We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.

Most people consider salary to be the biggest concern in the workplace. Undeniably, it is, but what hampers your career most is workplace discrimination. It can overshadow your morals and crush your confidence right in front of your eyes. Isn’t it? This blog delves into Discrimination in the Workplace, its significant types and how you can file a discrimination complaint. Read further to tackle workplace discrimination effectively.
Table of Contents
1) What is Workplace Discrimination?
2) Types of Workplace Discrimination
3) How to File a Discrimination Complaint?
4) What Employer Practices are Considered Unlawful?
5) Intentional and Unintentional Discrimination
6) Conclusion
What is Workplace Discrimination?
Workplace discrimination is the unjust treatment of employees based on characteristics like religion, sexual orientation, age, gender or disability. It could be a one-time or an ongoing incident like harassment. Discrimination typically happens between colleagues, or between an employer and an employee. Regardless of its purpose, discrimination is harmful.
In the UK, workplace discrimination remains a common issue. As per the CIPD Good Work Index 2024 , workplace disputes put stress on the job for approximately eight million UK workers. The most common forms of discrimination reported were:
a) 48% being humiliated at work
b) 35% had a heated argument
c) 34% received verbal abuse or insult
d) 20% experience discriminatory behaviour
Moreover, 42% employees reported feeling exhausted all the time compared to 18% who had no conflicts. Additionally, 37% felt constant under pressure compared to 15% of those without discrimination.
Those affected by discrimination expressed lower confidence level, lower trust and diminished belief in employer’s support. These statistics displays the need for early intervention to safeguard workplace discrimination and conflicts.
Types of Workplace Discrimination
Workplace discrimination often arises as an unfair treatment based on personal characteristics like:
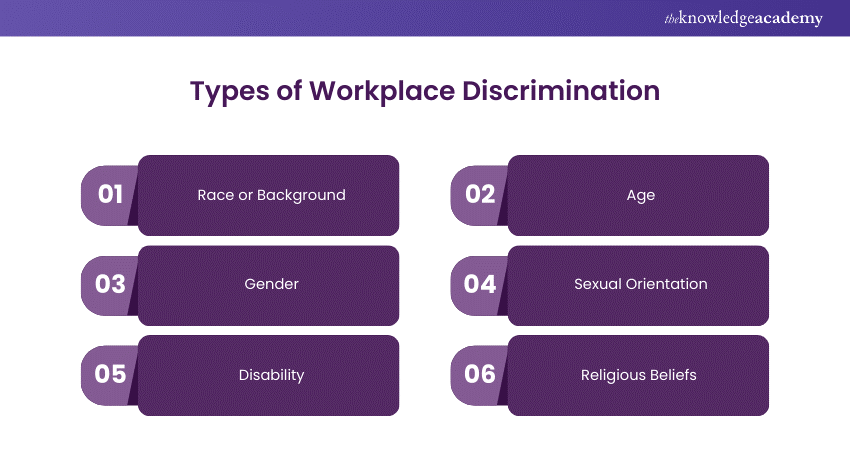
a) Race or Background: It contains mistreatment or lack of opportunities based on an individual's background.
b) Age: Age discrimination occurs when a person's age impacts employment decisions rather than their qualifications or skills.
c) Gender: Discrimination based on gender contains unequal treatment due to gender identity. This results in unequal pay, stereotyping, or sexual harassment. It can even influence transgender and non-binary individuals, with women experiencing it the most.
d) Sexual Orientation: Prejudiced behaviours like harassment, unlawful termination, or denial of benefits contribute to forming a hostile work environment for LGBTQ+ employees.
e) Disability: Individuals with physical or mental disabilities experience inequality like denial of concessions, biased hiring process, or are excluded from job options.
f) Religious Beliefs: Religious beliefs involve unfair treatment, such as discrimination, Workplace Harassment, or unjust job actions, such as denial of job chances or pay raises because of one's religious beliefs.
Protect your rights with our Employment Law Training – Join now!
How to File a Discrimination Complaint?
Here’s how you can file a discrimination complaint:

1) Gather Data
Collect the important details like the name, phone number, and address of the person involved and the one who experienced discrimination. If possible, gather contact details of any witness who can support your claim.
2) Log Experience
Create a brief report detailing the events, including information like the names, dates, times, and places. Record all relevant incidents to demonstrate a pattern of discrimination or harassment.
3) Submit Details
Send your recorded complaint to an established agency like the Equality and Human Rights Commission (EHRC). You do not need any specific recommendation to submit your complaint; provide a detailed description of the discrimination you have faced.
What Employer Practices are Considered Unlawful?
Understanding unlawful employer practices is essential for ensuring a compliant workplace. Here are some of the practices:
a) Discriminatory Employment Decisions: The law prohibits discriminatory employment decisions based on traits such as race, gender, age, or disability. For example, refusing to hire applicants based on their race or not promoting them because of their gender is not allowed.
b) Harassment: Employers are required to stop harassment that violates an employee's dignity or leads to a hostile, or humiliating atmosphere. This covers offensive jokes, remarks, or behaviours directed at a person's race, gender, or other characteristics that are protected.
c) Victimisation: It happens when an Employee is treated poorly after reporting discrimination, supporting another person's complaint, or being part of an investigation. This may lead to a demotion, termination, or other negative consequences because of their participation.
d) Failure to Make Reasonable Adjustments: Employers are required to make reasonable deal for disabled employees to prevent any disadvantages they may face in the workplace. It includes modifying workspaces, offering specific tools, or altering work schedules. Not making these changes could be seen as breaking the law.
e) Equal Pay Violations: Employers are required to ensure that both men and women receive the same pay for the same job to comply with equal pay laws regardless of gender.
Employers need to be aware of their legal duties and create policies to protect these unlawful practices.
Strengthen workplace relationships with our Employee Relations Training – Register now!
Intentional and Unintentional Discrimination
Intentional discrimination is a direct form of discrimination that happens when an employee gets treated unfavourably. The unfair acts are based on characteristics like age, gender, or race. There are three types of intentional disclinations namely.
a) Ordinary Direct Discrimination: Treating someone less favourably due to a protected characteristic; lawful only if 'objectively justifiable.'
b) By Association: Unfair treatment based on a protected characteristic of someone they're associated with.
c) By Perception: Discrimination based on the belief that someone has a protected characteristic, regardless of accuracy.
Unintentional discrimination is an indirect form of discrimination that are normally unintended. It occurs when a policy applies to everyone, but it puts those with protected characteristics at a disadvantage. For example, a company police requiring its employees to work late may indirectly affect those with childcare responsibilities, mostly women.
Conclusion
Discrimination in the Workplace is one of the most significant issues that undermines productivity, fairness, and employee well-being. Addressing it require careful measures like training, supporting culture, and transparent policies. Employers must foster a respectful atmosphere where all employees feel valued and protected. Tacking workplace discrimination promotes equality, enhance overall performance of employees. This will benefit both the organisation and the employees.
Promote equality in workplace with our Direct and Indirect Discrimination Training today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Report the incident to Human Resources and, if necessary, file a complaint with agencies like EHRC.

Workplace conflict arises due to harassment, unequal treatment, or exclusion based on protected traits. This leads to decreased productivity and morale.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 19 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various Employment Law Courses, including the Direct And Indirect Discrimination Training, Employment Law Training, and Commercial Law Training Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Employee Rights and Responsibilities.
Our HR Resources Blogs cover a range of topics related to Employment Laws, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your knowledge on Employment Law, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have got you covered.
Upcoming HR Resources – Learn about Human Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 Direct and Indirect Discrimination Training
Direct and Indirect Discrimination Training
Fri 24th Jan 2025
Fri 28th Mar 2025
Fri 23rd May 2025
Fri 25th Jul 2025
Fri 26th Sep 2025
Fri 28th Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


