We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Cloud Computing has revolutionised business operations worldwide by offering flexible and scalable solutions to meet their computing needs. To harness the power of the cloud, it's crucial to understand the different Cloud Computing Service Models. Each of these models plays a crucial role in helping organisations across the world.
According to Statista, the Public Cloud market is expected to reach 118.89 billion GBP in 2023. If you wish to explore each model's features, benefits, and use cases to make informed decisions about adopting the right cloud service model, this blog is what you need. Explore the world of Cloud Computing service models with this blog and learn about three core service models: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, and discover Cloud Computing Examples that showcase their applications.
Table of Content
1) Cloud Service Models in Cloud Computing
2) Why Does Your Business Need Cloud Computing?
3) Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
4) Platform as a Service (PaaS)
5) Software as a Service (SaaS)
6) Conclusion
Cloud Service Models in Cloud Computing
Service models refer to the three primary categories defining the level of services and resources that cloud service providers provide. These models are Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Except for these three, an additional model known as Function as a Service (FaaS) also exists, which acts as an abstraction layer for the rest of the models.
These model offers distinct features, benefits, and levels of control, allowing businesses to choose the one that best fits their needs.
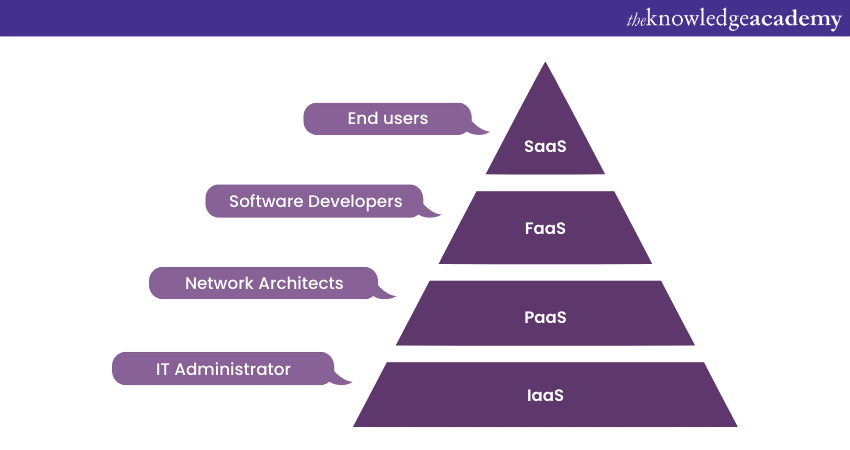
These service models are essential for organizations as they provide flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency. By leveraging Cloud Computing and Mobile Computing Service Models, businesses can shift their focus from managing and maintaining physical infrastructure to utilizing cloud-based resources. This enables them to reduce upfront investments, increase operational agility, and quickly adapt to changing business requirements.
Why Does Your Business Need Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing offers significant advantages for businesses, enhancing their operational capabilities and flexibility. By learning How Does Cloud Computing Work and leveraging cloud services, businesses can integrate applications, deployments, and networks, ensuring high performance and availability. This technology allows for rapid scaling of resources to meet fluctuating demands, promoting cost efficiency through pay-as-you-go models.
Enhanced collaboration is facilitated by providing access to data anytime, anywhere, which is crucial for remote work environments. Moreover, Cloud Computing centralises data storage, offering robust security and efficient data backup solutions, mitigating the risk of data loss. It also enables businesses to innovate faster and maintain operational efficiency by swiftly responding to disruptions and technological advancements.
Additionally, cloud service models like SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS provide tailored solutions to meet specific business needs, further optimising resource utilisation and improving overall business agility.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the most commonly available Cloud Computing service model. This model is responsible for providing virtualised computing resources over the internet. With IaaS, businesses can access and manage fundamental IT infrastructure components such as virtual machines, storage, and networks without the need for physical hardware on-site.
The service provider handles the infrastructure maintenance. This allows you to scale your resources up for greater use or scale it down for lower consumption based on demand. This flexibility and abstraction of infrastructure empower organisations to focus on their core business activities and reduce the burden of managing hardware infrastructure.
Features of IaaS
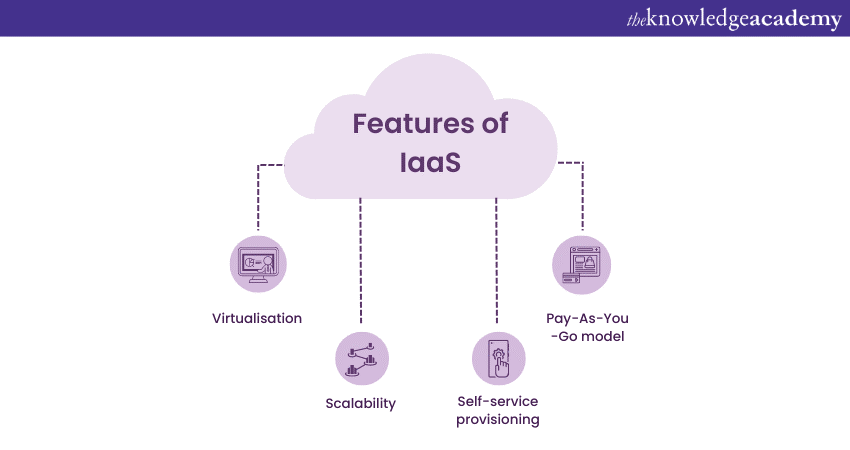
Benefits of IaaS
Implementing IaaS provides organisations with several benefits and advantages:
a) Cost Efficiency: IaaS eliminates the need for upfront infrastructure investments, reducing capital expenditures. Businesses can scale resources based on demand, paying only for what they use.
b) Flexibility and Agility: The scalable nature of IaaS allows for quickly adapting to the changing needs within organisations, enabling them to launch new projects, expand operations, or shrink infrastructure as required.
c) Resource Optimisation: With IaaS, businesses can optimise resource utilisation based on demand. This is done by dynamically allocating computing resources based on demand, improving efficiency and reducing waste.
Use Cases of IaaS
IaaS finds applications across various use cases, including:
a) Scaling Computing Resources: IaaS enables businesses to scale their computing resources on-demand to accommodate increased workloads during peak periods, ensuring optimal performance without the need for infrastructure investment.
b) Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Organisations can leverage IaaS to create robust disaster recovery solutions, replicating critical systems and data to remote data centres. This allows organisations to continue business even in a disaster or outage.
c) Development and Testing Environments: IaaS provides developers and testers with on-demand infrastructure to build, test, and deploy applications without any physical hardware. This accelerates the development cycle and reduces the time-to-market for new products and services.
Disadvantages of laaS
a) Limited Infrastructure Control: Although IaaS providers normally handle upkeep, upgrades, and management of the underlying infrastructure, this might also imply that users have less control over the environment and might not be able to make some adjustments.
b) Security Issues: Users must take responsibility for protecting their data and apps, which can be very demanding.
c) Restricted Access: Owing to legal regulations, Cloud Computing may not be available in some states or nations.
Learn to handle cloud infrastructure and Virtual Machines with Cloud Computing Training – sign up now!
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS is a popular Cloud Computing service model that gives developers a complete platform to build, deploy, and manage applications without the complexity of underlying infrastructure management.
PaaS offers a ready-to-use development environment with tools, frameworks, and runtime environments that streamline the application development process. By abstracting infrastructure management, PaaS enables developers to focus on writing code and accelerating the application development lifecycle.
Features of PaaS
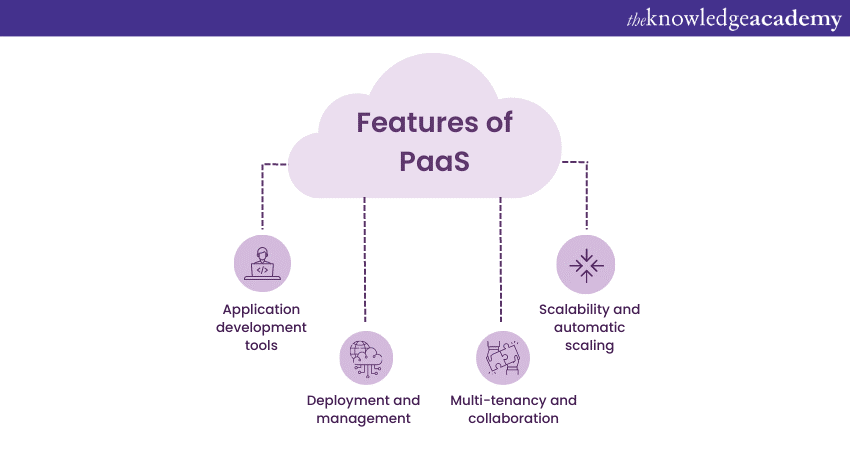
Benefits of PaaS
Adopting PaaS offers numerous benefits and advantages for businesses:
a) Faster Time-to-market: PaaS accelerates application development by providing ready-to-use development environments, pre-configured frameworks, and automated deployment capabilities. This reduces the time required to bring new applications to market.
b) Cost efficiency: By abstracting infrastructure management, PaaS eliminates the need for organisations to invest in hardware, software licenses, and maintenance. Businesses can focus on development while enjoying cost savings and predictable pricing models.
c) Scalability and Flexibility: PaaS platforms offer horizontal scalability, allowing applications to scale seamlessly to meet growing demands. This flexibility ensures businesses can handle increased user traffic or data volumes without disruption.
Use Cases of PaaS
PaaS finds applications across various use cases, including:
a) Web Application Development: PaaS provides developers with the necessary tools and environments to build, deploy, and manage web applications efficiently. It simplifies development, enhances collaboration, and enables rapid prototyping and iteration.
b) Mobile App Development: PaaS platforms offer specialised features and tools for mobile app development, including SDKs, cross-platform development frameworks, and testing capabilities. This streamlines the app development process and allows developers to focus on building innovative mobile experiences.
c) Data Analytics and Machine Learning: PaaS provides the infrastructure and tools for Data Analytics and machine learning projects. Developers can leverage pre-built libraries, frameworks, and scalable computing resources to process and analyse large datasets, train machine learning models, and derive valuable insights.
Disadvantages of PaaS
a) Limited Infrastructure Control: While PaaS providers handle maintenance, upgrades, and management of the underlying infrastructure, this can limit user control over the environment and certain adjustments.
b) Dependency on the Provider: Users rely on the PaaS provider for scalability, availability, and dependability, posing risks if the provider experiences disruptions or issues.
c) Restricted Flexibility: PaaS solutions may be less useful for some organisations if they cannot support specific workloads or applications, limiting their overall flexibility.
Try our Microservices Architecture Training and learn concepts of load balancing!
Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS is a frequently used Cloud Computing Service Model that provides you with internet-based software applications which work on a subscription basis. SaaS allows you to access and use applications hosted in the cloud without the need for installation or maintenance.
The service provider manages the infrastructure, security, and updates while users access the software through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need for organisations to invest in software licenses, hardware, and infrastructure management, providing a cost-effective and convenient solution for accessing and utilising software applications.
Features of SaaS
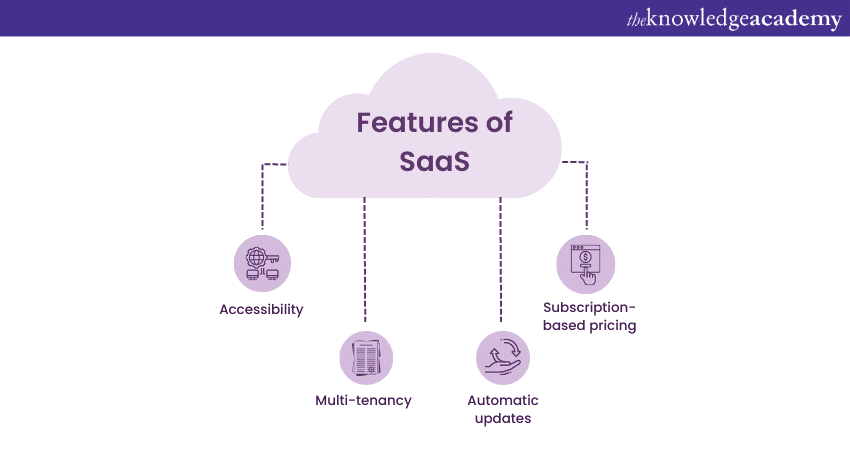
Benefits of SaaS
Adopting SaaS offers numerous benefits and advantages for businesses:
a) Cost Efficiency: SaaS can remove the need for upfront software licensing costs and infrastructure investments, allowing organisations to reduce IT expenses and allocate resources more efficiently.
b) Easy Deployment and Accessibility: SaaS applications can be quickly deployed without the need for complex installations, making them easily accessible to users through a web browser from various devices.
c) Scalability and Flexibility: SaaS applications can scale seamlessly to accommodate growing user demands, enabling organisations to add or remove users, features, or modules as needed.
Use Cases of SaaS
SaaS finds applications across various use cases, including:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): SaaS-based CRM platforms provide businesses with tools to manage customer relationships, sales pipelines, and marketing activities. These applications offer features like contact management, sales tracking, customer support, and analytics.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): SaaS ERP solutions integrate core business processes such as finance, inventory, HR and supply chain management into a cohesive, unified system. They streamline operations, improve efficiency, and enable real-time insights into organisational performance.
Collaboration and Productivity Tools: SaaS-based collaboration and productivity tools, such as Project Management, document sharing, and communication applications, enables teams to collaborate effectively, enhance productivity, and facilitate remote work.
Disadvantages of SaaS
a) Limited Customisation: SaaS solutions often offer less customisation than on-premises software, potentially forcing users to operate within the platform limitations set by the provider.
b) Dependency on Internet Connectivity: As SaaS is cloud-based, a stable internet connection is essential for proper functionality. Users needing offline access or operating in areas with poor connectivity may face issues.
c) Security Issues: Although SaaS providers ensure data security, the risk of security incidents and data breaches remains.
d) Limited Control Over Data: Organisations requiring stringent data control for regulatory reasons may be concerned about SaaS providers having access to their data
Conclusion
Cloud Computing Service Models have revolutionised how businesses access, develop, and utilise software applications and infrastructure. We hope this blog has you understand the numerous benefits of Cloud Computing and its models, such as cost efficiency, scalability, and flexibility, thus helping you make more informed choices in future and achieve greater achievement in the rapidly evolving digital world.
Try our Terraform Training to gain familiarity with loops, syntax and statements!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Common Cloud Deployment Model?

The Public Cloud is a common cloud deployment model where services are provided over the internet by third-party providers. It offers scalability, cost-effectiveness, and accessibility but may have limitations in data control and security.
What is the Most Expensive Cloud Model?

The Private Cloud is the most expensive cloud model, providing dedicated resources for a single organisation. It offers greater control, security, and customisation but requires significant investment in infrastructure and maintenance.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Cloud Computing Courses, including the Cloud Computing Training, Microservices Architecture and Terraform Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Benefits of Cloud Computing.
Our Cloud Computing Blogs cover a range of topics related to Cloud Computing, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Cloud Computing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Cloud Computing Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Cloud Computing Training
Cloud Computing Training
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


