures that could cripple the broader financial ecosystem.
c) Crisis preparedness: Basel III Buffers facilitate crisis preparedness by requiring banks to accumulate capital during favorable economic conditions. These buffers ensure that financial institutions are well-equipped to withstand the challenges of economic contraction. When comparing Basel II vs Basel III, Basel II had less stringent capital requirements, whereas Basel III introduced these buffers as a proactive measure to reduce the need for reactive interventions and taxpayer-funded bailouts during crises.
d) Investor and consumer confidence: The Buffers enhance investor and consumer confidence by underpinning the stability of financial institutions. Stakeholderscan trust that banks are sufficiently equipped to navigate adverse scenarios, leading to greater stability in financial markets and reduced volatility.
e) Long-term financial health: The Buffers encourage banks to adopt a more sustainable approach to financial health. The requirement to conserve capital during periods of growth discourages short-term profit maximisation at the expense of long-term stability, promoting a more balanced and prudent banking culture.
Unlock the intricacies of Basel III with our Introduction To Basel III course.
Impact on the banking landscape
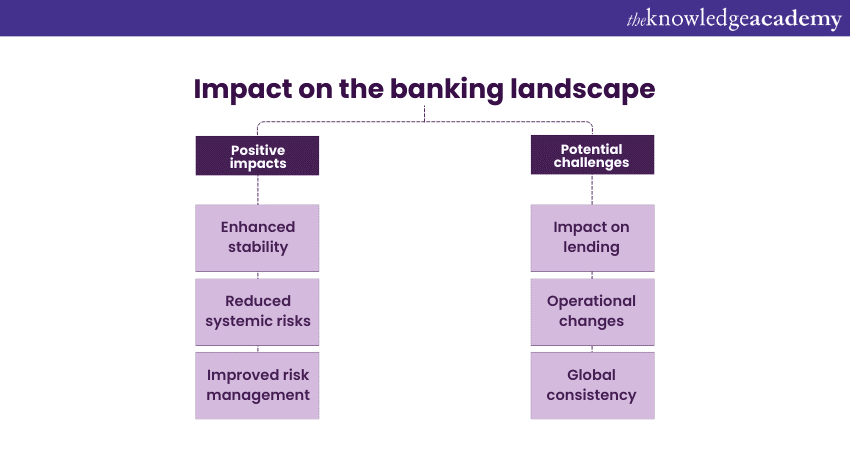
Basel III Buffers have brought about significant changes in the banking landscape, with both positive and potential challenges:
Positive impacts
a) Enhanced stability: Basel III Buffers being a key component of Basel III Capital Requirements have bolstered the stability of the banking sector by requiring banks to maintain ample capital reserves, reducing the likelihood of insolvency during financial crises.
b) Reduced systemic risks: The implementation of capital Buffers for systemically important banks has reduced the risks associated with their failure, enhancing the overall resilience of the financial system.
c) Improved risk management: Banks are incentivised to adopt robust risk management practices to avoid breaching capital buffer requirements, leading to a more prudent and vigilant banking environment.
Potential challenges
a) Impact on lending: Stricter capital buffer requirements may lead to reduced lending, particularly during economic upswings, potentially affecting economic growth.
b) Operational changes: Banks may need to make operational adjustments to maintain the required capital Buffers, including potential changes to dividend policies and risk management strategies.
c) Global consistency: Ensuring their consistent implementation of Basel III Buffers across different jurisdictions remains a challenge, as regulatory approaches may vary.
Stay ahead in finance - Register now in our Introduction to Basel IV Training.
Conclusion
Basel III Buffers represent a fundamental shift towards a more robust and stable banking sector. By mandating banks to maintain additional capital layers, these Buffers act as shock absorbers, reducing the vulnerability of financial institutions and the broader economy to economic downturns. While challenges and adjustments are inevitable, the integration of Basel IV alongside these enhanced measures further strengthens stability and reduces systemic risks, underscoring their vital role in shaping the future of banking and global financial resilience.
Navigate the world of compliance with confidence – Register now in our Compliance Training
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I ensure my organisation is in compliance with Basel III Buffers?

Ensuring compliance with Basel III Buffers involves a meticulous assessment of capital adequacy. Monitor and maintain regulatory capital ratios, specifically the Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) ratio, ensuring it exceeds the required minimum. Regularly review risk-weighted assets and leverage ratios. Implement robust risk management practices, stress testing, and contingency plans to navigate financial stress scenarios. Stay informed about regulatory updates, seek professional advice, and engage in transparent reporting to guarantee adherence to Basel III requirements, fortifying your organisation's financial stability and regulatory compliance.
How do Basel III Buffers contribute to the overall stability and resilience of the banking system?

Basel III Buffers play a pivotal role in bolstering the stability and resilience of the banking system. Comprising the Capital Conservation Buffer, Countercyclical Capital Buffer, and the Systemic Risk Buffer, they act as financial cushions. These buffers ensure that banks maintain adequate capital levels during economic downturns, periods of excessive credit growth, and in the face of systemic risks. By fortifying banks' capital positions, Basel III Buffers enhance their capacity to absorb shocks, promoting overall stability and mitigating the impact of financial stress on the banking sector.
How can my organisation stay updated on Basel III changes?

To stay updated on Basel III changes, your organisation can regularly monitor official communications from financial regulatory bodies, follow updates from the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), and engage with industry publications and financial news sources. Participating in relevant conferences, webinars, and seminars can provide valuable insights. Additionally, maintaining open communication channels with regulatory authorities and industry associations ensures timely awareness of developments. Leveraging specialised consultants or legal advisors with expertise in banking regulations can offer tailored guidance on implementing and adapting to Basel III changes.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Compliance Trainings, including Corporate Governance Course and Security Governance and Compliance Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into various Compliance Frameworks.
Our Compliance blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO and Compliance, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming ISO & Compliance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 PCI DSS Implementer
PCI DSS Implementer
Thu 5th Jun 2025
Thu 7th Aug 2025
Thu 2nd Oct 2025
Thu 4th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


