We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Cybersecurity and cyber-attacks have become an everyday talk among many. But do you know its seriousness and importance?If you are thinking, why should you consider establishing Cyber Security standards in your organisation? Then, you definitely should look into the following statistics derived from Statista’s research.
According to the survey conducted by Statista, the global cost of cybercrime was estimated at 7 trillion GBP in 2022. The cost of incidents caused due to malicious activities is expected to surpass 9.1 trillion GBP in 2023. And by 2026, it is estimated that the cybercrimes cost could exceed 16.6 trillion GBP, which is an increase of almost 150 per cent compared to the cost of 2022.
The research proves our point on how Cyber-attacks are increasing rapidly and the possible impact such illegal activities can have on the cost incurred to deal with them.
In this blog, we will discuss essential Cyber Security Principles you need to know as an Internet Service Provider or a Business owner.
Table of Contents
1) What are Cyber Security Principles?
2) Need for Cyber Security Principles
3) Top 10 Cyber Security Principles for Enterprises and Businesses
4) Top 10 Cyber Security Principles for Internet Service Providers
5) Conclusion
What are Cyber Security Principles?
The Cyber Security Principles are a set of guiding principles developed for improving the online security of Internet users. They protect and provide strategic guidance against cyber threats or malicious security breaches, and understanding the Cyber Kill Chain is crucial in identifying the stages of an attack and preventing it from escalating.
These principles have been developed to mitigate the cyber threats ingrained in internet use. The Cyber Security Principles can guide, inform, educate, support, and secure you against online crimes. Additionally, implementing tools like Tor in Cyber Security can further enhance your protection by ensuring greater privacy and security while navigating the internet.
Need for Cyber Security Principles
Cyber Security Principles are necessary to provide tactical guidance to understand and implement measures to protect an organisation from cyber threats. These principles, often referred to as cyber security essentials, can be understood better when you group them into four activities: Govern, Protect, Detect, and Respond.
a) Governing principles are used to identify and manage security risks.
b) Protecting principles help in implementing controls to reduce security risks.
c) Detecting principles help detect and understand cyber security events to identify cyber security threats.
d) Responding principles help in recovering and responding to cyber security incidents.
Interested in identifying attacks and vulnerabilities before it infiltrates? You can register with the CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst CySA+ Certification course for expert training and help.
Top 10 Cyber Security Principles for Enterprises and Businesses
Now, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of cybersecurity while discussing the 10 essential cybersecurity principles outlined in the National Cyber Security Centre (NCSC) guidance. These principles are highly effective for enterprises and businesses seeking to safeguard themselves against cyber-attacks.
Here are the 10 Cyber Security Principles for Enterprises and Businesses:
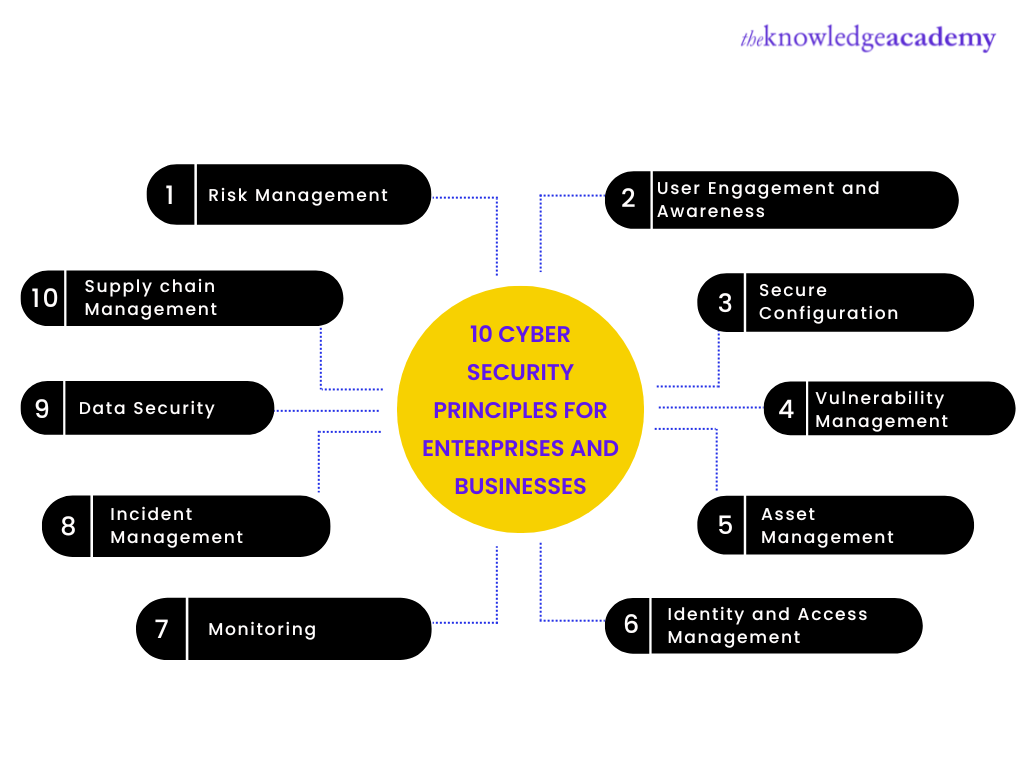
Risk Management
A good risk management approach will help you balance threats and bring you opportunities to deliver the best business objectives. This principle will help you ensure that the organisation's technology, information, and systems are safeguarded in the most suitable way.
User Engagement and Awareness
Involving people in a cyber security strategy to understand the way these people work to get their jobs done is a good security consideration. Provided the people are correctly engaged and follow a positive cyber security culture, they can be an effective resource in preventing malicious incidents. Encouraging feedback and suggestions will not only protect your organisation, but it can also demonstrate that you value your staff.
Secure Configuration
As technology constantly evolves, the requirement for better cyber security updates and configuration needs to be fulfilled. The systems and services that are maintained and updated effectively can protect your organisation from emerging cyber threats and risks. By following the necessary guidelines, it is crucial to maintain and update the system configuration to reduce the impact of a compromise.
Vulnerability Management
Cyber Security attacks are carried out mainly due to the attackers exploiting publicly disclosed vulnerabilities. Malicious attackers are always searching for a vulnerability to enter your system, illegally causing havoc in the organisation.
Hence, installing security updates is essential to protect sensitive data stored in your organisation. Finding a good vulnerability management process to address the most severe security issues will help your organisation to fix the vulnerabilities.
Asset Management
Asset management is about establishing and maintaining the requisite knowledge of all your assets. Gradually, as the number of systems grows, it becomes challenging to understand and sustain the technological information of all your assets. A careful assessment of your assets can expose you to the unpatched services, replacements and upgrades required and many other vulnerabilities which need to be addressed to minimise the risk of cyber-attacks.
Identity and Access Management
It is vital to ensure safe and protected access to data, systems, and services. Knowing who needs to be kept out, who or what requires access, and under what circumstances. You must select methods that will reliably establish and prove the identification of users, devices, or systems to make user control decisions.
An effective identity and access management strategy will make it difficult for attackers who pose as genuine users while making it easy for authorised users to give access to what they require.
Monitoring
Collecting and keeping records is essential to understand how your system works and is being used. In case of any risk or a potential security threat, the records maintained can be used to investigate the root cause of the risk. This monitoring process helps organisations to minimise security incidents by keeping track of any unusual behaviour.
Incident Management
An incident can cause a massive impact on the organisation to productivity, cost, and reputation. Good incident management can bring down the effect of these incidents. The ability to detect early and respond to incidents swiftly will help you prevent or reduce any further damage. Managing the incident tactically can help you minimise the operational and financial impact on the organisation.
Learn how Artificial Intelligence vs Cyber Security influences the future of digital safety and privacy.
Data Security
This principle involves relevant measures to protect data from unauthorised access, deletion, or modification. You must ensure data protection during the transit, at rest, and effectively destroy or dispose of the data stored after use. This ensures that the sensitive data is not recovered from the decommissioned devices.
As per the security measures, organisations should maintain an up-to-date offline backup copy of all the critical data to avoid any kind of profound loss or damage.
Supply chain Management
Most businesses depend on suppliers to deliver their goods, systems, and services. An attack on one of your suppliers or vendors could be just as harmful to you as one on your own company. As supply chains are frequently large and complicated, vulnerabilities can be introduced, created, or exploited at any point along the supply chain.
As a result, successfully safeguarding the supply chain can be challenging. Hence, it is essential to understand your supply chain. This includes commodity suppliers like cloud service providers and those with whom you have customised contracts. You need to support and encourage development to help increase supply chain security.
Are you an advanced professional with high-level experience and skills in a wide range of security areas? Then this Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect SC100 Training is for you.
Top 10 Cyber Security principles for Internet Service Providers
Following is a list of the top 10 Cyber Security principles for improving the online security of Internet Service Providers and minimising the rise in cyber-attacks.
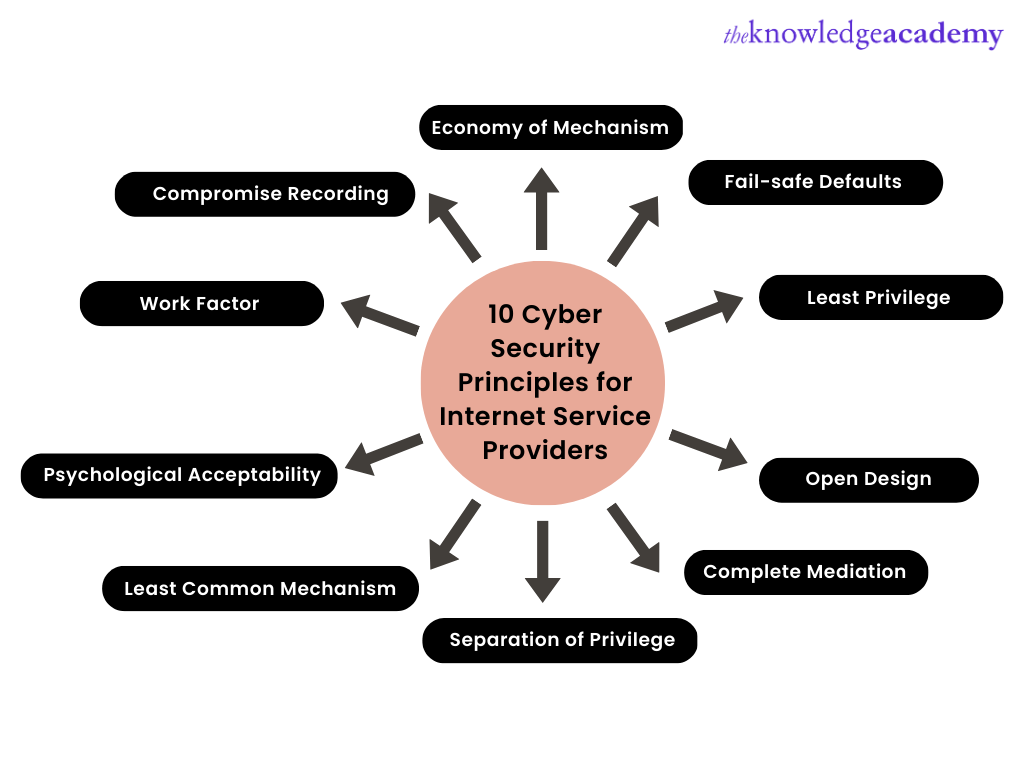
Here are the essential cybersecurity principles for Internet Service Providers (ISPs):
Economy of Mechanism
According to this notion, security measures must be as straightforward and compact as feasible. The economy of mechanism idea makes the design and deployment of security mechanisms easier. There are rarer chances for mistakes to occur with a straightforward and compact design and execution. Fewer components are needed to be checked as the checking and testing procedure is less challenging.
The interfaces between security modules should be as straightforward as feasible. Because the interface modules frequently make implicit assumptions regarding input, output, or the system's current state.
The module's activities can result in unexpected outcomes if these presumptions are incorrect. A simplified security architecture makes it easier for users and developers to comprehend. It allows for the rapid creation and validation of enforcement techniques.
Fail-safe Defaults
According to the fail-safe defaults principle, a system's default configuration should have a cautious protection strategy. Providing entry to an object is not recommended - when access, privileges/rights, or another security-related attribute is not immediately granted.
Example: If we allow a new user to access an operating system, the user's default group should have fewer access rights to files and services.
Least Privilege
According to this rule, a user should only have the necessary rights to carry out his duty. The assignment of rights given to the user needs to be controlled but not the user's identification. This implies that if the supervisor requests root access to a UNIX system, you shouldn't grant it unless the person in question has a responsibility that calls for that degree of access. Once such privileges are no longer required, these enhanced rights associated with a user identity should be deleted as soon as possible.
Open Design
According to this rule, a mechanism's security shouldn't depend on how secretly it was created or put into action. It implies that security is not increased by complexity. This idea runs counter to the notion of "security via obscurity." This theory applies to many security-related procedures of computers as well as information like passwords or cryptographic systems.
You can take an example of a DVD player with CSS (Content Scrambling System) security. The CSS is a cryptographic technique that guards against illegally copying DVD movie discs.
Complete Mediation
The restriction on information caching imposed by the entire mediation principle frequently results in the implementation of simpler mechanisms. This concept states that to verify access is permitted, every object's compliance with a protection system must be examined. Because the permissions might vary over time, performance enhancement approaches that preserve the details of earlier authorisation checks should be avoided.
The system should always verify the related access privileges whenever someone attempts to access an item. Once the subject's access privileges have been validated during the initial access, the system takes it for granted that the same access rights should be accepted for that subject to initiate further access.
Example: A website for online banking services that asks users to log in again after a certain amount of time is an effective measure in Cyber Security in Banking to prevent unauthorized access and protect sensitive information.
Separation of Privilege
According to this idea, a system should permit access depending on the fulfilment of many conditions. Due to its restrictions on access to system entities, this approach could potentially be limiting. Therefore, the two verifications should be carried out before the privilege is granted to the user. The two conditions that ought to be met are - the user must know the root password, and the user must be in the wheel group.
Least Common Mechanism
This concept argues that the methods allowing resources to be shared by several users should be limited as much as possible in systems having multiple customers. This principle may seem restrictive because it restricts distribution of resources.
For instance, if more than one person needs to access the same file or programme, they should do so over separate channels to avoid unintended effects that might compromise security.
Psychological Acceptability
According to this rule, a security measure shouldn't make a resource harder to access in case of the absence of a security measure. In computer security, the psychological acceptability concept acknowledges the role of people. Users won't apply the appropriate security mechanisms; if the security-related software or computer systems are difficult to set up, maintain, or use. For instance, if a password matches during the password-changing process, the password-changing application should explain why it was rejected instead of displaying a cryptic error message. However, the applications should not divulge any information that is not essential and might undermine security.
For instance, when we input the erroneous password, the system should only alert us that our user ID or password was entered incorrectly. It shouldn't just say that the password was incorrect because it would offer the attacker more information.
Work Factor
According to this rule, while creating a security system, the cost of defeating a security feature should be compared to the resources of a possible attacker. In some circumstances, it is simple to compute the cost of circumventing (also known as the "work factor"). In other words, the work factor is a widely used cryptographic metric to assess the robustness of encryption. Although it may not immediately relate to cybersecurity, the general idea does.
Consider the following scenario: If the number of tests needed to experiment for every potential four-character password is 264 = 456976. Then, one may consider a four-character password adequate if the prospective attacker had to test each experimental password at a terminal. On the other hand, a four-letter password would only be an obstacle for a possible intruder if they had access to an enormous computer that could attempt a million passwords every second.
Compromise Recording
According to the compromise recording concept, it is sometimes preferable to document the specifics of an intrusion rather than take a more complex precaution to avoid it.
Conclusion
This blog will help you analyze the top essential cybersecurity principles for Enterprises & Businesses, and Internet Service Providers. These guiding principles will help you understand the common cyber risks, including threats like Web Jacking in Cyber Security, which is a critical issue for online platforms. By following the steps and measures outlined, you can reduce online crimes and protect your systems from various cyber threats.
Are you interested in mastering skills to mitigate cyber-related risks? Then, register with the CCNA Cybersecurity Operation Training now!
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


