We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Artificial Intelligence (AI) has risen as a transformative force, fundamentally altering various sectors and our everyday experiences. As we stand at the threshold of an AI-driven future, it is crucial to understand the Characteristics of Artificial Intelligence that underpin this technological revolution. AI's ability to learn, solve complex problems, understand language, and make autonomous decisions is at the core of its impact.
According to Statista, the Artificial Intelligence market is expected to achieve a market size of approximately 192.4 billion GBP by 2023. This highlights the need for businesses and individuals to understand the features of AI to stay ahead of the competition. Further, read this blog to understand the Characteristics of Artificial Intelligence and its applications.
Table for contents
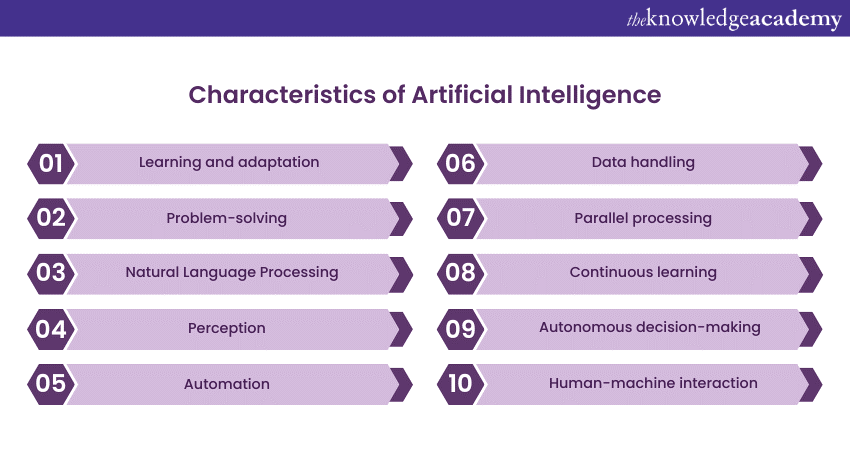
1) Characteristics of Artificial Intelligence
a) Learning and adaptation
b) Problem-solving
c) Natural Language Processing
d) Perception
e) Automation
f) Data handling
g) Parallel processing
h) Continuous learning
i) Autonomous decision-making
j) Human-machine interaction
2) AI in Practice
3) Conclusion
Characteristics of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence is an area of study that aims to develop intelligent entities or systems with the ability to replicate human-like cognition and actions. Artificial Intelligence systems possess a set of core characteristics that define their capabilities and functionalities which are described below:
Learning and adaptation
One of the fundamental characteristics of AI is its capacity to learn and adapt. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, enables systems to improve performance over time through continuous learning. Artificial Intelligence systems have the capability to examine extensive datasets, identify recurring trends, and formulate forecasts or choices grounded in this data. For example, in image recognition, AI models can better identify objects or faces with each exposure to new data. This characteristic of learning and adaptation is important in applications such as:
a) Recommendation systems: AI algorithms analyses user behaviour and preferences to suggest products, movies, or content tailored to individual tastes.
b) Natural Language Processing (NLP): Language models like GPT-3 can generate human-like text by learning from vast amounts of text data.
c) Self-driving cars: Autonomous vehicles use Machine Learning to adapt to changing traffic conditions and make driving decisions.
Unlock the potential of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning to supercharge your business – explore our Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Course today!
Problem solving
AI excels at solving complex problems that involve large amounts of data and decision-making. Unlike traditional programming, where explicit rules are coded, Systems can find solutions by analysing data and adjusting their internal parameters. It enables AI to tackle intricate tasks in various domains:
a) Medical diagnosis: AI can analyse medical data and assist in diagnosing diseases by recognising patterns and anomalies.
b) Optimisation: AI can optimise supply chains, transportation routes, and resource allocation to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
c) Game playing: AI has achieved superhuman performance in chess, Go, and video games by employing advanced problem-solving techniques.
Natural Language Processing
Natural Language Processing (NLP) stands as a fundamental component of AI, empowering machines to grasp, decipher, and produce human language. This capability forms the core of numerous AI applications, encompassing:
a) Virtual assistants: Virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant are capable of comprehending and providing responses to spoken instructions and inquiries through voice activation.
b) Language translation: AI-powered translation tools can translate text and speech between different languages.
c) Sentiment analysis: NLP analyses social media posts, customer reviews, and news articles to determine public sentiment and opinion.
Perception
AI systems can perceive their environment through various sensors. This is essential in applications like:
a) Computer vision: AI can interpret visual data, enabling tasks like facial recognition, object detection, and autonomous vehicle navigation.
b) Speech recognition: AI can convert spoken language into text, which is valuable for transcription services and voice assistants.
c) Environmental monitoring: AI can analyse sensor data to detect environmental changes, such as air quality or seismic activity.
Automation
Automation is a crucial feature of AI, as it can perform tasks with minimal human intervention. This is transforming industries by streamlining operations and increasing efficiency. Examples of AI automation include:
a) Manufacturing: Robots and AI-driven systems handle repetitive and dangerous tasks in manufacturing, such as welding, assembly, and quality control.
b) Customer service: Chatbots and virtual agents are capable of addressing customer queries and offering assistance around the clock.
c) Data entry: AI can streamline data entry and data extraction tasks, diminishing the requirement for manual data management.
Unlock the power of AI For Business Analysts and transform your strategies – Join our Artificial Intelligence (AI) For Business Analysts Course today!
Data handling
AI is adept at handling vast amounts of data efficiently. This is essential in today's data-driven world, where businesses and organisations rely on data for decision-making and insights. AI applications in data handling include:
a) Big Data analysis: AI algorithms have the capability to handle extensive datasets for the purpose of extracting valuable insights and identifying patterns.
b) Personalisation: It uses customer data to provide personalised recommendations in e-commerce, content streaming, and advertising.
c) Healthcare: It processes patient data for diagnosis, treatment recommendations, and drug discovery.
Parallel processing
AI systems can perform multiple tasks simultaneously, thanks to parallel processing. This allows it to tackle complex computations and real-time data analysis, contributing to faster decision-making. Examples include:
a) High-performance computing: AI-powered supercomputers can simulate complex phenomena, such as weather patterns, drug interactions, and nuclear reactions.
b) Financial trading: AI algorithms swiftly examine market data and swiftly execute trades, capitalising on market fluctuations within mere moments.
Continuous learning
AI's capacity for continuous learning allows it to adapt to new information and evolving situations. This is precious in applications where knowledge is constantly updated or changing. Examples include:
a) Cybersecurity: AI systems can learn to detect new cyber threats and adapt their defence mechanisms accordingly.
b) Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars continuously update their knowledge of road conditions and traffic to make real-time driving decisions.
Autonomous decision-making
AI systems can make autonomous decisions based on data and predefined rules. This is prevalent in applications like autonomous vehicles, where AI algorithms decide on driving actions in real time based on sensor data and safety rules. Independent decision-making also extends to robotics, where robots can perform tasks independently.
Human-machine interaction
AI systems are becoming more interactive and capable of understanding and responding to human emotions and intentions. This characteristic enhances user experiences in various applications:
a) Virtual Reality (VR): AI-driven VR environments can respond to user gestures, voice commands, and expressions, creating immersive experiences.
b) Gaming: AI-powered game characters can adapt their behaviour based on player actions, making games more engaging and challenging.
c) Customer service: AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents can provide more human-like interactions, improving customer satisfaction.
Empower your projects with the transformative potential of AI – embrace AI for Project Managers Course and stay ahead in the rapidly evolving tech-driven landscape!
AI in practice
Artificial Intelligence in practice has transformed industries, from healthcare and finance to transportation and retail. Explore its real-world applications, ethical concerns, and future trends in this concise guide.
Applications across industries
Artificial Intelligence has permeated various industries, revolutionised operations and enhancing user experiences:
a) Healthcare: It aids in early disease detection through image analysis, recommends personalised treatment plans, and provides 24/7 patient support via chatbots.
b) Finance: AI is crucial for fraud detection, algorithmic trading, and customer support through chatbots. Sentiment analysis helps predict market trends.
c) Manufacturing: AI-driven automation optimises processes, reduces downtime through predictive maintenance, and enhances supply chain management.
d) Retail: Personalisation algorithms improve shopping experiences, computer vision streamlines cashier-less checkout, and AI optimises inventory management.
e) Transportation: Autonomous vehicles rely on AI for navigation, promising safer roads and reduced traffic congestion. Public transportation systems benefit from route optimisation.
Ethical considerations
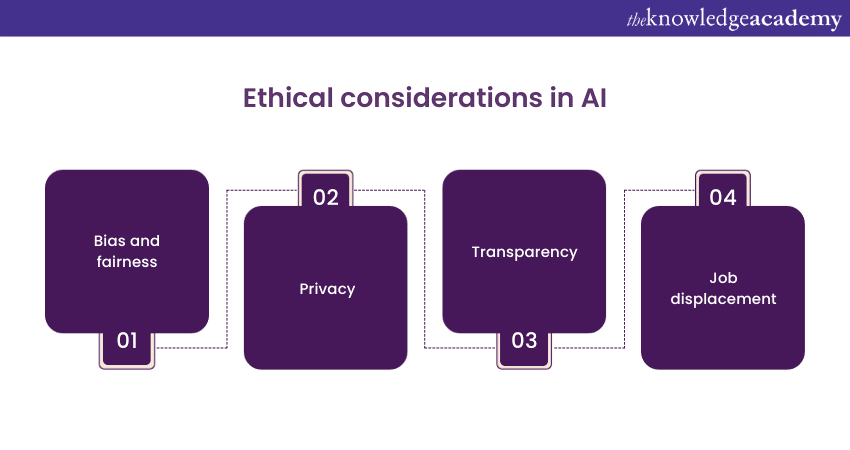
Artificial Intelligence's transformative power comes with ethical concerns:
a) Bias and fairness: It can exhibit biases from biased training data, affecting fairness in applications like hiring and lending. Mitigating bias is crucial.
b) Privacy: It often handles personal data, raising privacy concerns. Stringent regulations like General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA) are vital for data protection.
c) Transparency: Opacity in AI decision-making processes is a concern. Transparent AI models are essential for accountability and trust-building.
d) Job displacement: Automation driven by AI may displace jobs in certain sectors, necessitating proactive measures like reskilling and upskilling.
Future Trends
Artificial Intelligence's evolution continues, with these key trends on the horizon:
a) Advanced AI models: Cutting-edge models like GPT-4 promises even better natural language understanding and problem-solving capabilities.
b) Edge AI: Deploying AI on edge devices reduces latency and enhances privacy by processing data locally.
c) AI in healthcare: Its role in drug discovery, remote patient monitoring, and personalised medicine is set to expand.
d) AI ethics and regulation: Stricter guidelines and regulations will govern AI use, ensuring fairness, transparency, and privacy.
e) AI in Climate Science: It aids Climate Science by analysing environmental data, predicting weather patterns, and optimising energy consumption.
f) AI in space exploration: It is pivotal in analysing space data, planning space missions, and controlling autonomous space probes.

Conclusion
The Characteristics of Artificial Intelligence have catalysed innovation across sectors. These include learning, problem-solving, and Natural Language Processing. Ethical concerns and promising future trends underscore the need for responsible AI integration across industries, shaping a dynamic and transformative landscape.
Unlock the future with AI - Join our Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Training and embark on a journey of limitless possibilities!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to AI Course
Introduction to AI Course
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


