We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Design Thinking is like a breath of fresh air for the Banking industry. As banks grapple with the ever-increasing demand for personalised experiences and streamlined services, this methodology fosters innovation. Design Thinking in Banking represents a customer-centric approach that employs empathy, creativity, and rationality to solve complex problems.
The iterative process of Design Thinking includes understanding the user, defining problems, ideating solutions, prototyping, and testing, all of which combine to enhance efficiency and customer satisfaction. This paradigm shift is shaping the future of banking. This blog will explore Design Thinking in Banking and how the banking sector employs a creative problem-solving approach centred around customer needs.
Table of Contents
1) What is Design Thinking in Banking?
a) Stage 1: Empathise
b) Stage 2: Define
c) Stage 3: Ideate
d) Stage 4: Prototype
e) Stage 5: Test
2) Roles of Design Thinking in Banking
2) Benefits of Design Thinking in Banking
3) Challenges of Design Thinking in Banking
4) Conclusion
What is Design Thinking in Banking?
Design Thinking is a methodology that employs a cyclical process to gain insights into users, reframe challenges, and devise innovative solutions. It applies design concepts in a manner akin to human interaction with their surroundings. This approach is particularly effective for addressing complex or undefined challenges.
In our complex and interconnected world, it’s crucial to continually evolve Design Thinking abilities. This ensures a deep comprehension of customers and the agility to adapt swiftly to the dynamic shifts in their contexts and actions.
Traditional banking methods are at risk due to the emergence of FinTech startups in recent years. These new service providers challenge established banks with their latest Design Thinking in Business Strategies and customer-centric technologies.
Banks must adopt the latest business models to compete with these financial organisations in the current economic environment. Design Thinking skills can help banks achieve this, and understanding common Fintech Interview Questions can prepare professionals for the challenges of implementing these innovations. Design Thinking involves a total of five phases, which are discussed below:
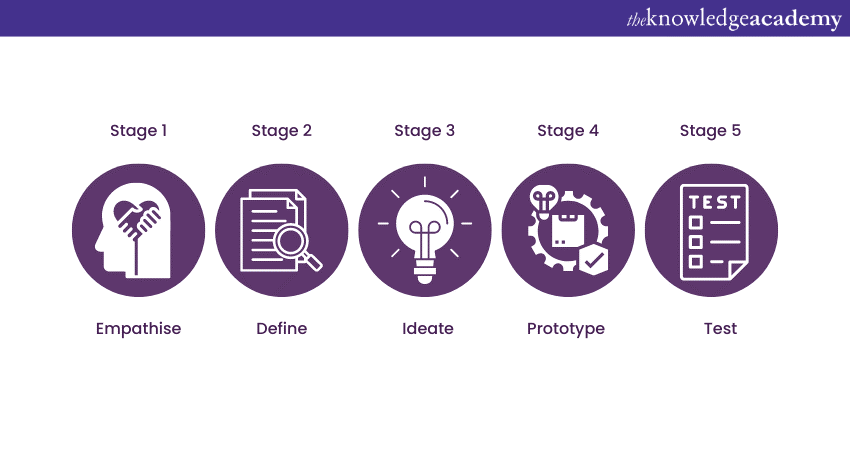
Stage 1: Empathise
The first step in Design Thinking is to empathise. Here, the focus is given to gaining an empathetic understanding of the problem to be solved. This is achieved through user research, i.e., understanding the user's needs. Only after that can be taken to ensure their needs are met.
Design-driven efforts promote reaching out to customers. The motive here is to discover the services that attract them to the offering. Getting in touch with customers in a local bank branch and collecting feedback about their banking experience can be a good example. It makes the management follow Design Thinking and become customer-centric.
Stage 2: Define
Once the problem has been identified, it’s time to accumulate all the information gathered during the first stage. These observations are then analysed and synthesised to define the core problems. These observations are called ‘problem statements’.
One important thing to remember is that organisations should not define the problem as their own need. Instead, they must pitch the problem statement from the users' perspective. For example, saying, “People should have insurance policies to deal with some unforeseen circumstances,” is far better than saying, “We need to sell more and more insurance policies to people.”
Stage 3: Ideate
The third step in Design Thinking is to create ideas. Once the problem has been identified and defined, it’s time to generate ideas. At this stage, you are expected to look for alternative ways to look at the design thinking problem and develop innovative solutions through brainstorming.
There are many techniques of creativity. One of the commonly used example is brainstorming. Brainstorming is typically the most used technique at this stage of creativity. It allows people to generate as many ideas as possible.
The worst possible idea is an unconventional technique. It's a method for seeking the worst solutions at this stage ‘purposefully’. This process helps people relax, boosts their confidence, and stokes their creativity so that they can examine these ideas, challenge their assumptions, and gain insights into great ideas.
Stage 4: Prototype
This is an experimental phase where the aim is to find the best possible solution to the problem. Many scaled-down suggestions are presented at this stage. These prototypes are confidential and can be shared and tested within the team (sometimes with other departments). Paper prototyping is the best example of this process.
Stage 5: Test
This is the final phase of the five-phase model in which solutions are tested. Since Design Thinking is iterative, the results are often used to redefine one or more further problems. Testing aims to get as deep in understanding the problem as possible. At this point, it’s time to put the product into the end user’s hands and ask for feedback. The whole process is experienced from the user's perspective.
Role of Design Thinking in Banking
Design Thinking is a human-centred problem-solving methodology that emphasises empathy, collaboration, and innovation. In the banking sector, this methodology is proving to be a game-changer, helping institutions enhance Customer Experiences, drive innovation, and adapt to changing market dynamics. A well-trained Banksman can leverage this approach to facilitate smoother processes and more effective solutions.
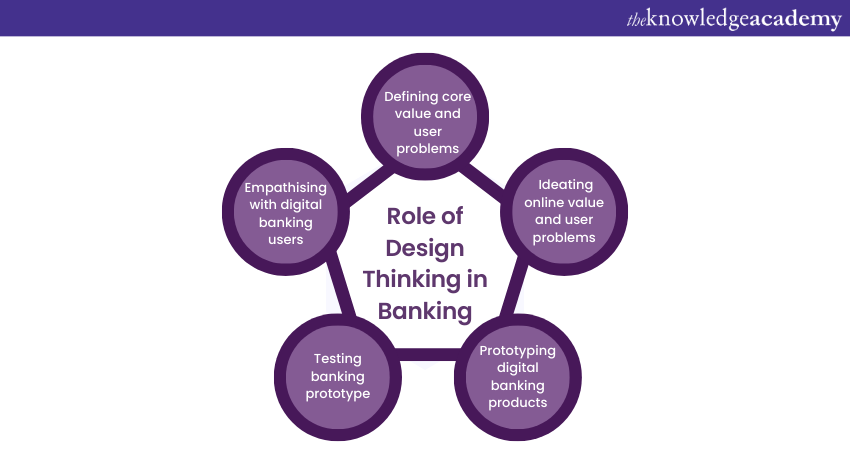
1) Empathising with digital Banking users: During the empathy stage, it is essential to collect a significant amount of data about customer needs, pain points, business goals, and product features. Thorough research can help gain knowledge about User Behaviour and find ways to enhance the onboarding experience for new users. Empathising is also crucial to determine if the digital Banking journey is frustrating.
2) Defining core value and user problems: During the empathise stage of a project, research can be conducted to gain insight into the issues the users face. This helps understand the users' needs and highlights potential areas for innovation. By compiling and analysing the data gathered during the research, you can identify common pain points and unmet needs, which can provide valuable insights for designing effective solutions.
3) Ideating online value and user problems: After the consumers' unanswered needs have been identified, the next step is to gather and explore various creative ideas to address those needs. At this stage, all team members collaborate to share ideas, brainstorm, and build upon each other's thoughts.
4) Prototyping digital Banking products: When prototyping digital Banking products, the aim is to determine which parts of the ideas are effective. It's essential to evaluate the impact of your ideas against their feasibility through receiving feedback. Additionally, the concept can change based on feedback, and the prototype can be updated accordingly.
5) Testing Banking prototype: Once you have developed a prototype, testing it with your target audience is crucial. This will help you determine whether your product meets the users' requirements and addresses their issues.
Additionally, do not hesitate to gather feedback from your customers and continuously improve your product. Doing so will ensure your product remains relevant and beneficial to your target audience.
While Design Thinking offers significant benefits to the Banking industry, it is not without challenges. Implementing design thinking requires a cultural shift within organisations, which can be met with resistance from traditional, risk-averse structures. Additionally, this process can be time-consuming and may require a significant initial investment in training and resources.
Unlock innovation and transform problem-solving with our Design Thinking for R&D Engineers Training – sign up now!
Benefits of Design Thinking in Banking
There are several Benefits of Design Thinking which can motivate the Banking companies to implement its concepts and processes.
a) Design Thinking is a tool for innovation. It helps create new products, services, and experiences that are more user-friendly and more efficient.
b) By incorporating Design Thinking, banks can develop in-house apps that cater to customers' needs. Based on Banking customers’ feedback and ideas, services can be improved accordingly.
c) Design Thinking can also help banks create or expand their brands. In the Banking industry, products like mobile banking apps and credit/debit cards shape the organisation's brand. So, banks’ strategy should consider how to provide a good brand experience to users. In order to achieve this, the product must offer the right features to the right people.
d) Design Thinking is a non-linear process, where one stage leads to the next with a logical conclusion. However, the results often redefine one or more further problems. Different teams within an organisation may conduct more than one stage concurrently.
e) Apart from banks or other financial institutions, it can also help Financial Advisors and Brokers better understand their clients‘ needs. The finance sector is full of complex concepts that many people find difficult to understand.
f) Design Thinking can help simplify this knowledge. This way, Design Thinking can help clients make better financial decisions. It is believed that all employees, regardless of their position and role, should begin to see themselves as Design Thinkers. It will help enhance the Customer Experience and provide banks with a competitive edge over their competitors
Challenges of Design Thinking in Banking
The Banking industry is highly regulated. Banks must abide by several norms. Sometimes, innovating and implementing new ideas is difficult because prospective changes must comply with regulations. This can sometimes reduce the scope and flexibility of Design Thinking.
Even if the norms don’t stop a bank, long-established traditions and ways of doing things can also be a hurdle in the path of Design Thinking. It's sometimes difficult to change the culture and mindset that has been used for a long time. Moreover, the Banking industry is complex and risk-averse. So, the management may resist implementing new changes to avoid risks.
Design Thinking is a customer-centric concept that focuses on fulfilling customers' needs and preferences. However, customers may sometimes resist change and not be open to new ideas and approaches, which can also create problems in implementing effective solutions.
Some organisations may not have a strong design team or the skills to implement Design Thinking effectively. Smaller organisations mainly deal with problems like training employees and investing in new tools and technologies due to limited budgets.
Unlock your potential as a visionary problem-solver with our Design Thinking Training – empower innovation today!
Conclusion
We hope you enjoyed reading this blog on Design Thinking in Banking and learned about it, its stages, advantages, and disadvantages. Design thinking is very useful in the banking industry. Especially when newly established fintech companies compete with the traditional banking system, it has become unavoidable for banks to accept new ideas.
Join our Creative and Analytical Thinking Training to enhance your problem-solving abilities and unlock your full creative potential!
Frequently Asked Questions
How are Design Thinking initiatives in Banking measured in terms of key metrics or indicators?

Design Thinking initiatives in Banking are measured using key metrics like customer satisfaction scores, Net Promoter Score (NPS), user engagement rates, time to market, innovation adoption rates, and overall impact on revenue and cost efficiency.
How can banks refine Design Thinking solutions based on customer feedback and User Testing?

Banks can refine Design Thinking solutions by collecting and analysing customer feedback, conducting iterative user testing, and implementing insights-based changes.
What are the other resources and offers provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 3,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 190+ countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.
What is Knowledge Pass, and how does it work?

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
What are related courses and blogs provided by The Knowledge Academy?

The Knowledge Academy offers various Leadership Courses including Design Thinking Course, Business Model Innovation Training and Business Development Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Design Thinking in Software Development methodologies.
Our Business Skills Blogs cover a range of topics related to Design Thinking, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Design Thinking Skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Successful People Management and Team Leadership
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 29th Aug 2025
Fri 10th Oct 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025






 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


