We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Imagine there’s a complex labyrinth of data where hidden treasures are waiting to be unearthed. In such a scenario, machines stand at the edge of becoming conscious to mimic what humans can do.
Stealing the scene, Data Science and Artificial Intelligence—the dynamic duo reshaping our world since the advent of digitalisation.
Data Science specialises in data applications to identify hidden patterns and insights. While AI breathes life into machines to enable them to replicate human intelligence. Together, they serve as the rewriters of the rules and bridge the gap between today and tomorrow.
In this blog, we will dive into the world of Data Science and Artificial Intelligence and explore how these dynamic fields complement each other by driving innovation and transforming industries.
Table of contents
1) What is Data Science?
2) What is Artificial Intelligence
3) Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: What’s the Difference?
4) Career Paths: Data Science vs Artificial Intelligence
5) Similarities Between Data Science and Artificial Intelligence
6) Salary Insights: AI Engineers vs Data Scientists
7) What Makes Data Science and AI Essential Today?
8) What Are the Applications of Data Science and AI?
9) Conclusion
What is Data Science?
Data Science is a discipline that leverages the advanced applications of data, technology, and expertise in specific domains. It consists of various activities that aim to extract meaningful insights and actionable knowledge from large sets of complex data. To describe it in brief, Data Science answer critical questions and solves real-world problems through an enormous power of data.
Core Components of Data Science
Data Science helps us turn information into meaningful insights. Let us look at the core components of Data Science:
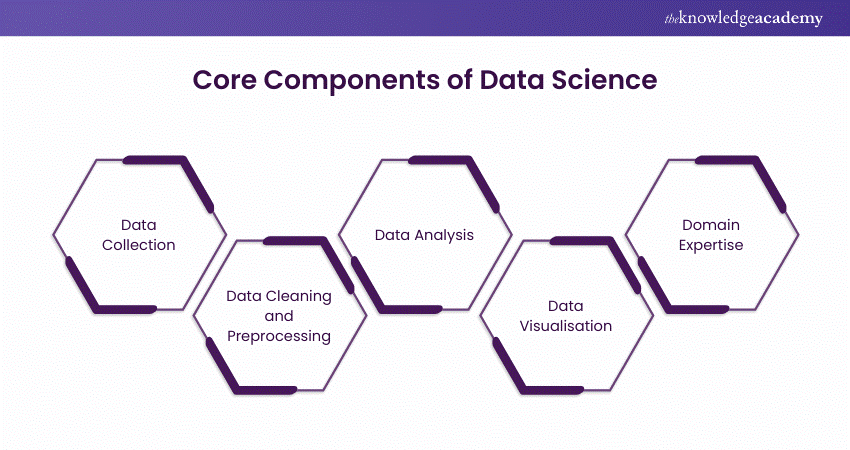
a) Data Collection: The process begins with data collection from various sources. These include databases, sensors, and social media. Data Scientists acquire these relevant data that aligns with the objectives of their analysis.
b) Data Cleaning and Pre-processing: Raw data is often complex and contains a lot of errors, such as missing values or inconsistencies. Data cleaning helps in painstaking tasks by rectifying these issues to make sure the data coming is accurate and reliable throughout the process.
c) Data Analysis: Data Scientists employ numerous Statistical and Analytical techniques to explore patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. The main objective of this phase is to perform Descriptive Statistics, Hypothesis Testing, and Exploratory Data Analysis. The aim here is to gain an understanding of the information contained within the dataset(s).
d) Data Visualisation: Turning data into actionable insights often involves presenting the findings visually. Data visualisation techniques like charts, graphs, and dashboards, help convey complex information to non-technical stakeholders in an easily digestible format.
e) Domain Expertise: Understanding the context of the data is crucial. Domain expertise, whether in healthcare, finance, marketing, or any other field, allows Data Scientists to interpret the results in a relevant and meaningful manner and address industry-specific problems.

What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is an evolving branch of Computer Science and Engineering. It focuses on creating systems and technologies capable of performing tasks that usually require human intelligence.These tasks rely on various cognitive functions, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and learning. They also include understanding natural language and perceiving how to interact with the environment.
Core Components of AI
Artificial Intelligence is transforming the way how we are living, working, and innovating today. Let’s look at the core components of Artificial Intelligence:
a) Machine Learning: Machine Learning is a foundational component of AI. It mainly comprises enabling computers to learn from data and make effortless decisions without the explicit programming knowledge. The common Machine Learning techniques include Supervised, Unsupervised, and Reinforcement Learning.
b) Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP is focused on enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This includes tasks such as Sentiment Analysis, Speech Recognition, and Language Translation. NLP is crucial for applications like chatbots and virtual assistants.
c) Computer Vision: Computer vision enables machines to interpret visual information from the world through images and videos. It finds a diverse range of applications in Facial Recognition, Object Detection, autonomous vehicles, and Medical Image Analysis.
e) Robotics: Robotics is a branch within AI that focuses on designing and building robots. These robots can effortlessly perform tasks autonomously or in collaboration with humans in fields ranging from manufacturing to healthcare.
Master Data Science with Python-driven insights- Join our Python Data Science Course now!
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence: What’s the Difference?
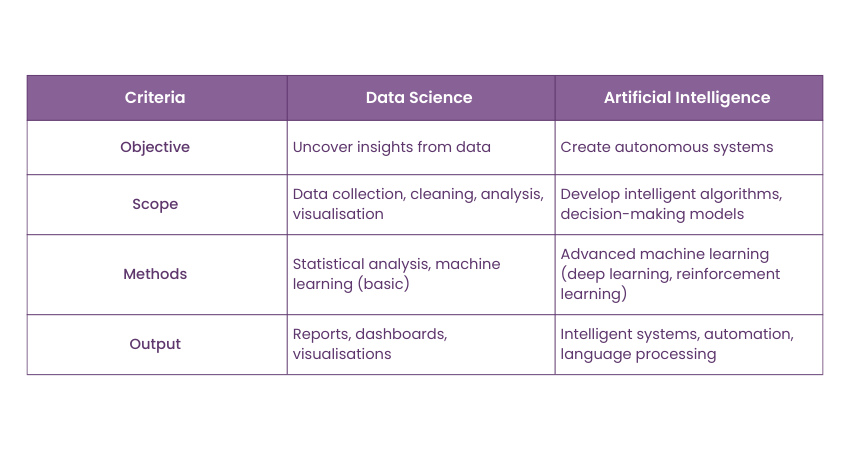
While both Data Science and Artificial Intelligence have some important similarities between them in terms of their data usage, they differ widely as objectives, scope, methodologies, and applications. Here are the key differences that set them apart:
1) Objectives
Data Science primarily involves uncovering insights, patterns, and relationships within data to make informed decisions. It majorly aims to answer questions like "What happened in the past?" and "Why did it happen?" Moreover, it lays major emphasis on Descriptive and Diagnostic Analytics.
In contrast, AI primarily aims to develop systems that can perform tasks autonomously, often without human intervention. It addresses questions like "What will happen in the future?" and "What should be done about it?" Here, the major emphasis is on Predictive and Prescriptive Analytics.
2) Scope
Data Science have a broader range of activities, including data collection, cleaning, analysis, and visualisation. It also serves as the foundational step for AI projects through performing necessary data and insights analysis.
In contrast, AI is a narrower field. It primarily focuses on creating intelligent Algorithms and models that can make human-driven decisions, understand natural language, and control autonomous systems. AI techniques are used within Data Science workflows to enhance Predictive Analytics capabilities and insights.
3) Methods and Techniques
Data Science employs various Statistical and Machine Learning techniques. These include Regression Analysis, Clustering, and Decision Trees. The main emphasis is on placing the interpretability of models and extracting meaningful insights from data.
On the other hand, Artificial Intelligence heavily relies on advanced Machine Learning practices such as Deep Learning, Reinforcement Learning, and Neural Networks. AI models are often complexprioritise accuracy and predictive performance over interpretability.
4) Outputs and Applications
Data Science typically generates reports, dashboards, and visualisations to communicate data trends and support informed decision-making. It is widely used in fields like business analytics, marketing optimisation, financial forecasting, and healthcare data analysis.
On the contrary, AI produces intelligent systems or applications that can automate tasks, make recommendations, understand and generate human language, and even perform creative tasks. AI applications are widely applied in contexts like autonomous vehicles, chatbots, recommendation engines, image and Speech Recognition, and Robotics.
Engineer accurate forecasting models with our Predictive Analytics Course - join now!
Career Paths: Data Science vs Artificial Intelligence
A data scientist's main focus is primarily technical, as it involves delving deep into Data applications. They are responsible for collecting and processing data, selecting the appropriate models, and interpreting results to make recommendations. Their work can also involve specific software or systems or even developing these systems themselves.
1) Types of Roles
a) Data Science Jobs: These jobs typically include Data Analyst, Data Engineer, Data Scientist, Machine Learning Engineer, Research Scientist, Data Visualisation Specialist, and Field-specific Analyst roles.
b) Artificial Intelligence Jobs: This field of job encompasses all Data Science roles and includes additional roles such as AI Tester, AI Engineer, Software Developer, Product Manager, and Marketing Specialists.
2) Skillset
a) Data Scientists: Data Scientists must showcase proficiency in Statistical and Algorithmic methods. They typically require a strong background in statistical mathematics, computer science, and expertise in applicable tools like Python and Hadoop.
b) Artificial Intelligence Professionals: AI professionals’ skillset varies according to the roles. For example, technical roles (e.g., AI Software Developer) require Programming Languages, Libraries, and tools. In contrast, non-technical roles (e.g., AI Tester) require Linguistic Skills, Creative Thinking, and User Interaction understanding.
3) Career Progression
a) Data Science: As tools grow more automated, the core Data Science roles might decrease. In this case, their career paths will be inclined toward paths like academic and cutting-edge application roles. These include Analyst roles, senior positions, Project Management, and Chief Data Officer.
b) Artificial Intelligence: Career progression depends on role focus. Some of the common leading career progressive roles include Chief Technology Officer, Chief Marketing Officer and Chief Product Officer. You need to consider which jobs might be automated in the next decade to future-proof your career.
Similarities Between Data Science and Artificial Intelligence
Both Data Science and AI employ tools, techniques, and Algorithms to analyse and leverage vast amounts of data. Here are some similarities between them:
1) Predictive Applications
Both Data Science and Artificial Intelligence make predictions using models learned from the analysis of previous data. For example, identifying and predicting diseases is based on past data (Time Series Data Analysis).
Similarly, Predictive AI Systems like Self-driving Cars can calculate distances between moving cars and their speeds. This enables them to avoid crashes by predicting when the vehicle in front will apply sudden brakes.
2) Data Quality Requirements
Both Data Science and Artificial Intelligence technologies can produce less accurate results if they are trained with inconsistent, biased, or incomplete data. It's important to consider several aspects when working with these technologies.
Firstly, algorithms might filter out new data if it doesn't match their original dataset. Secondly, they may prioritise certain attributes over others if the input data lacks variety. Lastly, if the input data is false, these algorithms can generate fictional information.
3) Machine Learning
Machine Learning (ML) is a sub-type of both Data Science and Artificial Intelligence. Here are the points to remember about Machine Learning:
a) Misconceptions: Not all AI uses ML, and not all data science solutions involve ML.
b) Model Classification: All ML models are considered data science models as well as AI Algorithms.
Deepen your understanding of Data Science with our Data Mining Course. Sign up now!
Salary Insights: AI Engineers vs Data Scientists
Artificial Intelligence Engineers and Data Scientists have competitive salaries due to their specialised skills in handling complex datasets and developing AI-driven solutions. With the rising demand for AI and data-driven decision-making across industries, professionals as Data Scientists and AI Engineers can expect lucrative compensation packages. Based on a Glassdoor, the average salary for AI Engineer is £55,233 per year in the United Kingdom. Their average additional cash compensation is £3,725, with a range from £1,735 to £7,994.
In contrast, the average salary for a Data Scientist Salary is £52,885 per year in the United Kingdom. Their average additional cash compensation is £4,901, with a range from £2,304 - £10,428.
What Makes Data Science and AI Essential Today?
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are equally crucial in today's world because they help us understand and utilise vast amounts of data. Here are some key qualities that highlight their importance:
1) Data Analysis and Decision Making: Data Science allows us to analyse large datasets, uncover patterns, and make informed decisions. This leads to better strategies in areas like healthcare, finance, and technology.
2) Automation and Intelligent Solutions: AI enhances data analysis by automating tasks and providing intelligent solutions. It powers technologies such as recommendation systems, virtual assistants, and autonomous vehicles, performing tasks faster and more accurately.
3) Driving Innovation and Efficiency: Together, Data Science and AI drive innovation and improve efficiency across various industries. They enable personalised customer experiences, predictive maintenance, and smarter decision-making.
4) Staying Competitive: In a world where data is constantly growing, Data Science and AI are essential for staying competitive and solving complex problems. They help businesses, governments, and individuals make sense of the data and use it effectively.
What Are the Applications of Data Science and AI?
Data Science and Artificial Intelligence (AI) have diverse applications that transform industries and improve daily life. Here are some key points that highlights their impact:
1) Healthcare: Data Science and AI assist in diagnosing diseases, predicting patient outcomes, and developing personalised treatment plans. AI-powered tools, such as imaging systems and drug discovery algorithms, have revolutionised medical research and care.
2) Business: These technologies enhance decision-making, optimise operations, and improve customer experiences. Companies use AI for chatbots, fraud detection, and recommendation systems, while data analytics helps identify market trends and customer preferences.
3) Transportation: Data Science and AI play a significant role in transportation by powering autonomous vehicles and improving traffic management systems.
4) Education: In education, they enable personalised learning experiences and automate administrative tasks.
5) Other Fields: With applications in finance, agriculture, and entertainment, Data Science and AI are shaping a smarter, more efficient world.
Apply Bayesian methods for advanced Data Science modeling- Sign up for our Probability and Statistics for Data Science Training now!
Conclusion
We hope you get an idea about the differences between the two of the most prominent fields of digitalisation. Data Science and Artificial Intelligence work together to transform data into insights and intelligent automation. This collaboration helps to drive innovation and highlights their importance in solving real-world problems. Understanding their unique roles and combined power is crucial in today’s data-driven world.
Optimise Neural Networks using Keras frameworks- Register for our Keras Training for Data Scientists now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Data Science helps with decisions using data, while AI handles tasks and solves problems. The suitable choice depends on your career goals. Both fields offer exciting opportunities and are essential in shaping the future of technology.

Yes, Data Science and Artificial Intelligence can certainly be the future of technology and business. They are revolutionising innovation across sectors like Finance, Transportation, Healthcare, and Entertainment, for automating highly intricate tasks.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers Data Science Courses including Advanced Data Science Certification, Python Data Science Course, and Keras Training for Data Scientists. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Big Data Analyst Job Description.
Our Data, Analytics and AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to transforming businesses, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. So, whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Data Science skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Python Data Science Course
Python Data Science Course
Mon 6th Jan 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Mon 26th May 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 20th Oct 2025
Mon 1st Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course


 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


