We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Big Data Management involves handling and analysing large data volumes generated by modern systems. It encompasses data collection, storage, analysis, and security to extract valuable insights. Effective management ensures accuracy and accessibility, enabling informed decision-making. As data grows, organisations must employ advanced tools and strategies for integration, transformation, and analysis. This enhances operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive edge in data-driven markets.
Table of Contents
1) A Brief Understanding of Big Data Management
2) What is the Importance of Big Data Management?
3) Benefits of Big Data Management
4) What are some Big Data Management Concepts, Techniques and Challenges ?
5) Top Five Big Data Management Tools
6) Big Data Management Best Practices
7) Conceptual Framework of Big Data Management
8) Future Perspectives of Big Data Management
9) Conclusion
A Brief Understanding of Big Data Management
So, what is Big Data Management? It is the practice of organising, governing, and ensuring the quality and security of large volumes of data. It is a process that involves the extraction, storage, management, and analysis of data to provide meaningful insights. This aids in decision making in organisations. To get a better understanding of this, let us look at some of its characteristics:
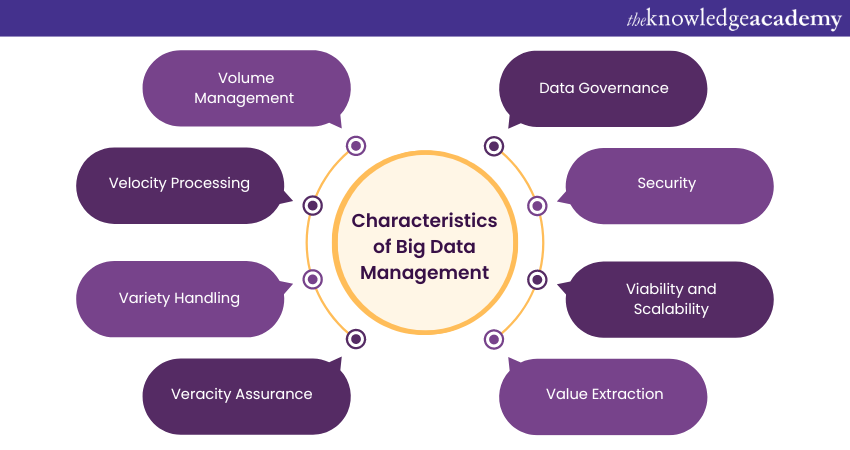
1) Volume Management: Big Data Management systems are designed to handle data at an enormous scale, encompassing petabytes and exabytes of data from various sources.
2) Velocity Processing: Given the fast pace at which data is generated and captured, these systems must process information swiftly to provide timely insights.
3) Variety Handling: These systems can manage data of varying types and formats. These range from structured datasets like databases, semi-structured like XML files, to unstructured data like emails, social media content, and more.
4) Veracity Assurance: The accuracy and truthfulness of data are paramount in Big Data Management. The system needs to guarantee the quality and reliability of the data being processed.
5) Value Extraction: The primary goal of this is to extract value from the massive volumes of data. This involves the application of analytical techniques and algorithms to discover patterns, correlations, and insights that can guide decision making.
6) Viability and Scalability: Big Data Management systems must be scalable and flexible to accommodate growing data volumes and complexities over time.
7) Security: With vast amounts of data, ensuring security and privacy becomes crucial. Hence, effective management systems implement robust security protocols and policies.
8) Data Governance: This involves the entire management of the usability, availability, integrity, and security of the data employed in an enterprise. This ensures the data is reliable, and actions taken on the data can be audited.
What is the Importance of Big Data Management?
The importance of Big Data Management is crucial for all organisations. As the variety, volume, and velocity of data continue to increase, effective management of Big Data becomes a crucial element for businesses, governments, and organisations of all sizes. Let's see their importance:
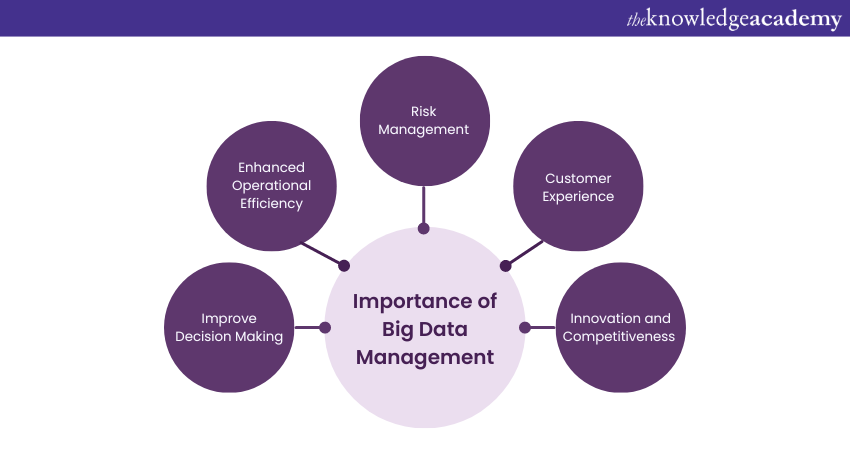
1) Improved Decision Making: Big Data Management allows organisations to analyse huge amounts of data. This leads to timely and well-informed decisions. This leads to timely and well informed decisions. It enables data-driven decision-making. This is where strategies and actions are based on concrete insights rather than intuition or guesswork.
2) Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By analysing Big Data, organisations can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and waste in their operations. This information can be used to streamline processes, enhance productivity, and reduce costs.
3) Risk Management: Big Data Management aids in identifying and mitigating risks. By analysing patterns and trends in the data, organisations can know the potential issues beforehand and develop strategies to manage them effectively.
4) Customer Experience: With Big Data, companies can understand their customers better. They get to know their preferences, behaviours, and needs. This knowledge aids in personalising offerings, improving customer satisfaction, and building customer loyalty.
5) Innovation and Competitiveness: Big Data can inspire new products, services, and business models, driving innovation. Additionally, it can offer a competitive edge by enabling businesses to understand market trends, customer behaviour, and competitor strategies.
Kickstart your journey to become a Data Expert with our Big Data Analysis Course today!
Benefits of Big Data Management
a) Big Data Management offers many benefits, enabling companies to utilise data for better decision-making, productivity, and staying ahead of the competition.
b) Cost Savings: Effective management cuts expenses by improving productivity, optimising distribution of resources, and reducing time of inactivity.
c) Improved Accuracy: An effective structure ensures that data is correctly formatted, purified, and free of errors, leading to accurate analytical results.
d) Personalised Marketing: utilising top-notch data insights to create customised marketing strategies and boost customer service, leading to increased consumer interaction.
e) Competitive Advantages: High-quality data and effectual management offer advanced analytics, granting organisations a competitive advantage over competitors lacking in data expertise.
What are Some Big Data Management Concepts, Techniques, and Challenges?
Let's delve into some of the key concepts, techniques, and challenges associated with Big Data Management:
1) Concepts:
a) Volume, Velocity, Variety, Veracity, and Value: These are the five Vs of big data. They represent a large amount of data (Volume), the speed of data processing (Velocity), different types of data (Variety), the trustworthiness of the data (Veracity), and the actionable insights extracted from the data (Value).
b) Data Lifecycle Management: This refers to the process of managing the flow of data throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation and initial storage to the time it becomes obsolete and is deleted.
c) Data Governance: This concept deals with the overall management of data availability, relevancy, usability, integrity, and security in an organisation.
2) Techniques:
a) Data Integration: This includes combining data from different sources and providing users with a singular view of these data.
b) Data Quality Management: This technique focuses on maintaining and ensuring the quality and reliability of the data.
c) Data Mining: It's a process used to explore large amounts of data to find consistent patterns and systematic relationships between variables.
d) Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Advanced analytical techniques like Machine Learning and AI are often used to analyse big data. Especially when it comes to predictive modelling and identifying trends and patterns.
3) Challenges:
a) Data Security: As the volume of data increases, so do the potential threats and vulnerabilities. Ensuring data security is a major challenge in Big Data Management.
b) Data Quality and Accuracy: Ensuring the quality, accuracy, and consistency of data can be challenging, especially with large volumes of data coming from various sources.
c) Storage and Processing: Storing and processing large volumes of data in Big Data in Retail requires robust and often costly hardware and software resources.
d) Lack of Skilled Personnel: There is a significant shortage of skilled professionals who understand Big Data. This can extract meaningful insights from it.
e) Integration of Data From Diverse Sources: Data is often collected from various sources in different formats. This makes it a challenge to integrate and analyse it effectively.
Boost your career with our expert-led Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course – Join now!
Top Five Big Data Management Tools
Various instruments are useful in handling large amounts of data, enhancing time organisation, and reducing costs effectively. Here are some notable ones:
a) IBM Infosphere Information Server: It is IBM's software used for combining, purifying, overseeing, and converting data.
b) SAS Data Management: SAS Data Management enables users to modify data, make changes to processes, and evaluate outcomes, which includes managing metadata and visualising lineage.
c) PowerCenter Informatica: It is a tool used to extract data from various sources and construct data warehouses.
d) Pentaho Business Analytics: An integrated BI platform for analysing data to facilitate data-informed decision-making.
e) Tableau: It creates visual representations in graph format by accessing databases, OLAP cubes, cloud databases, and spreadsheets.
Big Data Management Best Practices
As the use of big data increases, following best practices helps to maintain consistency and trust in the results of analytics.
1) Self-Service Data Management
Users have the ability to independently navigate data using the right tools, enabling self-service in managing big data.
2) Avoid Predefined Data Models
Predefined models are not effective when dealing with varied data sets. Utilise established protocols and teamwork settings to organise data.
3) Manage User-Driven Data Transformations
Users make essential changes to unprocessed data. Develop strategies to handle these changes and prevent disagreements.
4) Understand Architecture for Better Performance
Understanding the structure of Big Data and database execution methods is essential for developing efficient data applications.
5) Handle Data Explosion
Controlling the large quantity of data produced necessitates technology for processing streams, filtering, and capturing and storing valuable data.
Conceptual Framework of Big Data Management
You should know that a conceptual framework of Big Data Management provides a holistic view of the components, processes, and techniques. These are necessary to effectively handle, process, and extract value from large and complex data sets, especially when understanding the distinctions between Big Data and Data Mining. Here is an expansion of this framework:
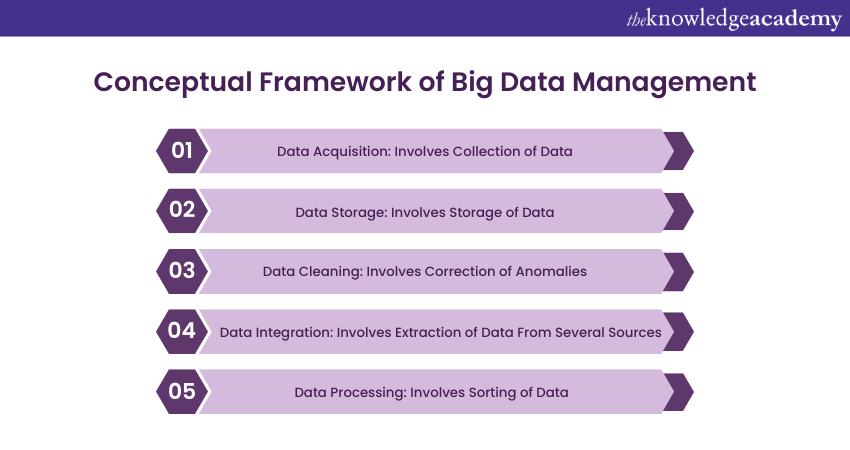
1) Data Acquisition: This is the first step in the Big Data Management process. This involves the collection of data from various sources. The data can be from diverse channels. It also involves social media, weblogs, sensors, transaction records, and more.
2) Data Storage: Once the data is acquired, it needs to be stored effectively. Given the volume and variety of Big Data, distributed storage systems like Hadoop's HDFS, Google's Cloud Storage, and Amazon's S3 are typically employed. They can handle large quantities of structured and unstructured data. This provides scalability and fault tolerance.
3) Data Cleaning: Data, especially when sourced from various channels, can have errors, inconsistencies, or missing values. Data cleaning or data cleansing involves identifying and correcting these anomalies to maintain the quality of the data.
4) Data Integration: This involves consolidating data from various sources and formats into a unified view. Extract, Transform, Load, or (ETL) processes are commonly used in this stage to extract data from different sources. This transforms it into a suitable format and loads it into a data warehouse.
5) Data Processing: With the cleaned and integrated data, processing or computation occurs. This can involve sorting, aggregation, statistical analysis, machine learning algorithms, and more.
Explore the world of Big Data Infrastructure with our Big Data Architecture Training – Sign up now!
Future Perspectives of Big Data Management
As we continue to generate unprecedented amounts of data, the future of Big Data Management is poised to evolve further, especially with the increasing emphasis on Big Data Security. This includes incorporating cutting-edge technologies and approaches to safeguard data while managing it effectively. Here are some future perspectives to consider:
1) Increased Adoption of Machine Learning (ML) and AI: As organisations grapple with larger and more complex datasets, the adoption of Machine Learning and AI will continue to increase. These technologies will enable more sophisticated data analysis and predictive modelling. This involves enabling organisations to extract deeper insights and make more accurate forecasts.
2) Integration of IoT with Big Data: With the proliferation of IoT devices, an enormous amount of real time data is being produced. This data can provide valuable insights when analysed and managed effectively. This involves leading to enhanced operational efficiency and customer experience.
3) Enhanced data security measures: As the volume and variety of data increase, so does the need for robust security measures. We can expect advancements in encryption, authentication, and other security protocols to protect sensitive information.
4) Quantum Computing: As Quantum Computing technology matures, it has the potential to revolutionise Big Data processing by performing complex calculations at unprecedented speeds.
5) More Focus on Data Governance: As regulations around data privacy continue to tighten, businesses will need to place greater emphasis on data governance to ensure compliance.
Conclusion
Efficient management of Big Data is essential to unlock the complete value of data, especially when comparing it to traditional data warehouses. By following top strategies and utilizing the appropriate tools, businesses can improve data precision, simplify processes, and acquire valuable perspectives. Successful management ensures that data stays dependable, easily reachable, and beneficial for decision-making. As data continues to grow, embracing new technologies and strategies will be crucial to staying competitive and maintaining efficiency, particularly when weighing Big Data vs Data Warehouse approaches. Fruitful management of large amounts of data turns complicated information into useful insights, leading to success and expansion.
Master Data Analysis with our Data Analysis Training Using MS Excel – Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Five Key Points for Managing Big Data?

The five main points involve utilising efficient tools, ensuring data precision, overseeing user-initiated changes, comprehending architecture, and addressing data growth through stream processing technology for enhanced storage and analysis.
What is Big Data Management Course?

A course on managing Big Data covers methods and software for managing large data sets, with an emphasis on integrating, processing, storing, and analysing data. Its goal is to provide professionals with the abilities to handle and extract valuable information from large sets of data.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Big Data and Analytics Training, including the Big Data Analysis Course, Data Science Analytics, and Advanced Data Analytics Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data vs Small Data.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Big Data, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data, Analytics & AI skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Hadoop Big Data Certification
Hadoop Big Data Certification
Thu 22nd May 2025
Thu 17th Jul 2025
Thu 18th Sep 2025
Thu 20th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


