We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Every time the topic of advanced technology springs up among tech-savvy circles, two terms frequently drive the conversation - Machine Learning and Deep Learning. These are like two sides of the same coin - Artificial Intelligence (AI). But it's also easy to get these two terms mixed up. So, what exactly are the distinctions between Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning?
This blog answers this question, shedding light on the key differences between Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning and outlining their strengths and exciting real-world applications. So read on and learn how they are quickly becoming the heart of modern technology!
Table of Content
1) Understanding Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning
2) Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Core differences
3) Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Real-world examples
4) Advanced Machine Learning applications
5) Advanced Deep Learning applications
6) Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Career Comparison
7) Is ChatGPT a Deep Learning Model?
8) Is CNN Deep Learning or Machine Learning?
9) Conclusion
Understanding Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning
Navigating the landscape of Artificial Intelligence necessitates a grasp of its two pillars: Machine Learning and Deep Learning. Let’s explore them in detail and uncover what makes them power Artificial Intelligence:
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning, often hailed as the bedrock of modern Artificial Intelligence, allows computers to undertake tasks without a rigid set of programmed instructions. Instead of relying on explicit coding for every conceivable scenario, ML uses algorithms that evolve and adapt by continually processing and learning from data.
This iterative learning method helps systems improve their performance, and facilitates data-informed and experience-driven decisions. ML is the silent powerhouse behind diverse applications we use daily, from predicting stock market fluctuations to delivering personalised content recommendations.
Deep Learning (DL)
Often perceived as the next frontier in AI evolution, Deep Learning delves even deeper into the complexities of data interpretation. Drawing inspiration from the complex architecture of the human brain, DL aspires to emulate human's inherent ability to discern patterns, process multifaceted data, and draw insights. This is achieved through layered structures, notably Neural Networks and more specifically, Deep Neural Networks. For those eager to dive into this field, learning Deep Learning with Python can provide an essential foundation for building such complex models effectively.
Each layer in these networks processes information, refines understanding, and passes on the distilled knowledge to subsequent layers. The importance of deep learning lies in this multi-layered approach, enabling nuanced data analysis—from recognizing faces in images to comprehending the subtle inflections in spoken language. In essence, while ML lays the groundwork, DL endeavors to push the boundaries of what machines can perceive and understand.
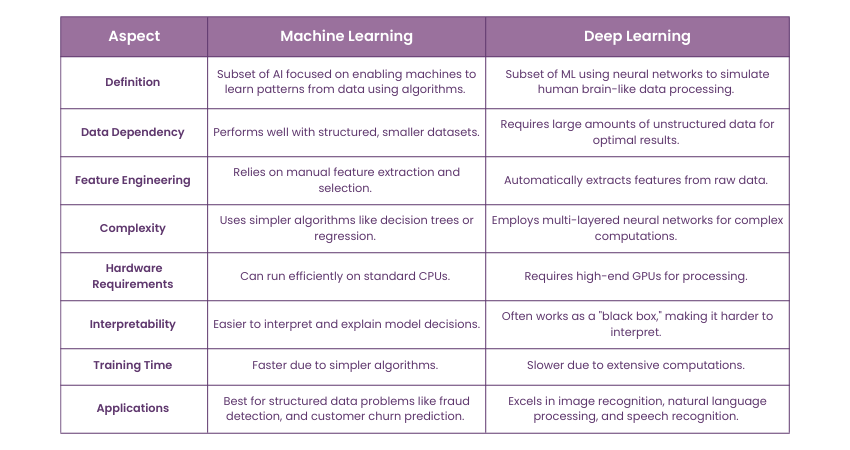
Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Core Differences
While Machine Learning and Deep Learning are subfields of AI, their methodologies, requirements, and operational complexities differ significantly. The following table summarises the distinctions between the two:
Master the fundamentals of AI and their real-world applications in our Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Courses today!
Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Real-world Examples
As the potential of Artificial Intelligence continue to expand, the differences between Machine Learning and Deep Learning become particularly essential. Through real-life examples, we can better understand their distinct operational mechanisms and their profound implications in real-world applications.
Image Recognition
Imagine a mobile application that identifies various animal species solely based on photos. Such a task, which requires the differentiation of subtle characteristics, brings the distinctions between Machine Learning and Deep Learning into sharp focus. Consider the following points:
a) A Machine Learning model for this task relies on explicitly provided features. Data Scientists must extract details like fur patterns, ear shapes, and tail lengths. The model's performance depends on the completeness and quality of these handcrafted features, limiting its potential.
b) In a similar task, a Deep Learning model, particularly a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), would sift through the same images without any predefined features. Instead, the model would 'teach' itself by identifying and learning features automatically through its layered structure.
c) Early layers might detect edges, while deeper layers could recognise complex patterns like fur textures. Given a sufficiently vast dataset, DL models can surpass ML models in image recognition, not just in accuracy but also in their ability to generalise images they've never seen before.
Speech Recognition
The voice-activated virtual assistants in our pockets, such as Siri or Alexa, showcase the transition from Machine Learning to Deep Learning in speech recognition. Earlier voice recognition systems leaned on Machine Learning algorithms which were fed features extracted from sound waves, such as:
a) Pitch.
b) Duration.
c) Intensity.
ML models attempted to transcribe or understand spoken language based on these features. However, they often struggled with variations in accents, speech speed, or background noise.
Modern voice recognition systems predominantly use Deep Learning, specifically Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs). In practical terms, this technology is useful for tasks like Connecting Alexa to TV, where models process raw audio to understand commands with precision. The resulting system can:
a) Adapt to diverse accents.
b) Understand context.
c) Recognise multiple speakers.
Boost your confidence with expert Machine Learning Interview Questions. Start prepping today!
Medical diagnoses
With its rich data and critical decision-making, the medical field presents an interesting arena for ML and DL comparisons. Consider the following:
An ML model in healthcare might operate based on structured data. Given a list of symptoms, patient histories, and lab results, it could predict potential diseases or medical conditions. While invaluable, its insights remain bound to the input data's structure and quality.
Deep Learning's prowess shines when handling unstructured data, such as medical images. A DL model, like a CNN, could process X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans to detect anomalies. By analysing thousands of images, it learns to identify subtle patterns, perhaps even those invisible to the human eye, like the early stages of a tumour. Consequently, it promises to deliver more accurate, early, and potentially life-saving diagnoses.
Master in-demand skills for applying AI to Microsoft Excel AI and ML With Excel Training today!
Advanced Machine Learning Applications
Diving deeper into Artificial Intelligence reveals the intricacies of advanced Machine Learning Applications. Some of these are as follows:
Fraud Detection
Machine Learning models for fraud detection primarily use supervised learning. The models are trained using datasets that comprise both legitimate and fraudulent transactions. Features might include transaction amount, location, merchant details, time of transaction, and the nature of the item/service purchased. Over time, the model recognises intricate patterns and associations that typically signify fraudulent activity.
With more advanced detection capabilities, businesses can significantly reduce financial losses due to fraud. This not only has economic benefits but also helps retain consumer trust. The timely detection and prevention of fraud can also serve as a deterrent, making malicious entities reconsider their tactics.

Predictive Maintenance
Sensors on machinery continuously collect temperature, vibrations, noises, and more data. Machine Learning models, using this data, learn the normal operational patterns of the equipment. When the equipment starts behaving anomalously – indicating wear, degradation or imminent malfunction – the model picks up these subtle cues long before a catastrophic failure.
Predictive maintenance plays a vital part in reducing unnecessary costs. Pre-empting breakdowns allows companies to avoid unplanned downtimes, which can be costly regarding production losses. Additionally, timely maintenance extends machinery lifespan, leading to capital expenditure savings.
Sentiment Analysis
Text data, sourced from various online platforms, undergoes preprocessing, including tasks like tokenisation, stop-word removal, and lemmatisation. ML models are trained to understand the context, nuances, and sentiments behind the processed text data. Using Natural Language Processing (NLP), these models can classify sentiments as positive, negative, or neutral.
Equipped with sentiment insights, businesses can make informed decisions about marketing campaigns, product launches, and public relations strategies. It offers them with a pulse on consumer sentiment, which enables proactive measures in Reputation Management.
Interested in machines and AI? Unleash their potential and your career prospects through our comprehensive Machine Learning Training today!
Advanced Deep Learning Applications
Venturing further into the complexities of Artificial Intelligence, you encounter the sophisticated realm of advanced Deep Learning Applications. Some of these are as follows:
Healthcare Imaging
Deep Learning models and Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) in particular are trained using vast datasets of labelled medical images. These models can discern between healthy and pathological tissues. The hierarchical nature of CNNs allows them to detect intricate patterns, ranging from larger organ structures to microscopic cellular anomalies.
Deep Learning in medical imaging can help revolutionise healthcare. Early detection of conditions like tumours can lead to timely interventions, improving patient prognosis. It also helps radiologists by reducing their workload and offering a second, highly reliable opinion.
Video Surveillance
Deep Learning models process video data frame by frame. Features are extracted using CNNs, and the temporal sequence of these features is analysed, often using Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory networks (LSTMs). This enables the recognition of suspicious activities or patterns over time.
Enhanced surveillance can drastically improve public safety. Rapid detection and response to potential threats help prevent crimes or emergencies. It also aids law enforcement agencies in post-incident investigations, providing crucial insights and evidence.
Generative Design
Using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), a two-network system is established. One network (the generator) produces designs, and the other (the discriminator) evaluates them. Over iterations, the generator produces increasingly refined designs based on feedback from the discriminator.
Generative design has the potential to disrupt traditional design and manufacturing paradigms. Industries can achieve optimised, innovative, and often unforeseen design solutions by rapidly generating and evaluating myriad design variations. This can lead to more efficient, ergonomic products tailored to specific requirements.
Learn everything about neural networks and Deep Learning models with our Deep Learning Training today!
Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning: Career Comparison
Artificial Intelligence has expanded exponentially over recent years, with both ML and DL at the forefront of this growth. For individuals considering a career in either domain, understanding the nuances between them can provide valuable insights into potential career trajectories, roles, and skill requirements.
Foundational Knowledge
Here are the principles that underpin the world of Artificial Intelligence:
a) Machine Learning: A career in ML generally requires a robust understanding of algorithms, data structures, linear algebra, and statistics. ML engineers and data scientists frequently employ traditional algorithms like decision trees, K-means Clustering, Support Vector Machines (SVM) and clustering techniques.
b) Deep Learning: In addition to the foundational knowledge required for ML, DL professionals need a deep understanding of neural networks, particularly architectures like CNNs (for image data), RNNs and LSTMs (for sequential data), and GANs (for generative tasks). Familiarity with GPU computing and optimisation techniques for neural networks is also crucial.
Tools and Technologies
Here are the innovative instruments and platforms that drive modern AI advancements.
a) Machine Learning: Common tools include Python (especially libraries like Scikit-learn, Pandas, and NumPy), R, SQL, and platforms like Jupyter and Tableau.
b) Deep Learning: DL practitioners predominantly use frameworks like TensorFlow, Keras, PyTorch, and Caffe. The ongoing debate of PyTorch vs TensorFlow highlights the distinct preferences of developers based on project needs and personal expertise. Given the computational demands of Deep Learning models, a proficiency in CUDA and experience with Cloud platforms like Google Cloud ML and AWS SageMaker can be beneficial.
Roles and Specialisations
Here are the diverse career paths and niche expertise within the AI landscape.
a) Machine Learning: Career roles in ML encompass ML Engineers, Data Scientists, Data Analysts, and Research Scientists. Specialisations can include Natural Language Processing (NLP), computer vision (to a certain extent), and reinforcement learning.
b) Deep Learning: DL specialists often have titles like Deep Learning Engineer or Deep Learning Researcher. Specialised roles include medical imaging, autonomous driving, speech recognition, and generative design.
Industry Applications
Here are the myriad sectors harnessing the transformative power of AI solutions.
a) Machine Learning: ML professionals often find finance roles (for risk assessment and fraud detection), e-commerce (for recommendation systems), healthcare (for predictive analysis), and many other industries that leverage data for insights.
b) Deep Learning: DL specialists have been in rising demand in industries like the automotive sector (for autonomous vehicles), entertainment (for content generation), healthcare (for advanced medical imaging), and tech giants developing virtual assistants.
Research and Development
Here are cutting-edge investigations and innovations shaping the future of AI.
a) Machine Learning: Research in ML focuses on improving existing algorithms, understanding data biases, developing new methodologies for diverse data types, and ensuring model transparency and fairness.
b) Deep Learning: Research in the Deep Learning Techniques domain often delves into developing novel neural architectures, optimisation techniques, transfer learning, and making DL models more interpretable.
Is ChatGPT a Deep Learning Model?
Yes, ChatGPT is a Deep Learning model based on transformer architecture, a neural network category designed for Natural Language Processing tasks. It has been trained on vast text data to generate human-like responses.
Is CNN Deep Learning or Machine Learning?
CNN is a Deep Learning model falling under the broader category of Machine Learning. They are specifically designed for processing structured data arrays, such as images, and are frequently used in computer vision tasks.
Conclusion
As the world of AI keeps rapidly expanding, the Deep Learning Vs Machine Learning debate becomes more prominent due to their distinct methods. Machine Learning offers foundational data analysis, while Deep Learning utilises intricate neural designs. The choice between them isn't about dominance but task suitability. Nevertheless, both are pivotal in shaping future innovations.
Interested in neural networks? Try our Neural Networks With Deep Learning Training!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which Tools/Languages Should I Prefer to Build Deep learning Models?

You can use Python because of its robust ecosystem for Deep Learning. If you are a beginner, you can use high-level libraries like Keras, which eases the experimentation process by providing abstraction to the unnecessary information hidden under algorithms.
What is the Best Language for Machine Learning?

The best Programming languages to learn Machine Learning are Python, R, Java and JavaScript.
What are the Other Resources and Offers Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is The Knowledge Pass, and How Does it Work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are the Related Courses and Blogs Provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning Courses, including the Machine Learning Course and the Deep Learning Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into the Goals of Artificial Intelligence.
Our Data, Analytics & AI Blogs cover a range of topics related to Machine Learning and Deep Learning, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Artificial Intelligence skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Data, Analytics & AI Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Introduction to AI Course
Introduction to AI Course
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


