We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
When it comes to understanding financial markets, the complexity and variety of Capital Market Instruments present a significant challenge. This often leads to confusion and difficulty in making informed investment decisions. Understanding these instruments, such as stocks, bonds, derivatives, and more, is crucial for effectively navigating Capital Markets's intricate world.
If you are curious to learn more about them, then this blog is for you. In this blog, you will learn about Capital Market Instruments in detail. Let's dive in to learn more!
Table of Contents
1) What are Capital Markets?
2) Instruments of the Capital Market
a) Equities
b) Debt securities
c) Derivatives
d) Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
e) Foreign Exchange Instruments
f) Money Market Instruments
g) Asset-backed securities
h) Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
3) Conclusion
What are Capital Markets?
Capital Markets are the markets where long-term financial assets are traded. These assets have a maturity period of more than one year and are used to raise long-term funds for the borrowers and provide long-term investment opportunities for the lenders. Capital Markets are divided into two types: The primary and secondary markets.
The primary market is the market where new securities are issued for the first time by the borrowers to the lenders. The borrowers can be the government, the public sector undertakings, the Private Sector companies, or financial institutions. The lenders can be the individuals, the institutional investors, the foreign investors, or the public at large. The primary market is also known as the new issue market or the initial public offering market.
The secondary market is where existing securities are traded among the lenders. The lenders can buy or sell the securities from other lenders or intermediaries such as stock exchanges, brokers, dealers, and market makers. The secondary market is also known as the stock market or the aftermarket.
Capital Markets play an important role in the economy, as they facilitate the mobilisation of savings and investments, the allocation of capital, the growth of the economy, and the development of the financial sector.
Instruments of the Capital Market
Capital Market Instruments are the financial instruments issued and traded in the Capital Market, representing the lenders' claims on the borrowers, as well as the rights and obligations of both parties in the Market in Financial Instruments Directive. These instruments can be classified into various types, such as equities, debt securities, derivatives, and more. Capital Market Interview Questions often explore these instruments in detail. Let’s explore these instruments further.
1) Equities
Equities are the instruments that represent the ownership of a company. They are also called stocks or shares. The holders of equities are called shareholders or stockholders. They have the right to receive dividends, vote on important matters, and share in the profits or losses of the company.

Equities are issued by the company in the primary market and traded in the secondary market. Equities are risky, as they are subject to market fluctuations and business uncertainties. However, they also offer high returns, as they appreciate in value over time and pay dividends.
2) Debt securities
Debt Securities are the instruments that represent the debt of a borrower. They are also called bonds or debentures. The holders of debt securities are called bondholders or debenture holders. They have the right to receive interest, principal, and collateral in case of default. Debt securities are issued by the borrower in the primary market and traded in the secondary market.
Debt securities are less risky, as they have a fixed interest rate and a fixed maturity date. However, they also offer low returns, as they are subject to interest rate risk and inflation risk.
3) Derivatives
Derivatives are the instruments that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as a stock, a bond, a commodity, a currency, or an index. They are also called futures, options, swaps, or warrants. The holders of derivatives are called traders or speculators. They have the right to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined price and time.
Derivatives are issued by the intermediaries in the primary market and traded in the secondary market. Derivatives are very risky, as they are subject to market volatility and leverage. However, they also offer high returns, as they can be used for hedging, arbitrage, or speculation.
4) Exchange-Traded Funds (ETF)
ETFs are the instruments that track the performance of a basket of securities, such as a stock index, a bond index, a commodity index, or a currency index. They are also called ETFs. The holders of Exchange-Traded Funds are called investors. They have the right to receive dividends, interest, or capital gains from the underlying securities.
Exchange-Traded Funds are issued by the fund managers in the primary market and traded in the secondary market. Exchange-Traded Funds are moderately risky, as they are subject to market movements and tracking errors. However, they also offer moderate returns, providing diversification, liquidity, and low costs.
Confidently step into the world of Capital Markets with our Capital Market Training – Sign up now!
5) Foreign Exchange Instruments
Foreign Exchange Instruments are the instruments that involve the exchange of one currency for another. They are also called forex or FX. The holders of foreign exchange instruments are called buyers or sellers. They have the right to receive or pay the difference between the exchange rates of the two currencies. Foreign exchange instruments are issued by banks or brokers in the primary market and traded in the secondary market.
Foreign exchange instruments are highly risky and subject to currency fluctuations and political uncertainties. However, they also offer high returns, which can be used for international trade, tourism, or investment.
6) Money Market Instruments
Money Market Instruments are the instruments that represent the short-term debt of a borrower. They have a maturity period of less than one year and are used to meet the borrowers' and lenders' short-term liquidity needs.
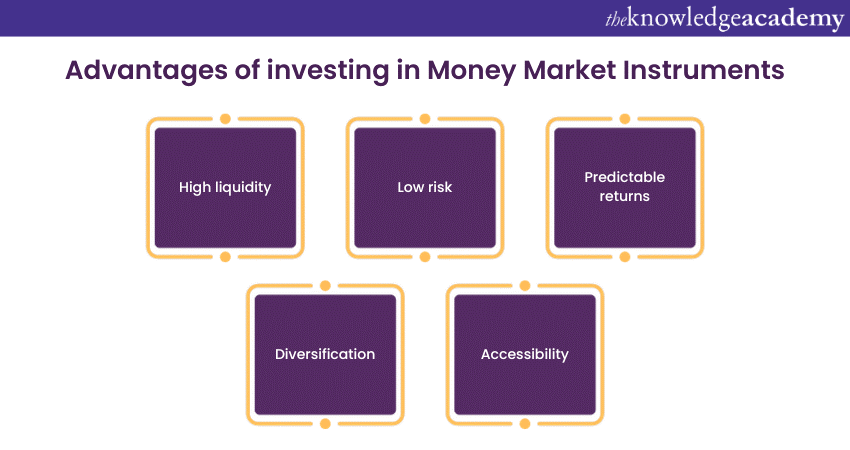
They are also called treasury bills, commercial papers, certificates of deposit, bankers’ acceptances, repurchase agreements, and interbank call money. The holders of Money Market Instruments are called lenders or creditors.
They have the right to receive interest and principal at maturity. Money Market Instruments are issued by the borrowers in the primary market and traded in the secondary market. Money Market Instruments are very safe, as they have a low default risk and a low interest rate risk. However, they also offer low returns, low-interest rates, and low-profit margins.
7) Asset-backed securities
Asset-backed securities are instruments backed by a pool of assets, such as mortgages, loans, receivables, or leases. They are also called ABS. The holders of asset-backed securities are called investors. They have the right to receive interest and principal from the cash flows generated by the underlying assets. Asset-backed securities are issued by the originators or the issuers in the primary market and traded in the secondary market.
Asset-backed securities are moderately risky, as they are subject to credit and prepayment risks. However, they offer moderate returns, providing diversification, liquidity, and credit enhancement.
Shape your financial future with our Financial Modelling and Forecasting Training – Sign up now!
8) Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs)
Real Estate Investment Trusts are the instruments that invest in real estate properties, such as residential, commercial, industrial, or retail. They are also called REITs. The holders of Real Estate Investment Trusts are called shareholders. They have the right to receive dividends, capital gains, and tax benefits from the income and appreciation of the properties.
Real Estate Investment Trusts are issued by trust managers in the primary market and traded in the secondary market. Real Estate Investment Trusts are moderately risky, as they are subject to market conditions and property management. However, they also offer moderate returns, providing diversification, income, and growth.
Conclusion
We hope you read and understand everything about Capital Market Instruments. Each of these instruments has its own features, advantages, and disadvantages. By understanding these instruments and the difference between Money Market and Capital Market, one can make informed decisions about investing in the Capital Market. For additional insights on regulatory frameworks, refer to the MiFID 2 PDF, which provides valuable information on market transparency and investor protection.
Elevate your financial expertise with our Accounting & Finance Training – Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
Upcoming Accounting and Finance Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Capital Market Course
Capital Market Course
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


