We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Muscles are essential for our daily movements and bodily functions, working in fascinating ways to keep us moving efficiently. Understanding the Differences Between Skeletal and Smooth Muscles is key to appreciating the complexity of our physiological systems. Dive into this blog to explore how these muscles operate and how their contractions enable our everyday activities.
Table of Contents
1) What are Skeletal Muscles?
2) Characteristics of Skeletal Muscles
3) What are Smooth Muscles?
4) Characteristics of Smooth Muscle
5) Difference between Skeletal Muscle and Smooth Muscle
6) Conclusion
What are Skeletal Muscles?
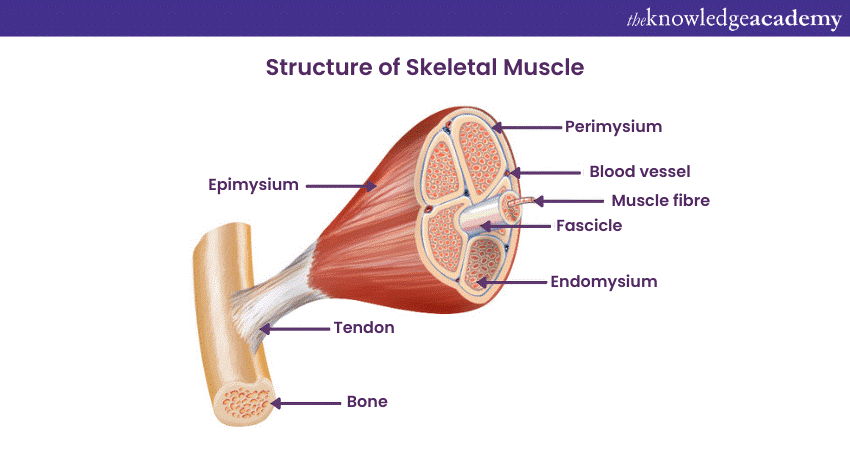
Skeletal Muscles are essential for body movements. Skeletal Muscle tissue is located close to bones and comprises striped Muscle fibres, like those found in the biceps, and is arranged parallel within muscle bundles. Their fibres are surrounded by the protective layer of connective tissue. Here's what the structure of a Skeletal Muscle looks like:
Characteristics of Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal Muscles exhibit several unique attributes that set them apart from other muscle types. Listed below are some of their main characteristics:
a) Voluntary Control: Skeletal Muscles are under conscious control, allowing volitional movement like walking or reaching.
b) Striated Appearance: These muscles show a striped or banded pattern under a microscope due to their organised structure.
c) Attachment to Bones: They are connected to bones via tendons, enabling the body's movement and stability.
d) Multinucleated Cells: Skeletal Muscle cells have multiple nuclei, aiding in their strength and repair.
e) Fatigue Resistance: While they can tire, Skeletal Muscles exhibit endurance for sustained activities.
f) Rapid Contraction: They can contract relatively quickly, contributing to swift movements and responses.
g) Controlled by the Nervous System: Skeletal Muscles respond to signals from the nervous system, allowing for precise and coordinated movements.
h) Adaptability and Growth: These muscles can increase in size (hypertrophy) or decrease (atrophy) based on usage, exercise, or inactivity. As a result, they show remarkable adaptability to varying conditions.
What are Smooth Muscles?
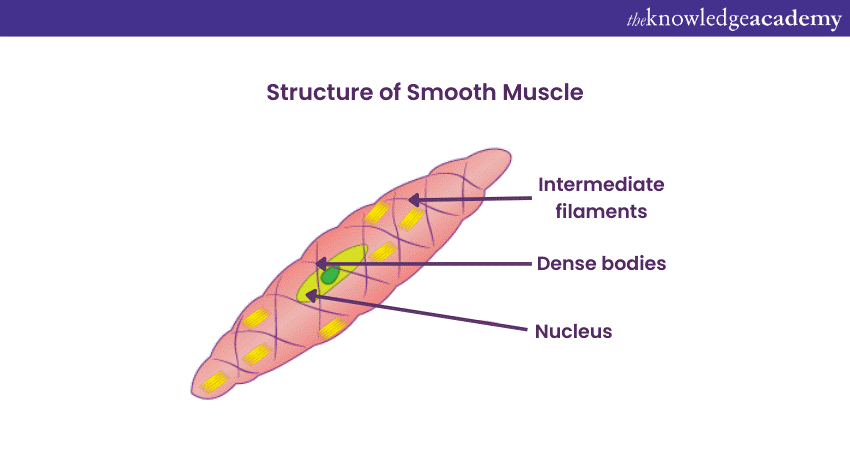
Smooth Muscle fibres have a spindle-like shape and don’t have the striped appearance seen in other muscle types. Unlike Striated Muscles, their cohesion relies on cell connections and protective coverings similar to other muscles. These muscles are typically found in the lining of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, operate involuntarily and function without direct control. Here's what the structure of a Smooth Muscle looks like:
Characteristics of Smooth Muscle
Smooth Muscles possess several distinctive features that differentiate them from other muscle types. Listed below are some of the characteristics of Smooth Muscles:
a) Involuntary Control: Smooth Muscles operate involuntarily, managing various internal organ functions without conscious direction.
b) Lack of Striations: Unlike Skeletal Muscles, Smooth Muscles lack a striped appearance and typically have a spindle-shaped structure.
c) Cell Connections: Cell junctions play a significant role in holding Smooth Muscle fibres together, ensuring their collective function.
d) Presence of Connective Tissue Sheaths: Like other muscle types, Smooth Muscles are surrounded by protective connective tissue coverings.
e) Location in Internal Organs: They line the walls of internal organs, including the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels, contributing to organ functionality.
f) Slow, Sustained Contractions: Smooth Muscles contract slower than Skeletal Muscles. As a result, they aid in prolonged functions like maintaining blood pressure or digestion.
g) Multi-unit and Single-unit types: Smooth Muscles exist in two forms—multi-unit, found in structures like blood vessels, and single-unit, prevalent in organs, each exhibiting distinct functionalities and responses to stimuli.
h) Response to Hormonal and Nervous Signals: They are regulated by both hormonal and nervous systems. These muscles adjust their contractions in response to various internal and external stimuli for organ and vessel function regulation.
|
Characteristic |
Skeletal Muscle |
Smooth Muscle |
|
Location |
Attached to bones by tendons |
Walls of internal organs (e.g., stomach, intestines, blood vessels) |
|
Control |
Voluntary (under conscious control) |
Involuntary (not under conscious control) |
|
Appearance |
Striated (striped) under a microscope |
Non-striated (smooth) under a microscope |
|
Nuclei |
Multinucleated fibres |
Single nucleus in each cell |
|
Contraction type |
Quick and powerful |
Slow and sustained |
|
Function |
Enables movement (e.g., walking, running) |
Facilitates involuntary processes (e.g., digestion, blood circulation) |
|
Structure |
Long, cylindrical fibres |
Short, spindle-shaped cells |
|
Antagonistic action |
Work in pairs for movement |
Contract rhythmically and continuously |
Transform your life today! Discover the secrets of Healthy Lifestyles Training and thrive like never before!
Difference Between Skeletal Muscle and Smooth Muscle
Skeletal Muscles and Smooth Muscles are two distinct types of muscle tissues, each with unique characteristics and functions within the human body. Here are some of the major differences between Skeletal Muscle and Smooth Muscle:
Skeletal Muscles, also known as Striated or Voluntary Muscles, are attached to the bones by tendons and are under conscious control. These muscles enable movement, such as walking, running, and grasping objects. They are named "striated" due to their striped appearance under a microscope, caused by the arrangement of muscle fibres.
On the other hand, Smooth Muscles, also called Involuntary or Non-striated Muscles, are found in the walls of internal organs, like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. Unlike Skeletal Muscles, Smooth Muscles operate involuntarily, meaning they are not under conscious control. Their contractions are slow and sustained, facilitating functions like digestion, blood circulation, and organ processes. Smooth muscles lack the striations seen in Skeletal Muscles, and they appear smooth under microscopic examination.
Structurally, Skeletal Muscles consist of long, multinucleated fibres, while Smooth Muscles have shorter, spindle-shaped cells with a single nucleus. Skeletal Muscles work in pairs; one muscle contracts while the other relaxes, providing the necessary antagonistic action for movement. In contrast, Smooth Muscles contract rhythmically and continuously, maintaining a steady pressure or flow within organs.
Skeletal Muscle Contractions
Skeletal Muscle contractions are under voluntary control, meaning they respond to conscious commands, allowing for intentional movements. These contractions are characterised by their quick and rapid cycles of contraction and relaxation. This enables swift and coordinated actions.
The activation of Skeletal Muscle contractions involves the binding of calcium with troponin, a process pivotal in initiating the Muscle's response. These contractions rely solely on neural input, with signals from the nervous system orchestrating the muscle's movements. Skeletal muscles are typically attached to bones and tendons, facilitating movement and stability in the body.
Transform lives with health expertise sign up for our Active and Healthy Lifestyles Training!
Smooth Muscle Contractions
Smooth Muscle contractions are involuntary, operating without conscious direction. They exhibit a slower and more sustained pattern of contraction and relaxation, suited for functions that require endurance. Initiated by the binding of calcium with calmodulin, this process triggers the cycling of cross-bridges, influencing the muscle's activity.
Unlike Skeletal Muscles, Smooth Muscle contractions are influenced by neural, hormonal, or chemical changes, adapting their contractions to various internal and external stimuli. These muscles are predominantly found lining the walls of internal organs like the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. They play a crucial role in organ functionality and regulation. It plays a crucial role in organ functionality and regulation.
Conclusion
In this blog, you learnt about the Difference Between Skeletal and Smooth Muscles. We talked about how Skeletal Muscles move quickly in our bodies, unlike Smooth Muscles, which work independently and stay contracted for longer. We hope you found this blog informative and meaningful for your career aspirations.
Advance your career in nutrition with our Nutrition And Fitness Training – join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Skeletal Muscles fatigue faster due to their reliance on anaerobic metabolism during high-intensity activities, which causes lactic acid to build up. Smooth Muscles, on the other hand, fatigue slowly as they rely on aerobic metabolism and are designed for prolonged, low-intensity contractions.

Yes, Smooth Muscle is more energy-efficient than Skeletal Muscle. It uses less ATP for contractions and maintains force for extended periods due to its slow, sustained contractions. This makes them ideal for functions that require prolonged tension with minimal energy expenditure.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Healthy Lifestyles Training, including the Active and Healthy Lifestyles Training, Develop Cognitive Behavioural Therapy Training, and Life Coach Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Healthy Lifestyle Choices.
Our Health & Safety Blogs cover a range of topics related to Healthy Lifestyles, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Wellness skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course




 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


