We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Have you ever wondered why you say “better” instead of just “good” when comparing two things? This simple comparison highlights the essence of Degrees of Comparison. They are the key to making your descriptions more precise and engaging. Be it for writing an essay, telling a story, or simply chatting with friends, understanding them can elevate your communication. But how do you use them effectively, and why are they so crucial in your daily communication?
In this blog, we’ll explore the three Degrees of Comparison: positive, comparative, and superlative. We’ll break down their rules, provide practical examples, and show you how to use them. Let’s dive in and uncover its secrets!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding the Degrees of Comparison
2) The Importance of Degrees of Comparison
3) The Three Degrees of Comparison in English Grammar
4) How to Use Degrees of Comparison?
5) Conclusion
Understanding the Degrees of Comparison
Degrees of Comparison are used to compare one thing to another. Understanding these degrees helps in constructing clear and precise sentences. In English Grammar, they play a crucial role in descriptive writing and Effective Communication. They allow you to express varying levels of qualities, making our descriptions more vivid and accurate.
The Importance of Degrees of Comparison
Understanding the Degrees of Comparison is essential for effective communication. Let's look at their significance in detail:
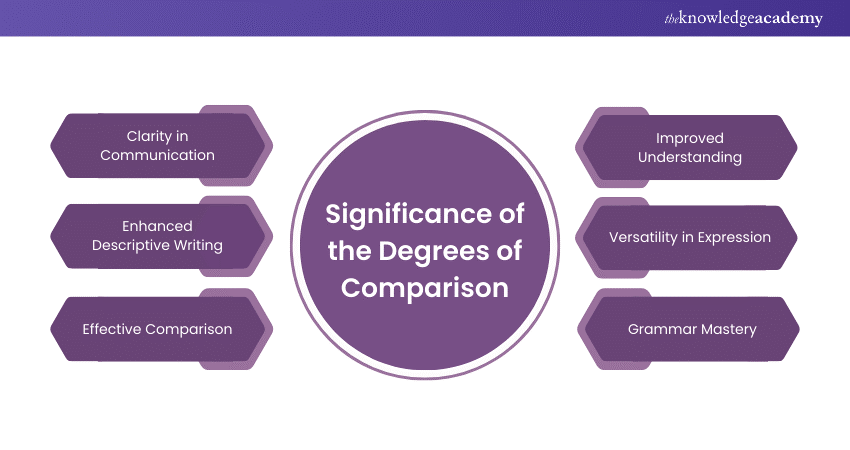
a) Degrees of Comparison help in making your descriptions clear and precise, allowing you to convey the exact level of a quality or characteristic.
b) They enrich your writing by providing a way to compare and contrast different items, people, or situations, making your descriptions more vivid and engaging.
c) Using Degrees of Comparison, you can effectively compare multiple items or people, highlighting differences and similarities in a structured manner.
d) They aid in better understanding and interpretation of information by clearly indicating the extent of a quality or characteristic.
e) Degrees of Comparison offer flexibility in expression, enabling you to describe varying levels of qualities in both written and spoken language.
f) Mastering Degrees of Comparison is essential for proper grammar usage, contributing to more accurate and effective communication.
Learn the secrets to engaging and inspiring your audience - sign up for our Public Speaking Training now!
The Three Degrees of Comparison in English Grammar
Degrees of Comparison are utilised to make comparisons. In English Grammar, there are three forms of them:
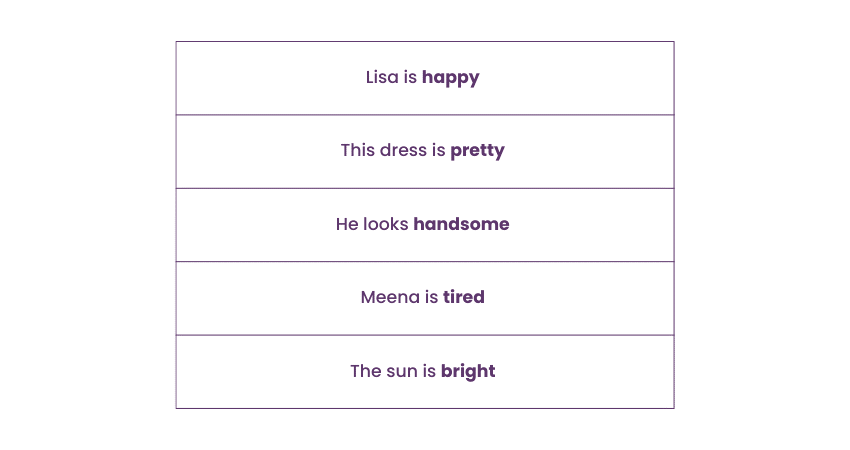
1) Positive Degree of Comparison
The positive Degree of Comparison is essentially the original form of the adjective. This degree does not facilitate any comparison; it merely provides information about a particular quality possessed by a noun.
For example:
2) Comparative Degree of Comparison
The comparative Degree of Comparison is used to compare two nouns that share the same quality or to compare the particular quality of a noun at two different times.
For example:

It indicates which of the two has a greater or lesser degree of the specified quality. This form is used to compare two entities directly.
Speak English with confidence and clarity - register for our English Speaking Course today!
3) Superlative Degree of Comparison
The superlative Degree of Comparison represents the highest Degree of Comparison. It is used to compare similar qualities shared by more than two nouns, showing which of these nouns possesses the greatest or least degree of the mentioned quality or qualities.
For example:

How to Use Degrees of Comparison?
Using Degrees of Comparison correctly is essential for clear and effective communication. By understanding the rules and nuances of positive, comparative, and superlative degrees, you can effectively use them to enhance your communication. Let’s explore how to utilise them:
a) Positive Degree: This is the base form of the adjective or adverb, used when no comparison is being made. For example, “She is tall.” Here, “tall” is the positive degree, simply describing the height of one person without comparing it to others.
b) Comparative Degree: This form is used to compare two items or people. It often involves adding “er” to the end of the adjective or using “more” before the adjective. For example, “She is taller than her brother.” Here, “taller” is the comparative degree, comparing the height of two people. For adjectives with more than two syllables, use “more” (e.g., “more beautiful”).
c) Superlative Degree: This form is used to compare three or more items or people, indicating the highest degree of quality. It often involves adding “est” to the end of the adjective or using “most” before the adjective. For example, “She is the tallest in her class.” Here, “tallest” is the superlative degree, comparing the height of one person to everyone else in the group. For adjectives with more than two syllables, use “most” (e.g., “most beautiful”).
d) Irregular Comparisons: Some adjectives and adverbs have irregular comparative and superlative forms that do not follow the usual rules. For example, “good” becomes “better” in the comparative degree and “best” in the superlative degree. Similarly, “bad” becomes “worse” and “worst.”
e) Using ‘Than’ and ‘The’: When using the comparative degree, “than” is often used to show the comparison (e.g., “She is smarter than him”). When using the superlative degree, “the” is typically used before the adjective (e.g., “She is the smartest in the class”).
f) Adverbs in Comparison: Adverbs can also be compared using Degrees of Comparison. For example, “He runs fast” (positive), “He runs faster than his friend” (comparative), and “He runs the fastest in the team” (superlative).
g) Contextual Appropriateness: Ensure that the Degree of Comparison used is appropriate for the context. For instance, use the comparative degree when comparing two items and the superlative degree when comparing three or more items.
h) Avoiding Double Comparatives and Superlatives: Do not use double comparatives or superlatives, such as “more better” or “most tallest.” These are grammatically incorrect. Use either the comparative or superlative form alone.
Conclusion
By mastering the Degrees of Comparison, you can make your descriptions more vivid and precise. Be it highlighting subtle differences or showcasing the best, these can aid in effective communication. Master the art of comparison and elevate your language skills!
Enhance your ability to connect, persuade and inspire - sign up for our Communication Skills Course now!
Frequently Asked Questions

Rule 2 states that the comparative degree is used to compare two items or people. This often involves adding “er” to the adjective or using “more” before it, such as “taller” or “more beautiful.”

The superlative degree is often considered very difficult as it involves comparing three or more items, indicating the highest or lowest degree of a quality.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Communication Skills Courses, including the English Grammar Course, English Speaking Course, and Public Speaking Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Assertion and Reason.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Communication strategies, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 English Grammar Course
English Grammar Course
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Fri 21st Feb 2025
Fri 25th Apr 2025
Fri 20th Jun 2025
Fri 22nd Aug 2025
Fri 17th Oct 2025
Fri 19th Dec 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


