We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Data plays a crucial role in decision-making processes for businesses and organisations in the modern digital era. Data Analytics and Data Visualisation are two essential components of the data-driven world.
While they may sound similar, they serve different purposes and have distinct methodologies. In this blog, we will expand on the Differences Between Data Analytics and Data Visualisation, shedding light on their different features, benefits and limitations.
Table of Contents
1) What is Data Analytics?
2) What are the types of Data Analytics?
3) What are the components of Data Analytics?
4) What is Data Visualisation?
5) What are the types of Data Visualisation techniques?
6) What are the advantages of Data Analytics and Visualisation?
7) What are some popular tools?
8) Data Analytics and Visualisation: Key differences
9) Conclusion
What is Data Analytics?
Data Analytics is a multifaceted process that involves examining, interpreting, and transforming raw data into meaningful insights. It amalgamates a wide range of techniques and methodologies aimed at uncovering patterns, trends, and valuable information hidden within vast datasets. The primary goal of Data Analytics is to derive actionable knowledge that can be used to make informed decisions and solve real-world problems.
At its core, Data Analytics is about asking questions about the data and finding answers through rigorous analysis. It begins with data collection from various sources, including databases, sensors, websites, and social media platforms. The data collected may be structured, such as databases and spreadsheets, or unstructured, such as text documents and images.
Once the data is gathered, the next step is data cleaning and preparation. This crucial phase involves removing errors, inconsistencies, and outliers to ensure the accuracy and integrity of the data. Data analysts must transform the data into a suitable format for analysis, ensuring it aligns with the objectives of the analytics process. Now, the application of statistical and mathematical algorithms helps in identifying patterns and relationships, clustering data points, and applying machine learning techniques for predictive modelling.
Data Analytics finds applications in various fields, including business, finance, healthcare, marketing, and science. Businesses use Data Analytics to optimise operations, enhance customer experiences, and gain a competitive edge. In healthcare, it aids in diagnosing diseases and predicting patient outcomes. In marketing, it helps identify customer preferences and target audiences effectively.
What are the types of Data Analysis?
The Data Analysis technique you decide to acquire depends on the kind of information you have. Accordingly, there are two main Data Analysis techniques. Namely, Qualitative and Quantitative. Let’s see what each means:
1) Quantitative Data Analysis
This type of Data Analysis is more on the side of the statistical nature of your data. It describes what is happening with the trends and whether they are showing a rise or fall. Below are the two types:
Descriptive analysis: This type of Data Analysis shows the patterns and trends in a particular database. It includes processes such as percentages, calculating frequencies, and measures of central tendency.
Inferential analysis: It is used to examine the differences and correlations between specific data sets. The processes include t-Tests, ANOVA, and Chi-Square.
2) Qualitative Data Analysis
While Quantitative analysis is focused on numeric data, Qualitative is the absolute opposite. It deals with non-numeric data. Additionally, Qualitative Data generally shows how your data is changing.
What are the components of Data Analytics?
Data Analytics components refer to the different techniques. It can be used for processing any dataset. These include:
1) Text Analytics: This is the technique used for the autocorrect feature in phones and software like Microsoft Word. It includes analysing large amounts of text that match with the algorithm. These applications include linguistic analysis and pattern recognition.
2) Data Mining: One of the most critical elements is determining behavioural patterns in inpatient data during trials. As the name suggests, Data Mining breaks down large chunks of data into smaller pieces. It is used to fit specific purposes.
3) Business Intelligence: This is one essential process for all successful businesses. It includes transforming data into actionable strategies for a particular commercial entity.
What is Data Visualisation?
Data Visualisation is an artful and powerful technique that involves representing complex data and information visually through charts, graphs, maps, and other graphical elements. Its primary objective is to present data in a visually engaging and easily understandable format, enabling viewers to grasp patterns, trends, and insights effortlessly.
At its core, Data Visualisation is about transforming raw data into visual representations that communicate information effectively. It goes beyond traditional data tables and textual reports, leveraging the power of visual perception to enhance data comprehension. By presenting data visually, it becomes more accessible and relatable, making it easier for both technical and non-technical audiences to interpret and draw conclusions.
Data Visualisation uses a variety of graphical tools and techniques to depict data. Common types of visualisations include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts, scatter plots, heat maps, and geographical maps. Each kind serves a specific purpose and can represent different data characteristics.
Data Visualisation finds applications across various industries and domains. In business, it helps identify sales trends, customer preferences, and market insights. In journalism, Data Visualisations accompany news stories to provide data-driven context. In scientific research, visualisations aid in presenting complex findings and research outcomes.
Transform complex data into stunning visuals with our Data Visualisation Training With D3 – join now!
What are the types of Data Visualisation techniques?
Just like Data Analytics, there are several types of Data Visualisation techniques. People choose them largely depending on the type of data that needs to be modelled with the intended purpose. It is worth noting that some Visualisations are manually created. Meanwhile others are automated. Listed below are some of the popular Visualisation techniques:
1) Histograms
2) Graph
3) Fever Charts
4) Heatmap Visualisation
5) Infographics
6) Dashboards
7) Geospatial
What are some popular tools for Data Visualisation?
Some of the most popular Data Visualisation tools on the market include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, Google Charts, Looker, QlikView, Grafana, FusionCharts, Chartist.js, and D3.js. Data Engineers use them to visualise and present complex information. Hence, these software can help you to effectively convey critical message.
Yellowfin is another Data Visualisation tool that supports a drag and drop builder. It helps in building reports and dashboards without worrying about SQL. It also contains dozens of out-of-the-box visualisations that non-technical end-users and analysts alike can use quickly and easily.
What are the advantages of Data Analytics and Visualisation?
Data Analytics and Visualisation are crucial elements of a business’ decision-making process. It helps stakeholders to recognise patterns and devise profitable business strategies. Here are some of the benefits of Data Analytics and Visualisation:
1) Better decision-making: Using skilled Data Analysts and the right software is necessary. This is how companies can identify market trends. It is used make better business decisions to boost sales and profits.
2) Better insights: Companies get better insights into their customer base. Using Data Analytics and Visualisation, companies can disintegrate large customer data down into smaller sets. It can be used to understand the target audience better.
3) Improving productivity and revenue growth: By looking at the results from Data Analytics and Visualisation, companies understand which areas they need improvement and which ones to invest in. It also helps in deciphering what processes need to be automated for better efficiency.
4) Realising changes in market behaviour: With a real-time Data Analytics and Visualisation Dashboard, company stakeholders can quickly identify changes in market behaviour. This helps in making appropriate business decisions.
5) Business trends: One of the most valuable applications of Data Analytics and Visualisation. It allows businesses to examine the present and past trends. It helps to make predictions that determine all future strategies for the business.
6) Data relationships: This is one of the biggest benefits of Data Analytics and Visualisation. It helps companies to understand relationships between independent data sets. This in turn help in making business decisions based on these results.
7) Ease of understanding: The value of Data Visualisation is straightforward. It allows people to interact with and understand data. Whether simple or sophisticated, the appropriate visualisation can get everyone on the same page, regardless of their degree of knowledge.
Data Analytics and Visualisation: Key differences
Now that we know what is Data Analytics and Visualisation is, we will now dive into Data Visualisation vs Data Analytics. This section of the blog will expand on the key differences between Data Visualisation and Data Analytics.
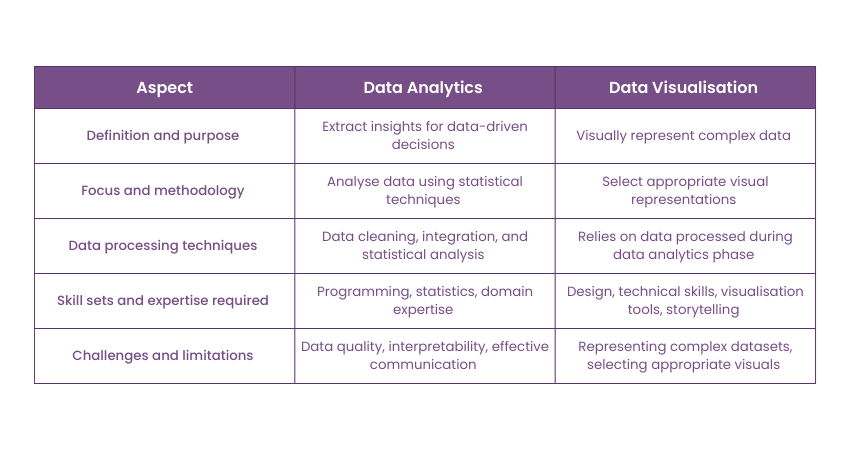
Definition and purpose
Data Analytics involves the systematic examination of datasets to draw meaningful conclusions and extract valuable insights. It encompasses various techniques, including statistical analysis, machine learning, Data Mining, and data exploration.
The primary purpose of Data Analytics is to answer specific questions, uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data, and gain actionable knowledge. It empowers businesses to make informed decisions, optimise processes, improve efficiency, and enhance overall performance.
Data Visualisation is the art of representing data visually through charts, graphs, maps, and other graphical elements. Its purpose is to simplify complex data and present it in an easily understandable and engaging manner. By transforming raw data into intuitive visuals, Data Visualisation facilitates quick comprehension of information and helps identify patterns, outliers, and trends. It enhances data communication, making it accessible to a broader audience and enabling stakeholders to grasp key insights effortlessly.
Want to unlock the power of Data Analytics? Join our Advanced Data Analytics Course now.
Focus and methodology
Data Analytics aims to uncover the "what" and "why" behind the data, seeking explanations for past events and predicting future outcomes. Data Visualisation, on the other hand, concentrates on the presentation of data rather than the data itself. It focuses on selecting appropriate visual representations that effectively convey insights to the audience.The methodology includes choosing the right chart types, colours, and design elements to enhance understanding and engagement. Data Visualisation aims to communicate the "what" discovered through Data Analytics in a visually compelling way, facilitating decision-making based on the insights.
Data processing techniques
Data Analytics involves various data processing techniques to prepare the data for analysis. Data cleaning is crucial to eliminate errors and inconsistencies that could skew results. Data integration amalgamates data from multiple sources to create a unified dataset for analysis. Data transformation standardises data formats and scales variables for more meaningful comparisons. Exploratory data analysis helps in understanding the data's distribution and characteristics before applying statistical techniques.
Data Visualisation does not directly involve data processing. However, it relies on the data preparation carried out during the Data Analytics phase. The data needs to be well-organised and analysed before creating visual representations. The processed data serves as the foundation for the design of visually appealing and informative graphics.
Want to take your Data Science skills to the next level? Join our Big Data Analytics & Data Science Integration Course now!
Skill sets and expertise required
Data Analytics professionals require a diverse skill set to navigate the complexities of data analysis. Proficiency in programming languages like Python or R is essential for data manipulation and modelling. Strong knowledge of statistical concepts and machine learning algorithms enables them to apply appropriate techniques. Domain expertise allows analysts to interpret the results in the context of specific industries or business problems.
Data Visualisation experts need a combination of creative and technical skills. Design principles and data storytelling proficiency enable them to create compelling visuals. Proficiency in Data Visualisation tools like Tableau, Power BI, or D3.js is essential for implementing design concepts effectively. Additionally, an understanding of human perception and cognition helps in designing visuals that resonate with the audience.
Challenges and limitations
Data Analytics faces challenges related to data quality, especially when dealing with large, messy, or incomplete datasets. Ensuring data privacy and complying with data protection regulations is another significant challenge. The interpretability of complex analytical models can be difficult, and communicating technical findings to non-technical stakeholders requires effective data storytelling skills.
Data Visualisation has limitations in effectively representing multi-dimensional and highly complex datasets. Choosing the wrong visualisation type or misrepresenting data can lead to misinterpretation or biased conclusions. Addressing the diverse needs of different audiences and ensuring visual accessibility for all users is also challenging.
Conclusion
All in all, Data Analytics and Data Visualisation are essential pillars of the data-driven world. While Data Analytics delves into uncovering insights and patterns, Data Visualisation transforms these findings into visually appealing representations. By understanding the unique aspects of each field and combining their strengths, businesses can harness the power of data to make informed decisions and drive success in the digital era. Hope we can provide you with the detailed comparison of Data Analytics and Visualisation that you were looking for!
Unlock the power of data with our comprehensive Data Science & Analytics Training. Sign up now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Data Visualisation is about presenting large amounts of information (Big Data) in easy and understandable ways. This work can be done by both - Data Analysts or Data Scientists. However, it's becoming more common for organisations to employ specialist Data Visualisation Analysts.

The availability of huge volumes of data is leading to an increased demand for professionals with good Data Visualisation skills.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Data Analytics and AI courses, including Big Data and Analytics Training, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Courses, AI Voice Assistant Training, and Data Science Courses. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Data Preprocessing in Machine Learning.
Our Data Analytics and AI blogs cover a range of topics related to AI, ML, and tech advancements, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Analytic skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Data Analysis and Visualisation with Python
Data Analysis and Visualisation with Python
Thu 1st Jan 1970







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


