We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Picture this: Your business runs like a well-oiled machine, with every process flowing smoothly, no bottlenecks, no mistakes. Sounds like a dream, right? But what if we told you this could be a reality with Business Process Management (BPM)? This game-changing strategy helps businesses optimise their operations. Moreover, the Business Process Management market size is expected to grow at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 11.83% from 2025 to 2030.
But here’s the real question: How do you get started, and how can you keep improving over time? In this comprehensive blog, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about Business Process Management. So, let’s get started!
Table of Contents
1) What is BPM?
2) Importance of Business Process Management
3) Types of Business Process Management
4) Stages of BPM Lifecycle 5) What are the Benefits of Business Process Management?
6) What are the Challenges of Business Process Management?
7) BPM Best Practices
8) Business Process Management Use Cases
9) Conclusion
What is BPM?
BPM is a Strategic Business Management methodology aimed at optimising and improving an organisation's workflows. This approach leads to higher efficiency, greater flexibility, and improved quality outcomes, driving overall business success. Business Process Management is critical in enhancing operational performance and driving overall business success by focusing on the following:
1) Systematic analysis
2) Design
3) Execution
4) Monitoring
5) Refinement of business processes
At its core, Business Process Management means the meticulous examination and enhancement of how work is done within an organisation. This encompasses various activities, from identifying key processes to documenting their steps, analysing their performance, and making informed decisions to refine them.
BPM is a guiding framework that enables Businesses to identify inefficiencies, eliminate bottlenecks, and standardise processes for consistent and improved results. It aims to ensure that workflows are aligned with the organisation's goals and responsive to changes in the market, technology, and customer needs.
Importance of Business Process Management
Business Process Management plays a monumental role in modern organisations by delivering a multitude of benefits that contribute to their growth and success. The significance of BPM extends across various aspects of Business operations, fostering efficiency, agility, and overall excellence. Let's explore some of them below:
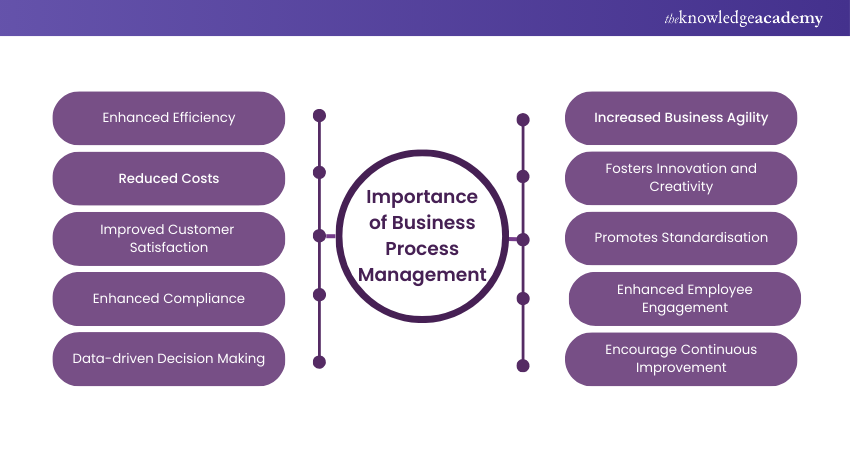
1) Enhanced Efficiency and Productivity: Business Process Management identifies bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies in processes, leading to streamlined workflows and improved resource allocation. This, in turn, accelerates task completion and enhances overall productivity.
2) Reduced Costs: Efficient Business Process Management minimise wastage of time, effort, and resources, resulting in lower operational costs. Organisations can allocate resources more effectively by optimising processes and maximising their value.
3) Improved Customer Satisfaction: Business Process Management ensures that customer-facing processes are fine-tuned for quick response times, accurate deliveries, and exceptional service quality. Satisfied customers drive loyalty and repeat Business.
4) Enhanced Compliance and Risk Management: Effective Business Process Management ensures processes are aligned with regulatory requirements and industry standards. This minimises the risk of legal issues, penalties, and reputational damage.
5) Data-driven Decision Making: Business Process Management generates data insights by monitoring process performance and outcomes. This data empowers informed decision-making, guiding strategies and actions based on evidence.
6) Business Agility: Business Process Management allows organisations to adapt swiftly to changes in the market, technology, or customer preferences. Optimised processes make it easier to pivot and respond to new opportunities.
7) Innovation and Creativity: With streamlined operations, employees have more time to focus on innovation and creative problem-solving. Business Process Management frees them from manual, repetitive tasks, fostering a culture of innovation.
8) Standardisation and Consistency: Business Process Management promotes standardised processes across the organisation, ensuring consistent quality in products and services. This consistency builds trust with customers and stakeholders.
9) Employee Engagement: Efficient processes reduce the frustration caused by cumbersome workflows. Employees can focus on meaningful tasks, leading to higher job satisfaction and engagement.
10) Continuous Improvement: Business Process Management is not a one-time endeavour, as it encourages a cycle of continuous improvement. By regularly assessing and refining processes, organisations stay competitive and relevant.
Business Process Management is not just a tool for optimising workflows. It's a strategy that fosters growth, innovation, and sustainability. Embracing BPM enables organisations to operate efficiently, respond swiftly to changes, and deliver superior value to customers, all of which are essential for thriving in today's dynamic business landscape.
Empower your decisions with precision with our Decision Making Skills Training – Sign up now!
Types of Business Process Management
BPM encompasses various approaches and methodologies tailored to address different organisational needs and challenges. These distinct types of BPM offer flexibility in optimising processes, catering to diverse industries and Business contexts. Let's explore the different types of Business Process Management:
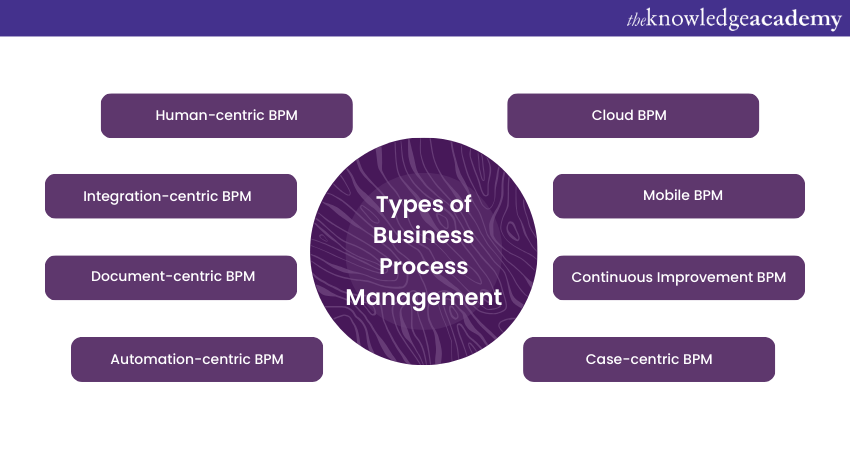
1) Human-centric BPM: Human-centric Business Process Management focuses on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of processes that involve human interactions. It emphasises empowering employees, enhancing collaboration, and providing them with the tools and insights needed to perform their tasks more efficiently. This type of BPM often integrates user-friendly interfaces, task management systems, and collaboration tools to streamline human-driven processes.
2) Integration-centric BPM: Integration-centric Business Process Management emphasises the integration of various software applications, systems, and data sources to streamline end-to-end processes. It aims to eliminate data silos and reduce manual handovers between different systems. By automating data flow and communication between applications, this type of BPM enhances the efficiency of cross-functional processes.
3) Document-centric BPM: Document-centric Business Process Management focuses on optimising processes that heavily rely on document-based workflows. It aims to digitise and automate document management, routing, approval, and archiving processes. This type of BPM ensures that documents are easily accessible, traceable, and compliant with regulatory requirements.
4) Automation-centric BPM: Automation-centric Business Process Management strongly emphasises automating repetitive and rule-based tasks within processes. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and workflow automation tools are often utilised to execute routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on more value-added activities. This type of BPM enhances efficiency by reducing manual interventions.
5) Case-centric BPM: Case-centric Business Process Management is suitable for processes that involve complex and unstructured scenarios, such as customer service inquiries, claims processing, or legal cases. It provides a dynamic framework for managing and resolving cases that require collaboration, decision-making, and adaptability. This type of BPM is particularly useful for industries where each case requires a unique approach.
6) Continuous Improvement BPM: Continuous Improvement Business Process Management emphasises the iterative enhancement of processes over time. It involves regular monitoring, analysis, and optimisation to identify and address inefficiencies. This type of BPM aligns with a culture of continual improvement, where even well-optimised processes are subject to refinement.
7) Mobile BPM: Mobile Business Process Management caters to the increasing demand for mobile access to processes and data. It enables employees to initiate, track, and manage processes using mobile devices. This type of BPM enhances flexibility and efficiency, especially for remote or field-based workers.
8) Cloud BPM: Cloud Business Process Management leverages cloud technology to offer scalable and flexible solutions for process management. It allows organisations to access BPM tools and resources without investing in extensive on-premises infrastructure.
Choosing the appropriate Types of Business Management Process depends on an organisation's specific needs, objectives, and existing processes. Whether focusing on human interactions, automation, integration, or other factors, the diverse types of BPM provide a comprehensive toolkit for enhancing efficiency and achieving Business goals.
Unlock the art of strategic business administration with our Business Administration Course – Sign up now!
Stages of BPM Lifecycle
The lifecycle of Business Process Management is a structured approach that guides organisations through the stages of identifying, designing, executing, monitoring, optimising, and reengineering their processes. This comprehensive process ensures continuous improvement and alignment with Business goals. Let's explore the lifecycle of BPM:
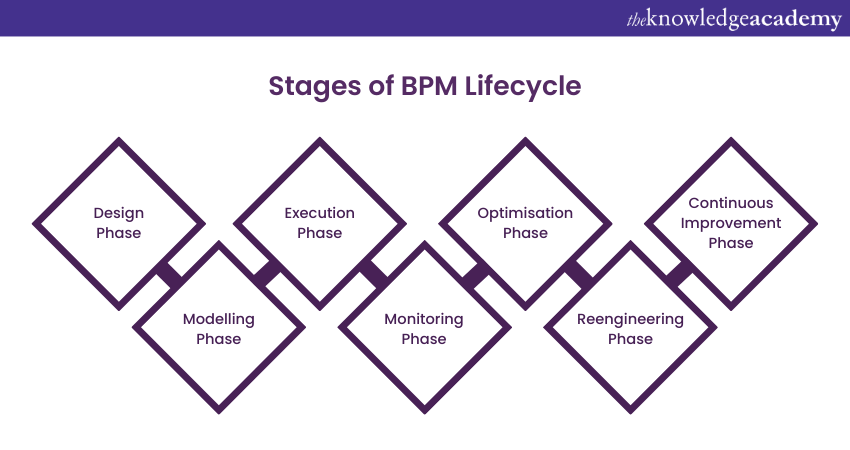
1) Design Phase: In this initial stage of Business Process Management, organisations identify key processes and define their objectives. They map out the existing workflows, determining how tasks, data, and interactions flow. The design phase sets the foundation for the subsequent stages by clarifying process goals and requirements.
2) Modelling Phase: Process models are created in this Business Process Management stage, providing visual representations of how workflows operate. These models help stakeholders understand the process steps, dependencies, and interactions. Process modelling aids in analysing inefficiencies and identifying potential improvements.
3) Execution Phase: With the process models in place, organisations transition to executing the designed Business Process Management workflows. This involves carrying out tasks and activities as outlined in the models. Organisations can use Business Process Management automation tools and technology solutions to streamline and optimise execution.
4) Monitoring Phase: Continuous monitoring of Business Process Management is crucial for identifying deviations from expected outcomes. Here, Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are tracked to measure efficiency, effectiveness, and compliance. Monitoring ensures that processes remain aligned with objectives.
5) Optimisation Phase: Based on the data collected during monitoring, organisations analyse process performance and identify areas for improvement. Bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies are addressed through adjustments to the process design or execution. Optimisation enhances overall efficiency and quality.
6) Reengineering Phase: At times, processes require more significant changes to address fundamental issues. Reengineering involves a holistic redesign of processes, often leveraging insights gained from the optimisation phase. It aims to create transformative improvements rather than incremental changes.
7) Continuous Improvement Phase: Business Process Management is a continuing endeavour. The lifecycle continuously cycles through the phases, refining processes based on evolving organisational needs, external factors, and technological advancements. This culture of continuous improvement ensures that processes remain efficient and relevant over time.
From initial design to continuous improvement, each phase contributes to enhanced efficiency and better decision-making. As a result, organisations can gain a competitive edge in the dynamic Business landscape.
Acquire the skills to turn your creativity into successful events – register for our Event Management Course.
What are the Benefits of Business Process Management?
Business Process Management (BPM) offers numerous advantages that can significantly enhance an organisation's operations and overall performance. Here are some key benefits:
a) Improved Efficiency: Streamlines processes to reduce waste and enhance productivity
b) Enhanced Agility: Allows businesses to adapt quickly to market changes and customer demands.
c) Better Compliance: Ensures processes adhere to regulatory requirements and standards
d) Increased Transparency: Provides clear visibility into processes, aiding in better decision-making.
e) Cost Reduction: Identifies and eliminates inefficiencies, leading to cost savings
What are the Challenges of Business Process Management?
While BPM can be highly beneficial, it also comes with its own set of challenges that organisations need to address. Here are some common challenges:
a) Complex Implementation: Requires significant time and resources to implement effectively.
b) Resistance to Change: Employees may be resistant to new processes and technologies.
c) High Initial Costs: Initial investment in BPM tools and training can be substantial.
d) Continuous Improvement: Requires ongoing monitoring and optimisation, which can be resource-intensive.
e) Integration Issues: Ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and processes can be challenging.
BPM Best Practices
For effective Business Process Management (BPM), focus on aligning processes with organisational objectives, engaging stakeholders during implementation, and regularly monitoring performance, improving efficiency, and fostering ongoing Business Process Improvement. The benefits of business process improvement will ensure that the organisation can adapt quickly to changes and remain competitive.
Business Process Management Use Cases
BPM is commonly applied to streamline workflows, enhance customer onboarding, strengthen compliance management, and optimise supply chains. It also aids in automating repetitive tasks and improving cross-departmental collaboration.
Conclusion
To sum up, Business Process Management is not just about improving efficiency – it's a strategy for fostering continuous improvement and innovation. With this, companies can optimise operations, boost customer satisfaction, and maintain a competitive edge. The secret lies in constantly refining processes to adapt to evolving needs.
Excel in any Business Environment and transform your Leadership abilities– join our Management Courses.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are BPM Principles?

Business Process Management (BPM) principles emphasise aligning processes with organisational objectives, improving efficiency, and fostering ongoing improvement. Core principles include customer focus, adaptability, collaboration, and effective use of technology.
What are the Objectives of BPM?

The primary objectives of BPM are to streamline workflows, minimise costs, boost productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction. Additionally, BPM aims to ensure regulatory compliance, drive innovation, and help organisations respond effectively to evolving market conditions, supporting sustainable business success.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Management Courses, including the Business Process Improvement Training, Senior Management Training, and Performance Management Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Essential Crisis Management Tools.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Business Process Management, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Leadership Skills Training
Leadership Skills Training
Fri 11th Apr 2025
Fri 27th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 24th Oct 2025
Fri 12th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


