We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In modern technology, the volume, variety, and velocity of data have escalated to unprecedented levels. According to Statista, the global data sphere is projected to grow to more than 180 Zettabytes (ZB) by 2025. This highlights the exponential growth of data Due to this growth, managing and processing vast amounts of information efficiently has become a necessity. This is where the Big Data Database comes in.
Big Data Databases are crucial in managing data and providing the infrastructure to store, manage, and analyse large volumes of data. Today, the market is teeming with various solutions, each offering unique features and capabilities. This comprehensive blog explores the top eight Big Data Databases that have captured the spotlight this year, along with features. Read ahead to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What is a Big Data Database?
2) Best Big Data Databases to Use
a) Apache Cassandra
b) Amazon DynamoDB
c) Apache Spark
d) Amazon Redshift
e) Apache HBase
f) Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
g) MongoDB
h) Apache Hadoop
3) How to Choose the Right Big Data Database?
4) Conclusion
What is a Big Data Database?
A Big Data Database is a powerful tool designed to store, manage, and analyse massive amounts of data. Unlike traditional databases, which might struggle to handle the scale and complexity of Big Data, these specialised databases offer features and optimisations that make them well-suited for the task. They allow organisations to make sense of their data, uncover insights, and make informed decisions. The following image shows how Big Data Database manages large amounts of data:
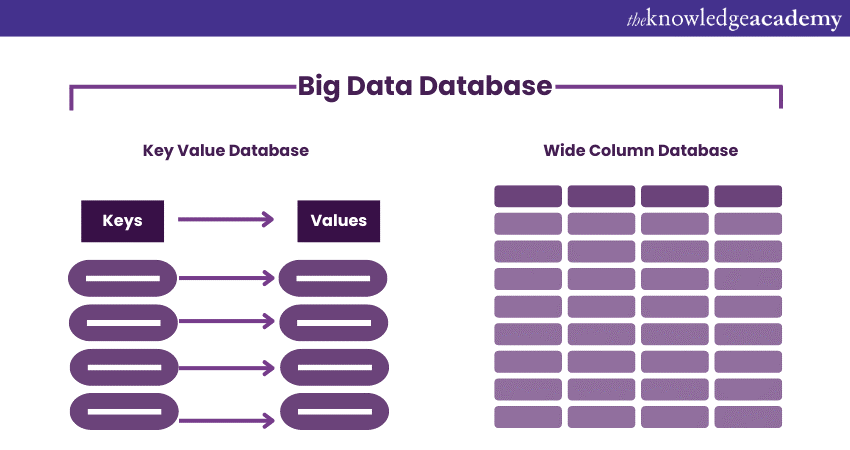
Big Data Databases differ from traditional databases based on the following key aspects:
a) Scalability: Big Data Databases are built to scale horizontally, allowing them to expand seamlessly as data volume grows without sacrificing performance.
b) Data Variety: They accommodate various data types, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, making them suitable for handling diverse sources like text, images, videos, and sensor data.
c) Data Velocity: These types of databases process data in real-time or near-real-time, supporting applications that require quick responses and analytics on streaming data. In the context of the Role of Big Data in the Hospitality Industry, such systems enable hotels to instantly track guest preferences and booking patterns, thus enhancing customer satisfaction.
d) Complex Queries: These databases are optimised for complex queries and advanced analytics, often utilising distributed computing frameworks for parallel processing.

Best Big Data Databases to Use
Now that we have a clear understanding of what Big Data Databases entail let's delve into the best options available today:
1) Apache Cassandra
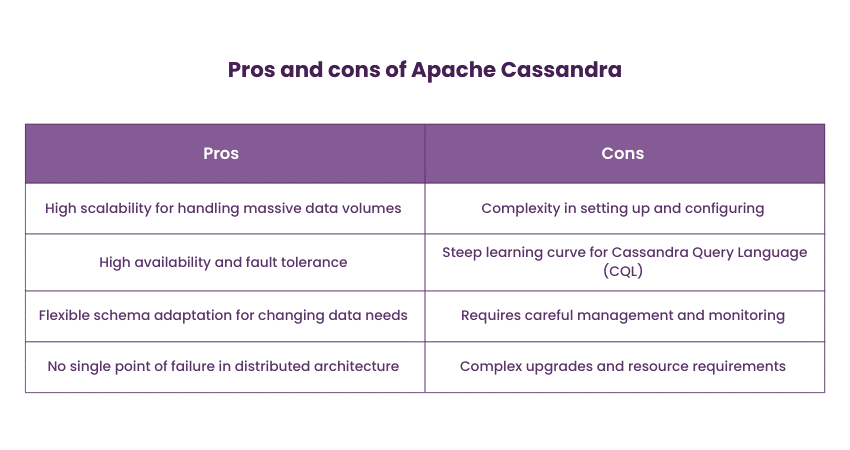
Apache Cassandra is a distributed NoSQL Database created to handle large volumes of data across multiple servers while ensuring high availability and fault tolerance. It utilises a peer-to-peer architecture that allows each node to act as a coordinator, ensuring data distribution and query routing. Cassandra's architecture supports linear scalability through horizontal expansion.
Cassandra is commonly used for applications that require high-speed data ingestion and real-time analytics, such as sensor data monitoring, time-series data analysis, and content management systems. When integrated with Apache Spark Architecture, Cassandra enhances its ability to handle complex analytics and large-scale data processing. Apache Cassandra is used by companies like Apple, Netflix, and Instagram to manage large-scale data. The following are the pros and cons of Apache Cassandra:
2) Amazon DynamoDB
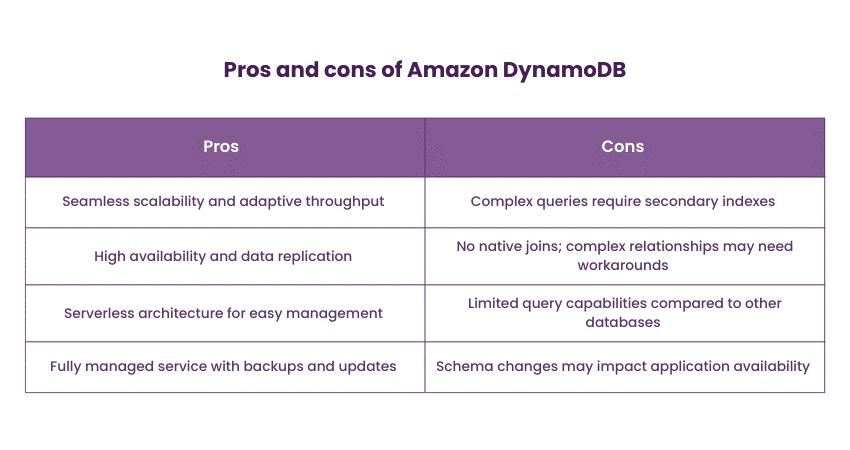
Amazon DynamoDB is a fully managed NoSQL Database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It offers seamless scalability, automatic replication, and low-latency performance. DynamoDB accommodates both key-value and document data models while offering inherent security features. Amazon DynamoDB is well-suited for applications with variable and unpredictable workloads, such as e-commerce platforms, gaming leaderboards, and real-time data analytics, making it a strong contender in the DynamoDB vs. MongoDB comparison. The following are the pros and cons of Amazon DynamoDB:
3) Apache Spark
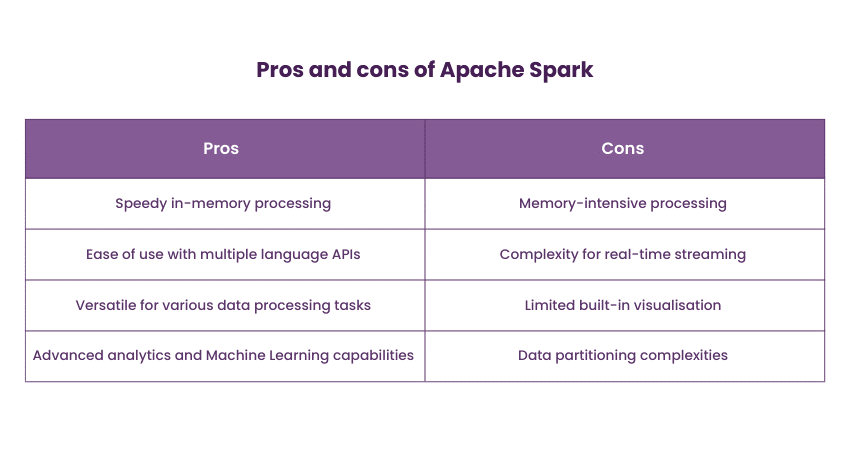
Apache Spark has emerged as a game-changer in the world of Big Data processing. Unlike traditional databases, Spark is not solely a Big Data Database but a powerful in-memory data processing framework. It supports batch processing, interactive queries, and real-time streaming, making it versatile for various data processing needs.
Spark finds applications in a variety of use cases, including real-time data processing, Machine Learning, graph analysis, and Extract, Transform and Load (ETL) tasks. Its ability to process data in memory significantly accelerates processing speeds, enabling organisations to derive insights quickly.
Supercharge your Big Data journey with our specialised Apache Spark Training – Register now to gain hands-on experience!
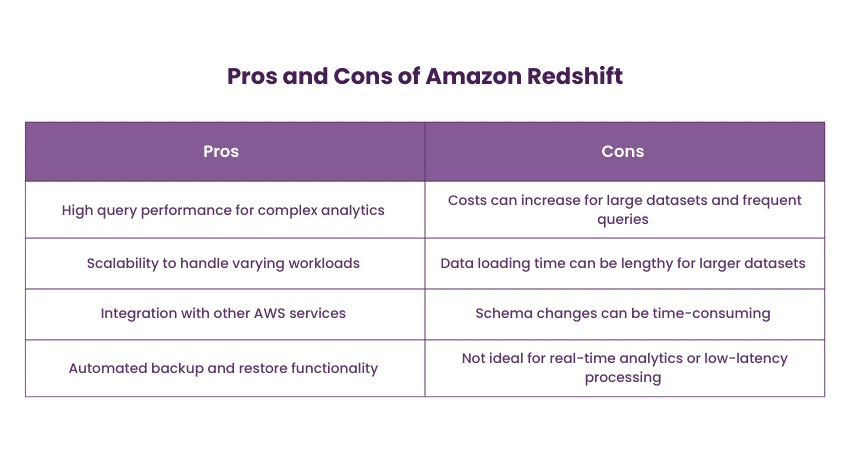
4) Amazon Redshift
Amazon Redshift is a cloud-based data warehousing Database that Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers. It utilises columnar storage and parallel processing to provide fast query performance for large datasets. Redshift integrates seamlessly with other AWS services, allowing organisations to build comprehensive data pipelines.
Amazon Redshift is ideal for organisations that require complex data analysis and reporting. It's particularly suitable for Business Intelligence and Data Warehousing scenarios, providing the necessary infrastructure to derive insights from massive datasets while taking advantage of cloud scalability.
Master relational databases with our expert-led Relational Databases & Data Modelling Training – join now for enhanced database expertise!
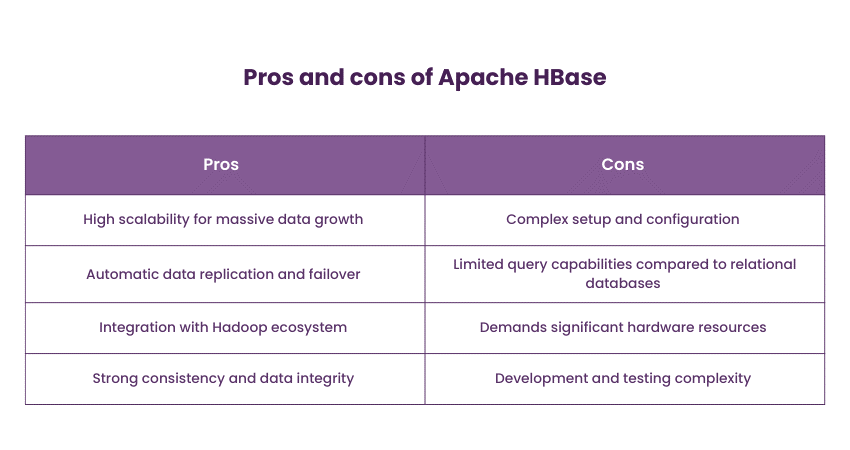
5) Apache HBase
Built on top of the Hadoop ecosystem, Apache HBase is a distributed, column-oriented NoSQL Database. It's designed for large-scale, sparse data sets and is particularly well-suited for real-time read and write operations. HBase's scalability and fault tolerance make it a solid option for applications requiring high-throughput data access.
HBase is commonly used for applications that require random read-and-write access to large volumes of data, such as time-series databases, social media platforms, and sensor data storage.
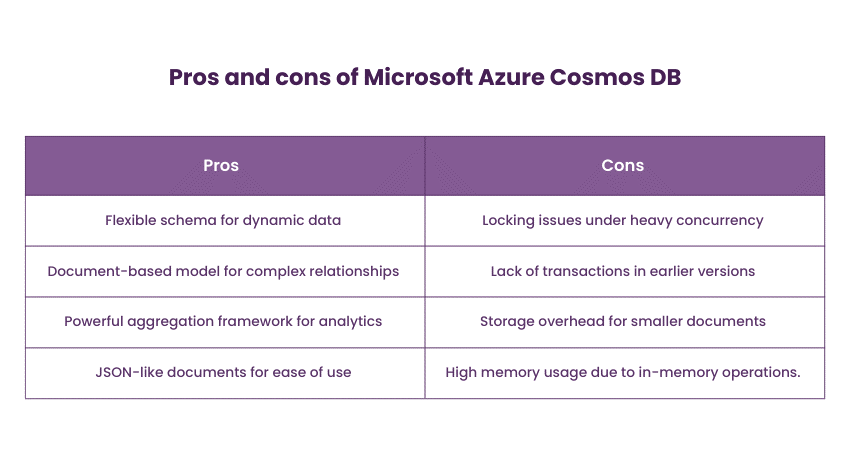
6) Microsoft Azure Cosmos DB
Azure Cosmos DB is a popular globally distributed, multi-model database service by Microsoft Azure. It supports multiple Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), including document, key-value, graph, and column family. As a result, it enables developers to build applications with various data models. Cosmos DB's global distribution and automatic scalability ensure high availability and low-latency data access.
Azure Cosmos DB is suitable for applications requiring global scalability, high availability, and support for multiple data models. Cosmos DB is utilised in applications that require low-latency access to data across different geographic regions, including gaming, Internet of Things (IoT), and personalised content delivery.
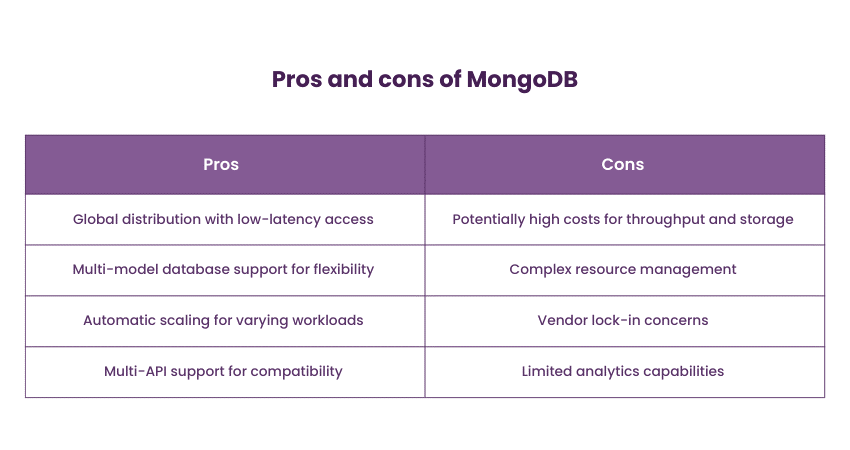
7) MongoDB
MongoDB is a popular document-oriented NoSQL Database known for its flexibility in handling unstructured and semi-structured data. It stores data in JSON-like BSON format, enabling developers to store complex structures and arrays in a single document. MongoDB's architecture supports horizontal scalability through data sharding. It is used by companies like Adobe, eBay, and Bosch for applications ranging from content management to IoT data storage.
MongoDB is well-suited for applications with evolving schemas and requirements, making it a favourite among developers who need to iterate quickly. Content management systems, real-time analytics, and applications dealing with user-generated content benefit from MongoDB's ability to adapt to changing data structures.
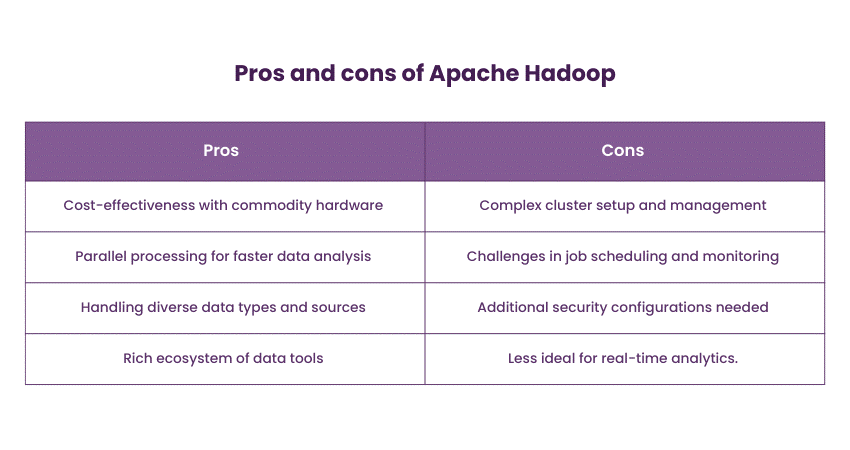
8) Apache Hadoop
Apache Hadoop has maintained its status as a foundational technology in the Big Data ecosystem. It consists of two major components: Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) and MapReduce. HDFS is designed to store vast datasets across commodity hardware and provide fault tolerance through data replication. MapReduce enables parallel processing of data, making it suitable for distributed computing tasks.
Hadoop is commonly employed in scenarios where massive data storage and batch processing are essential. When comparing Hadoop vs MongoDB, it’s clear that while Hadoop excels in offline data analysis, data preparation, and large-scale data warehousing, MongoDB offers a more flexible, real-time approach for handling unstructured data. Hadoop's open-source nature and vast ecosystem of tools contribute to its enduring popularity. Exploring Hadoop Interview Questions can provide deeper insights into its architecture, use cases, and best practices.
Become a certified Big Data and Hadoop Solutions Architect with our specialised Big Data And Hadoop Solutions Architect Course - sign up today!
How to Choose the Right Big Data Database?
Choosing the right Big Data Database is a critical decision that can significantly impact your organisation's ability to handle, analyse, and extract value from large volumes of data. When evaluating them for your organisation's needs, consider the following factors to choose the right Database :
1) Data Volume and Variety: Assess the scale and types of data your application or use case involves. Different Databases excel at handling structured, semi-structured, or unstructured data. Choose a database that can accommodate your data volume and variety without compromising performance.
2) Scalability: Consider the scalability requirements of your application. Ask whether your data and workload grow over time. Opt for Databases that offer horizontal scalability through features like sharding, allowing you to distribute data across multiple nodes.
3) Performance: Evaluate the Database's performance in terms of read and write operations, query processing speed, and latency. For real-time analytics, databases with low-latency capabilities are essential.
4) Data Model: Determine whether a document-based, key-value, columnar, or graph Database model best suits your data and use case. Each model has strengths and weaknesses depending on data relationships and access patterns.
5) Query Language and APIs: Consider the ease of querying and interacting with the database. Some Databases offer SQL-like languages, while others use specialised query languages or APIs. Choose a database with a query language that aligns with your team's skills.
6) Consistency and Availability: Depending on your application's requirements, decide between Databases offering strong consistency for data integrity or eventual consistency for improved availability and fault tolerance.
7) Integration: If you're utilising cloud infrastructure, explore databases that seamlessly integrate with your chosen cloud provider. This integration can streamline deployment and management processes.
8) Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the Database's pricing model, considering factors such as licensing costs, hardware requirements, and operational expenses. Cloud-based databases may offer cost savings and flexibility.
Conclusion
The best Big Data Databases mentioned above play a crucial role in modern data-driven applications, providing scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Each database brings its own strengths and features to the table, allowing organisations to choose the one that aligns best with their requirements.
Unlock the power of Big Data with our comprehensive Big Data and Analytics Training – register now and upgrade your skills!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Database is Best for Big Data?

The best Database for Big Data depends on specific needs. Popular choices include Apache Cassandra for scalability, MongoDB for flexibility, and Amazon Redshift for data warehousing and complex queries.
What is an Example of a Large Database?

An example of a large database is Amazon's DynamoDB. This NoSQL database service is completely managed and supports high-traffic applications like Amazon.com. It provides seamless scalability, low latency, and robust performance for massive data workloads.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Training, including Hadoop Big Data Certification, Big Data Architecture Training, Big Data Analysis and Big Data And Hadoop Solutions Architect. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analyst Job Description.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data Databases, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data and Analytics skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Data Science Analytics
Data Science Analytics
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


