We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Eager to learn how Conditional Probability can transform your data analysis journey? Conditional Probability is the key concept of probability theory under predictive analysis that helps understand the influence of one event over others. Continue reading this blog to understand the definition of Conditional Probability, its formula, key examples, practical uses, properties, etc. Let's kickstart this engaging, data-driven journey!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding What is Conditional Probability
2) Conditional Probability Formula
3) Conditional Probability Examples
4) Practical Uses of Conditional Probability
5) Properties of Conditional Probability
6) Connecting Conditional Probability and Bayes' Theorem
7) Comparing Conditional Probability with Joint and Marginal Probability
8) Conclusion
Understanding What is Conditional Probability
Conditional Probability is a concept that analyses how the probability of one event's occurrence affects the occurrence of its succeeding one. In simple words, it's the way of influencing one event over the latter.
For example, if today it is cloudy (assuming it is event A), then the probability of occurrence of rain tomorrow (event B) is directly influenced by the preceding day of event A (when the day was cloudy). Conditional Probability is denoted as P(A∣B).
Conditional Probability Formula
The Conditional Probability is expressed as:
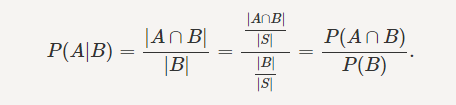
This means that if the Probability of event A, given that event B has already occurred, is equal to the probability of both A and B occurring simultaneously (A ∩ B), which are divided by the probability of event B.
Conditional Probability Examples
The one example is already explained earlier the other examples are:
1) Rolling a Die
Suppose you roll a die. If you want to find the probability of the number 6, given that the number should be even, you first identify all the even numbers in die rolling. As a result, only one favourable outcome will be there out of three possible outcomes. So, the Conditional Probability will be 1/3.
2) Marbles in a Bag
Let’s suppose you have a bag filled with three red marbles and two blue marbles. If you want to find the blue marble drawing probability given that the marble drawn is not red, you first analyse the blue marble's quantity.
Thus, the probability will be one divided by two, where numerator 2 is the number of blue marbles while denominator 2 is the number of red marbles from the total difference in the number of marbles.
3) Multiple Conditional Probabilities
Let’s say you have a deck of cards. If you want to know the probability of drawing a heart, given that the card drawn should be red, you first need to find out the number of red cards, which will be 26, where 13 red cards are hearts. Thus, the probability will come out to be ½ by dividing 13 by 26.
Optimise data for accurate forecasts with our Predictive Analytics Course – register today!
Practical Uses of Conditional Probability
Conditional Probability is used in several applications, ranging from medicinal to finance disciplines. A few practical uses of Conditional Probability are:
1) Finance Applications: Conditional Probability is used by investors to analyse investment risks under the given market conditions. This ability helps to make seamless and data-driven decisions.
2) Medical Diagnostics: Healthcare professionals utilise the applications of Conditional Probability to evaluate the probability of diseases based on the symptoms and test results.
3) Machine Learning Models: Bayesian inference, Naive Bayes, and other similar ML models use Conditional Probability concepts to enhance their prediction capabilities, helping them boost their work in applications like spam detection.
Properties of Conditional Probability
There are numerous properties of Conditional Probability. A few of its primary properties are described below:
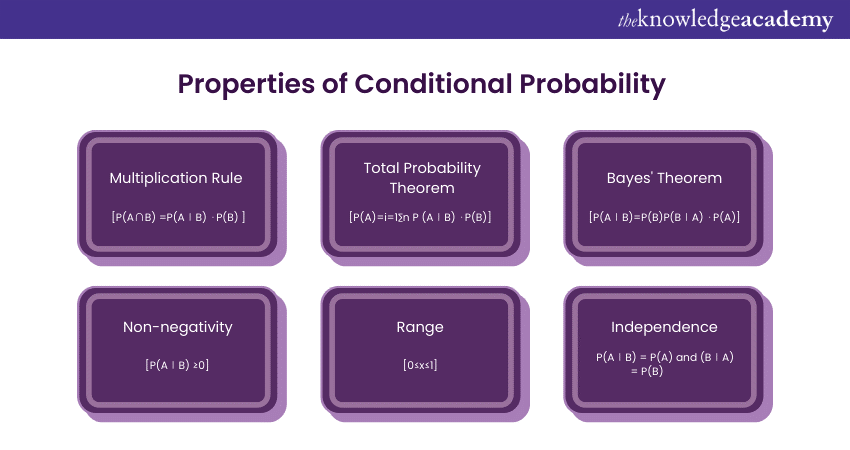
1) Multiplication Rule: The joint probability of events A and B occurring simultaneously can be expressed as
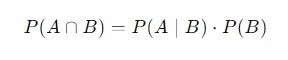
2) Total Probability Theorem: If B1, B2 …, Bn are mutually exclusive and exhaustive events, then the probability of any event A can be expressed in the form of
3) Bayes Theorem: The Bayes theorem provides a mathematical framework to redefine probabilities based on new evidence. It is denoted using the formula:
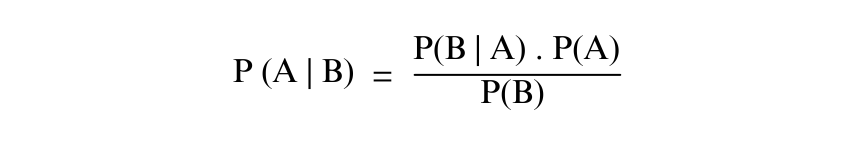
The Bayes Theorem formula is largely useful in reverse reasoning and is widely applied in fields such as statistics and machine learning.
4) Non-negativity: Conditional probabilities are always non-negative. This means:
P(A∣B) ≥0
5) Range: The value of Conditional Probability ranges from 0 to 1, which is
0≤x≤1.
6) Independence: If events A and B are independent, then

Connecting Conditional Probability and Bayes' Theorem
Bayes Theorem and Conditional Probability are closely connected concepts pertaining to Probability theory. The Bayes Theorem offers numerous ways to update probabilities on the basis of new evidence. It allows you to perform the reverse conditional probabilities, helping find P(B|A) when you already have P(A|B), P(A) and P(B).
The formula for Bayes Theorem is given as:
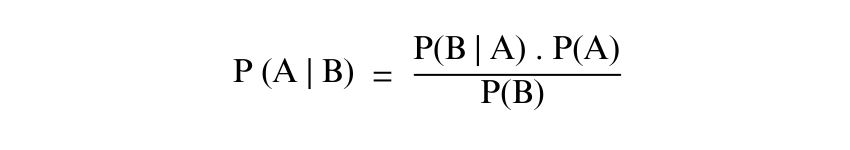
Develop insightful predictive models with our Data Mining Training- book your seats now!
Comparing Conditional Probability with Joint and Marginal Probability
Conditional, joint and marginal probability are largely interconnected. Where marginal probability gives us a broader overview of the formula, joint and conditional probabilities offer deeper insights into the relationship between events. It is important to understand their critical functions with respect to statistical analysis.
a) Joint Probability: Joint Probability refers to the probability of two events happening together. For instance, the probability of flipping a coin and rolling a die at the same time is a joint probability.
b) Marginal Probability: Marginal probability is the probability of the occurrence of a single event, irrespective of the other evolving factors. It can be derived from the joint probability by summing up all the possible outcomes of the other event(s).
Analyse data using decision trees- register today for our Decision Tree Modeling Using R Training!
Conclusion
We hope you understand Conditional Probability. This powerful tool enables seamless predictive analysis by allowing you to evaluate events systematically while incorporating prior occurrences. Moreover, gaining insight into its formula, practical applications, and properties enhances your data-driven decision-making skills. Whether you are working in finance, Independent Events in Probability, or Machine Learning (ML), mastering these concepts can significantly improve your analytical capabilities.
Extract progressive insights from textual data- kickstart your Text Mining Training now!
Frequently Asked Questions
How Can Conditional Probability Be Used to Determine Unconditional Probability?

You need to use the Total Probability Theorem concept by adding all possible probabilities under multiple given conditions. Then, you need to multiply each Conditional Probability by its corresponding event probability and add these results together. This way, you can find the unconditional probability from its counterpart.
What Are the Rules of Conditional Probability?

The rules of Conditional Probability are the multiplication rule and Bayes Theorem. The formula for both is explained in this blog.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Science Courses, including Probability And Statistics For Data Science Training, Predictive Analytics Course, and Text Mining Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Regression Analysis.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to data science, analytics, and artificial intelligence, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your technical skills in data analysis and machine learning, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Probability and Statistics for Data Science Training
Probability and Statistics for Data Science Training
Thu 10th Apr 2025
Thu 12th Jun 2025
Thu 14th Aug 2025
Thu 9th Oct 2025
Thu 11th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


