We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In today’s world, businesses are growing at a faster rate than ever before. Undoubtedly, technology and the Internet are at the core of this growth. But some believe this technological dependency is like a pandora’s box waiting to be opened. And when it does open, it’s going to create a list of problems when it comes to Cyber Security. And that’s where Cyber Security Standards come in to save the day.
According to Statista, about 22 per cent of the surveyed companies that experienced Cyber Attacks lost between 82,000 GBP to 411,350 GBP. With a single Cyber Attack, a company has a lot to lose as it compromises their security and results in loss of customer trust. This could dwindle the growth of small companies, and it’s already hard for them to get an International Certification like ISO.
But other Cyber Security framework standards and certifications are available that cost a lot less and are much easier to get. This blog will teach you about Cyber Security Standards and their types.
Table of Contents
1) Let’s find out what are Cyber Security Standards
2) List of Cyber Security Standards – Explained
a) ISO 27001
b) ISO/IEC 27031
c) ISO/IEC 27032
d) ISO/IEC 27035
e) ISO 22301
f) The IASME Governance Standard
g) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM)
h) PCI-DSS
i) Minimum Cyber Security Standard
j) GDPR
k) PAS 555
l) FINRA
3) Conclusion
Let’s find out what are Cyber Security Standards
Cyber Security Standards are a set of rules and guidelines that can improve an organisation's cyber security. Companies can use these standards to detect vulnerabilities in their security and deploy strategies to ensure the safety of their Cyber Space. Cyber Security Standards can improve the safety and security of a company’s Cyber Space.
Gain a deeper insight into managing the risks involved in Cyber Security. Register for our Cyber Security Risk Management Course now!
List of Cyber Security Standards - Explained
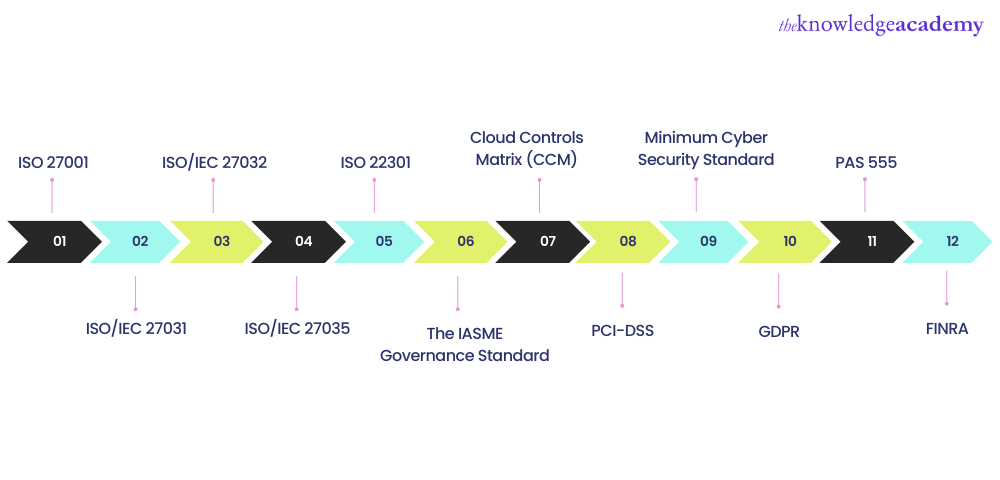
Let’s take a look at some of the lists of Cyber Security Standards:
a) ISO 27001
ISO 27001 is a standard defined by the ISO on how to practice and maintain the Information Security Systems in an organisation. It has three main components, namely:
1) Confidentiality: Confidentiality defines the protection of the Data and System and Network in an organisation/ Other than that, it emphasises some key security concepts like encryption and password management.
2) Integrity: Integrity ensures the Data, system or Network is not tampered with or destroyed. In addition, it provided the quality is well maintained and not downgraded at any point. No Unauthorised modification, upload or download of data.
3) Availability: When authorised users try to access the data, there should not be any interference. And ensuring only the authorised users get to access the data and prevent any unauthorised access. Apart from this, ensuring the availability of critical resources necessary for everyday operations like power backup, storage backup, server alternatives, and online and offline safety requirements.
b) ISO/IEC 27031
Provide guidelines for ICT (Informational and Communication Technology) readiness and business continuity for public and private organisations, regardless of size. It also provides methods to identify and work on critical areas like performance criteria, design and implementation. As a result, we can implement the PDCA cycle to ensure no disruption in an organisation’s ICT RBC (Readiness for Business Continuity).
1) Plan: Allows a company to define and identify its objectives, methods, targets and risk management and improves overall readiness to achieve quality and deliver results.
2) Do: This step is about implementing the IRBC policy, Operating procedures and processes we have defined in our planning phase.
3) Check: The check phase is about assessing and measuring the overall performance relative to the URBC Policy and then sending the report to the supervisors for review.
4) Act: Once the review is done, the organisation has to take appropriate preventive and corrective measures to improve the IRBC.
Benefits:
1) Improves an organisation’s ICT readiness and overall security
2) Creates a Business Continuity Program
3) Improves sustainability and its survivability
c) ISO/IEC 27032
The ISO/IEC 27032 focuses specifically on Cyber Security. It provides guidelines on protecting your systems and data from cyber-attacks and external attacks. It is necessary since you are one of many who have access to your Data. Your partners and other third-party vendors might also have access to your data. This standard focuses on all those aspects and helps you better manage your information sharing with your clients and suppliers.
d) ISO/IEC 27035
Now, the ISO/IEC 27035 is all about Cyber Security Incidents and how to manage them. It provides some best practices and guidelines for creating an incident management plan. Some of the critical components of 27035 are listed below:
1) Detect: Detecting if there’s any incident.
2) Report: Reporting the Security incidents so that we can come up with countermeasures. Reporting immediately allows us to assess the seriousness of the security incident.
3) Assess: Assess how the incident happened in the first place and its seriousness. Once the severity of the risk is defined, come up with an appropriate response.
4) Respond: Responding to the security Incident based on the initial assessment and implementing appropriate measures to mitigate and recover from the incident, as well as deploying countermeasures to prevent such incidents in the future.
Apply: Updating the security policies based on what they have learned from the issue.
e) ISO 22301
ISO/IEC 22301 gives guidelines for BCMS (Business Continuity Management Systems). It stresses the importance of Business Continuity. The Goals of this standard are listed below:
1) Understanding the necessities and requirements of an organisation to create business continuity policies.
2) Operating procedures, responsiveness and capabilities so that the organisation’s operations can continue without disruptions.
3) Observing and assessing, and improving the overall performance of BCMS.
4) Providing methods to improve the quality and quantity of the end product.
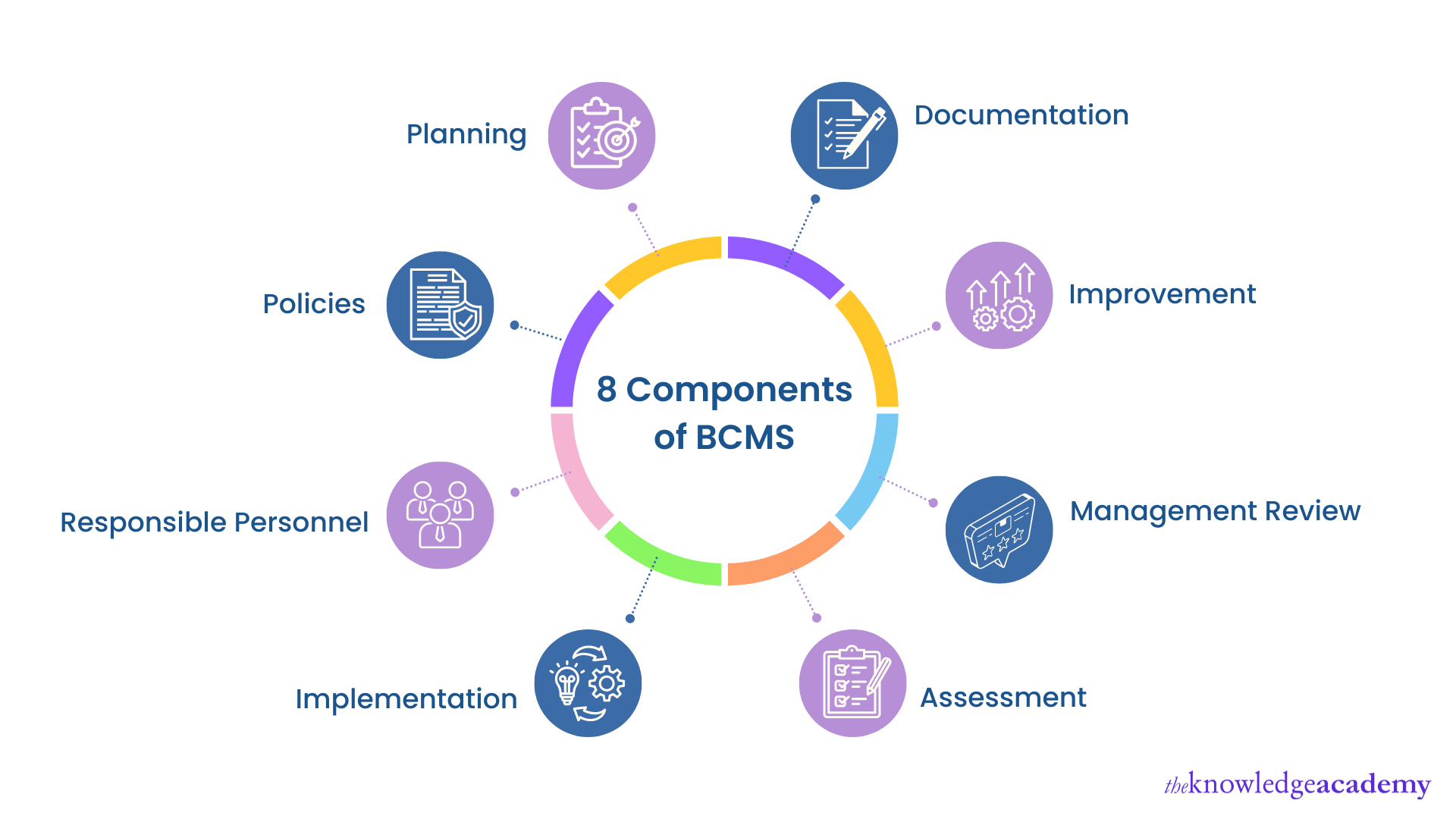
Components of BCMS
1) Planning: Come up with a feasible plan to ensure business continuity.
2) Policies: Creating Business Continuity Policies to allocate the responsibilities to the proper personnel.
3) Responsible Personnel: Having the right people with well-defined responsibilities ensures smooth operation.
4) Implementation: Implementing the Policies to produce qualitative and quantitative results.
5) Assessment: Check out and assess the performance of these policies now and then.
6) Management Review: Management reviews the Business Continuity report generated during the Assessment to take appropriate actions.
7) Improvement: Improving the procedures based on the feedback after the management review.
8) Documentation: Thorough documentation is critical for performance evaluation and future references.
Learn about Cyber Security threats businesses face today. Sign up for our Certified Cyber Security Professional Course now!
f) The IASME Governance Standard
The IASME Governance Standard is designed to improve the Cyber Security of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises (SMEs). Between 2009-2010 research about IASME was conducted in the UK. The IASME was later created in 2010 to demonstrate the Cyber Security capabilities of SMEs who don’t want to go through the complex and rigorous ISO Certification procedures.
Benefits:
1) Much more affordable than ISO Certifications.
2) Extraordinarily flexible, and the requirements are simple compared to ISO standards.
3) Very much in line with the Government of the UK‘s ten steps to Cyber Security.
4) Gives them a guided approach to the Supply chain.
5) Overall enables small businesses to have the competitive business advantage of having a certification and compete at the highest stage.
g) Cloud Controls Matrix (CCM)
The Cloud Control Matrix (CCM)is a security framework created by the Cloud Security Alliance (CSA) for Cloud Computing. It covers over seventeen domains with 197 control objectives to provide guidelines on which security controls to be implemented and by which actor within the supply chain of the Cloud.
It gives guidelines to auditors about the CCM audit areas and provides them necessary tools to perform a CCM-related assessment.
h) PCI-DSS
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS) is a set of standards created by major payment processing companies like MasterCard, Visa and American Express etc., in 2004. PCI-DSS are standards and guidelines selected by a company that receives payment through its payment gateway. If a company uses to process and stores client data like name and card information, they must be accepted by this standard.
i) Minimum Cyber Security Standard

Minimum Cyber Security Standard was created in collaboration with the NCSC and the UK government. It was designed to adhere to meet and exceed the minimum set of security standards within its departments.
Goals of this Standard:
1) To identify appropriate cyber security processes.
2) Identify and catalogue sensitive information, Key services they hold.
3) Ensure minimum access is given to sensitive data.
4) Ensure access to sensitive data is given only to authorised systems and users.
5) Ensure systems that contain sensitive data are protected.
6) Prevent cyber-attacks on highly privileged accounts.
7) Take other steps to identify other common Cyber Attacks.
8) Have a well-defined planning and tested response to Cyber Attacks.
9) No disruption in Business continuity and operations.
j) GDPR
General Data Protection & Regulation is a data protection and privacy law created by the EU. It was created to deploy proper security measures to ensure transparency and confidentiality of data.
k) PAS 555
PAS 555 was created by the British Standards Institution to focus on a results-based approach rather than focusing on the problem. It is created to give specific guidelines for creating an effective cyber-Security plan.
l) FINRA
FINRA was founded in 2007 as a self-regulatory organisation to regulate financial exchanges and Brokerage firms. They create and enforce the rules for the members registered with them who handle clients’ funds. These members can be brokers and dealers as well as monetary exchanges.
Conclusion
After reading this blog, we hope you got a clear picture of Cyber Security Standards and how they can benefit Small and Medium-sized organisations.
"Then, check out our Courses on Cyber Security Training to learn how to prevent and manage Cyber Security threats.
Get Ahead in the Cyber Security Field: Prepare with Key Cyber Security Interview Questions!"
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Certified Cyber Security Professional (CCS-PRO)
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 5th Dec 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


