We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

In a world where quality is paramount, ISO Certifications ensure organisations adhere to internationally recognised standards. The Difference Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 often needs to be clarified as both are extensively about Quality Management Systems (QMS). While both prominent certifications focus on Quality Management, each is designed for specific industries. Thus, understanding their differences is crucial to implement the right standard and modify business operations accordingly.
Know the Difference Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485. Gain insights into Regulatory Compliance, Risk Management, and the path to organisational excellence. Read now!
Table of Contents
1) Understanding ISO 9001
2) A brief overview of ISO 13485
3) Key Differences Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485
4) Differences in requirements of ISO 9001 and ISO 13485
5) Conclusion
Understanding ISO 9001
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) provides several Quality Management standards,and ISO 9001 is the most widely recognised one. It offers organisations a framework to establish and maintain effective QMS, enhancing customer satisfaction and improving performance.
ISO 9001 focuses on customer satisfaction, continual improvement, and process efficiency. It covers various aspects such as customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, evidence-based decision-making, and relationship management.
ISO 9001 serves a crucial purpose in the QMS domain. Its primary objective is to assist organisations in achieving and maintaining a certain level of customer satisfaction by meeting their requirements and continually improving their processes.
A brief overview of ISO 13485
ISO 13485 is an internationally recognised standard designed explicitly for organisations involved in the Medical Device industry. It sets the requirements for a comprehensive Quality Management System that ensures the safety and effectiveness of medical devices throughout their lifecycle.
ISO 13485 focuses on establishing and maintaining processes that meet customer and regulatory requirements at every stage, from design, development, production, and service. This standard focuses on Risk Management, traceability, and documentation to ensure the highest product safety and quality in the medical device industry.
ISO 13485 Certification validates an organisation's commitment to consistently meeting regulatory and customer requirements. Thus, it helps maintain the safety and performance of medical devices and supports the delivery of high-quality medical devices.
The purpose of ISO 13485 is to establish a robust Quality Management System specific to the Medical Device industry. It aims to ensure that organisations involved in designing, developing, manufacturing, and servicing medical devices consistently adhere to stringent regulatory requirements and provide safe and effective products.
Boost your compliance skills with ISO 13485 Training Courses – Take the first step towards mastery today!
Key Differences Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485?
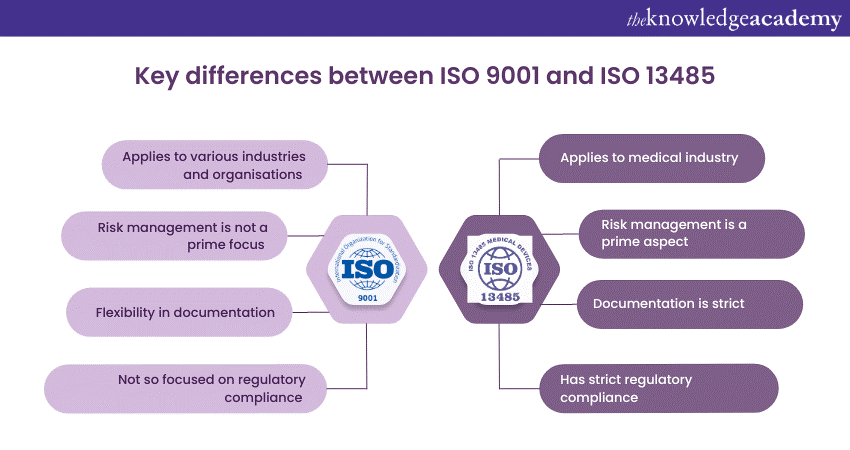
Even though both ISO 9001 and ISO 134845 work towards the same goal of creating a gold standard for products and services, they differ on several parameters due to their industry applications. Here are some notable Difference Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485:
Regulatory requirements
ISO 9001 can be applied in any organisation, irrespective of their domain. However, when ISO 9001 is applied to the industries, it is not necessary that they follow all the industry regulatory requirements.
Since the medical industry is highly regulated, ISO 13485 has strict Regulatory Compliance. It aligns with specific Regulatory Requirements, such as the European Union's Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and the United States of America's Food and Drug Administration's (FDA) Quality System Regulation (QSR).
Learn the basics of ISO 9001 with our ISO 9001 Foundation Training – join now!
Risk management
Risk management is not the prime focus of ISO 9001 but forms a part of the Quality Management System guidelines provided by the standard. It encourages organisations to identify and manage risks impacting quality and customer satisfaction.
Risk management holds a prominent position within ISO 13485 standards. It requires organisations to establish comprehensive processes for identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks associated with medical devices, including product safety and regulatory Compliance Risks. It also obliges medical device manufacturers to take in and analyse customer grievances. After this is done, they are also obliged to provide the after-sale reports, to see if they are in accordance with the product they had manufactured. For example, if a medical device is not functionally feasible, but its sales are sky rocketing, then the manufacturers will be answerable for the same.
Role of management
ISO 9001 highlights the importance of Leadership and Management commitment in establishing and maintaining an effective Quality Management System. Top management is responsible for defining quality objectives, maintaining customer focus, and providing necessary resources for implementation and improvement.
ISO 13485 also emphasises the role of management in Quality Management. However, management's responsibilities in the Medical Device industry expand to include specific regulatory requirements. Also, ISO 13845 specifies that the management should appoint a singular member who should be responsible for each aspect of QMS. They must ensure compliance with applicable regulations, maintain the safety of medical devices, and establish risk management processes.
Documentation requirements
ISO 9001 allows organisations to determine the extent of documentation required for their Quality Management Systems. It focuses on maintaining documented information necessary for effective process control and evidence of conformity.
In contrast, ISO 13485 has more specific documentation requirements due to the strict regulatory environment of the Medical Device industry. It necessitates comprehensive documentation of processes, procedures, and records to ensure traceability, risk management, and regulatory compliance.
Ready to enhance your understanding of ISO 9001? Our ISO 9001 Training can help you take your first step towards implementing a successful Quality Management System.
Product realisation
In ISO 9001, the product realisation process involves several stages. These stages include planning, design and development, purchasing, and product or service provision. The products also need to be monitored and measured so that the product's conformity meets specified requirements.
On the contrary, organisations implementing ISO 13485 must establish and maintain documented procedures for each stage of product realisation. It also requires organisations to provide in-depth details to improve customer satisfaction. This standard gathers all these documented procedures and stages and then culminates them into specific standards for production and the supply chain.
Differences in requirements for ISO 9001 and ISO 13485
The major Differences Between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 are highlighted in their requirements (clauses), as discussed below:
Requirements for ISO 9001
ISO 9001 states organisations need to establish an effective Quality Management System. The key ISO 9001 Requirements are organised into the following clauses:
a) Context of the Organisation (Clause 4): States that organisations must determine internal and external factors that can influence their ability to achieve an outcome. Organisations must determine the issues which hinder their purposes and strategic decisions. These include identifying the needs and expectations of interested parties, for example, customers, regulatory bodies, and other stakeholders.
b) Leadership (Clause 5): This clause emphasises the important role of top management in establishing and maintaining an effective QMS. The top management is required to engage in the establishment, implementation and continuous improvement of the system. The management shall also be responsible for establishing a quality policy which aligns with the purpose of the organisation and strategic direction.
c) Planning (Clause 6): This clause outlines the necessity to establish a systematic approach to plan QMS. Organisations determine and assess risks and opportunities which can impact the achievement of the planned outcomes of QMS. This clause also outlines that the organisations should follow measurable quality objectives. These objectives must be consistent with the quality policy and drive improvement throughout the organiation.
d) Support (Clause 7): This Clause outlines the necessity to provide resources, competence, awareness, communication and already documented information to establish and maintain an effective QMS. This Clause also outlines that organisations must determine and provide Human Resources, infrastructure, technology, and financial resources. According to this Clause, organisations also need to ensure that they are performing tasks which affect the QMS’s performance.
e) Operation (Clause 8): This clause outlines that the organisations must plan and control their business operations and QMS to help customers meet their needs and requirements. Organisations must plan, implement and control these processes to meet product or service requirements effectively. This Clause also specifies that organisations must determine and review customer requirements, whether it be statutory or regulatory, related to the products and services of the organisation.
f) Performance Evaluation (Clause 9): This clause outlines that organisations must monitor, measure, analyse, and evaluate their Quality Management System's performance to ensure that it is effective and drive continuous improvement. Organisations are obligated to monitor and measure their customers’ satisfaction. This includes obtaining and analysing information from customer reviews – whether the organisation has achieved their standard or not.
g) Improvement (Clause 10): This clause outlines the importance of organisations to continuously improve their processes and performance. It also specifies that these organisations must establish processes that address the nonconformities and implement some corrective actions that eliminates these causes. Clause 10 also outlines that organisations should identify and implement opportunities for improvement so that these can be initiated through monitoring and measuring results, audits, management reviews and customer feedback.
Enhance your knowledge more on ISO Standard for Quality Management of medical devices – sign up now for our ISO 13485 Lead Implementer Course!
Requirements for ISO 13485
The following are the key ISO 13485 Requirements:
a) Quality Management System (Clause 4): The Clause 4 of ISO 13485:2016, titled Quality Management System, is necessary to establish the foundation of QMS in the context of medical devices. Under this clause, organisations must establish, document, implement, maintain and continuously improve their QMS that is in accordance with the organisation’s purpose and context. It also specifies requirements for the control of records to show conformity to specified requirements and effective operation of QMS. The records taken should be legible, identifiable, and retrievable.
b) Management Responsibility (Clause 5): According to Clause 5, the top management of the organisation is required to establish and maintain a QMS for medical devices. They must ensure that the devices should be available, promote awareness , customer requirements, regulatory requirements and establish a proper framework of quality policy. They must also identify customer focus to adress any customer feedback or grievances properly.
c) Resource Management (Clause 6): Clause 6 of ISO 13485, outlines the requirements for proper provision and management of resources within a medical device QMS. It also requires organisations to have sufficient resources to establish, implement, maintain and improve their QMS. This clause also outlines the necessity for organisations to establish contingency plans which addresses situations that can have an impact on the quality of products. Moreover, organisations must also plan for events such as power failures, equipment breakdowns and other emergencies.
d) Product Realisation (Clause 7): Clause 7 of ISO 13485:2016, titled “Product Realisation”, requires organisations to outline the requirements for the processes that are involved in the realisation of medical devices. It also outlines that the organisations must ensure that the processes are planned, controlled, and monitored efficiently. Moreover, organisations should also ensure that the purchased products are conformed to the specific requirements, it is correctly identified and traced throughout the entire production process.
e) Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement (Clause 8): This clause outlines the requirements for monitoring, measuring, analysing and improving their QMS for medical devices. It emphasises that the organisations must maintain records which provide evidence of conformity to requirements and effective operation of QMS. These organisations are also encouraged to implement preventive actions which eliminates the cause of potential nonconformities. This approach also helps in preventing issues that arises and contributes to the continuous improvement of QMS.
Learn about the different applications of ISO 13485 with our ISO 13485 Lead Auditor training.
Conclusion
ISO 13485 requires a stronger focus on regulatory compliance, risk management, and documentation compared to the broader application of ISO 9001 across various industries. Despite the Difference Between ISO 9001 and 13485, both standards promote a process-oriented approach, customer focus, continual improvement, and management responsibility. The choice between ISO 9001 and ISO 13485 depends on industry-specific needs and regulatory requirements. Implementing either standard can lead to improved customer satisfaction and business success.
Learn all essential knowledge about the ISO 13485 standard and learn the relationship between ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 in certification audits with our ISO 13485 Foundation training.
Frequently Asked Questions

If you understand ISO 9001 and ISO 13485, you can enhance the QMS practices in your organisation. Along with that, you can also meet customer expectations, comply with regulations and improve operations efficiency. With ISO 9001 and ISO 13485, you will be also able to mitigate risks and gain a competitive edge from your competitors.

Industries such as manufacturing, service providers, construction, healthcare, aerospace, etc., benefit from implementing ISO 9001 and ISO 13485.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 13485 Training, including ISO 13485 Foundation, ISO 13485 Lead Auditor and many more. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What is ISO 13485.
Our Health and Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 13485, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Compliance skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


