We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
DNS is the unsung facilitator that seamlessly connects our human-friendly Domain Names to the intricate web of IP addresses that computers understand. DNS in Application Layer serves as a directory that translates Domain Names into IP addresses.
Our blog will delve into the pivotal role of DNS in the Application Layer, uncovering its mechanisms, benefits, and challenges. It will also shed light on this vital technology that makes the internet accessible to us all. Understand the DNS in application layer, how it functions, the different DNS server types in use, DNS security issues, and the technological history through this blog. Read more!
Table of Contents
1) What is DNS in Application Layer?
a) The role of DNS in the Application Layer
b) DNS resolution process
2) Benefits of DNS in Application Layer
3) DNS in Application Layer: Challenges and concerns
4) Conclusion
What is DNS in Application Layer?
The Domain Name System (DNS) plays a key role in the Application Layer. It changes website names into numbers called IP addresses, which computers need to find each other online.
When you type a website's name into your browser, it initiates a DNS query to a DNS server, which then finds its database or sends the request to other servers until it finds the corresponding IP address. DNS makes the internet easier to use because we can type names instead of long numbers.
DNS also handles different kinds of record typeske Mail Exchange (MX) records for emails and Canonical Name (CNAME) records for aliasing. Without DNS, the internet would be harder to use, and finding websites by name would be tough.
Learn effective troubleshooting methodologies to address diverse IT issues with our IT Support and Solution Course – join today!
The Role of DNS in the Application Layer
DNS acts like a directory service for the internet, translating human-friendly Domain Names into numerical addresses that computers use to interact with each other. When you type a website's name into your browser, your computer asks a DNS server for the website's number. The DNS server looks up the number and tells your computer where to go.
This translation process is essential for smooth internet navigation. Without DNS, users would need to remember and input complex numerical IP addresses to access websites, which would be incredibly inconvenient and prone to errors. DNS simplifies this process by allowing us to use easy-to-remember Domain Names instead.
DNS resolution process
The DNS resolution process is the steps that a computer takes to translate a Domain Name into an IP address. The resolution process involves multiple steps, including querying authoritative name servers, caching, and iterative queries, all of which contribute to the efficient functioning of DNS.
Benefits of DNS in Application Layer
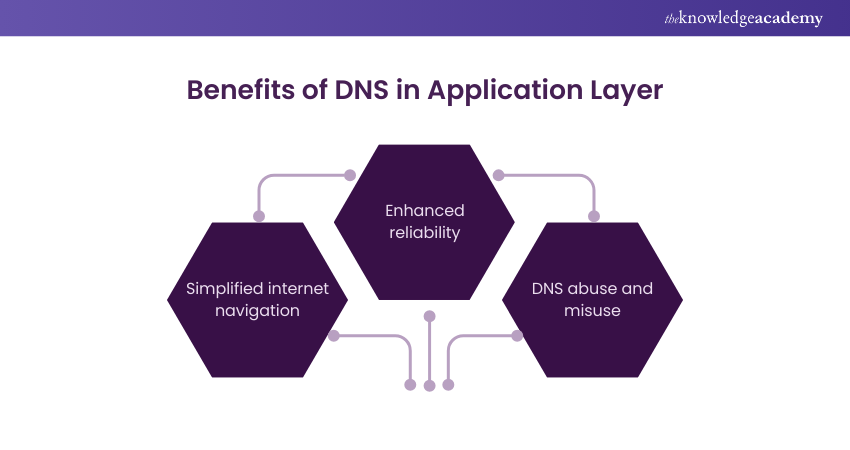
a) Simplified internet navigation: DNS translates Domain Names into IP addresses. This makes it easy for users to access websites using familiar names instead of complex numerical addresses.
b) Enhanced reliability: DNS servers cache frequently accessed domain-to-IP mappings, reducing the time and resources needed to look up addresses and improving internet performance.
c) Scalability: DNS supports a distributed architecture, allowing for effective resolution of Domain Names to IP addresses even as internet traffic and the number of connected devices continue to grow.
Learn about security planning to protect against risks with our Security Management, Planning, and Asset Protection Course – join today!
DNS in Application Layer: Challenges and concerns
Here are the challenges and concerns of DNS in the Application Layer:
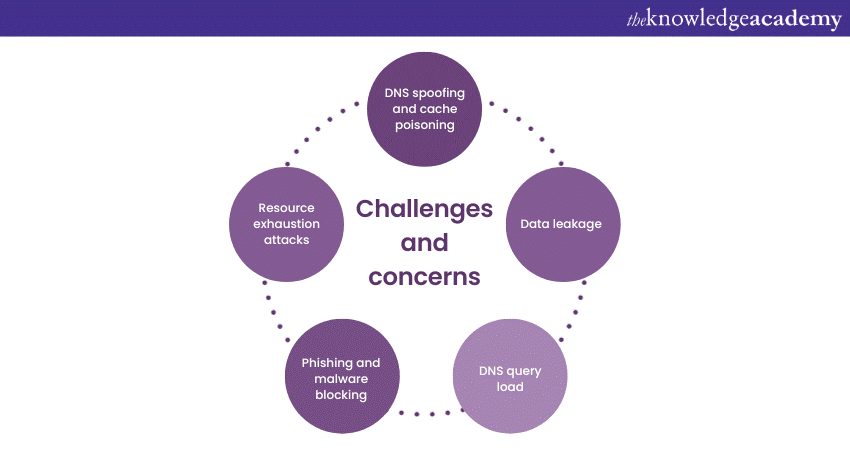
a) Security vulnerabilities: DNS is prone to various attacks, such as DNS spoofing and cache poisoning, which can compromise the integrity and availability of DNS services, leading to potential data breaches and unauthorised access.
b) DNS performance and latency: Inefficient DNS resolution processes or network congestion can delay website access and overall slower internet performance, impacting User Experience and productivity.
c) DNS amplification attacks: Attackers exploit misconfigured DNS servers to amplify their attack traffic, causing significant disruption to targeted networks and services, leading to downtime and financial losses.
d) Lack of DNSSEC adoption: Despite offering enhanced security through cryptographic authentication of DNS data, adoption of DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) remains relatively low, leaving DNS infrastructure vulnerable to tampering and spoofing attacks.
e) DNS abuse and misuse: Cybercriminals leverage DNS for activities, such as botnet command and control, domain DNS Hijacking, and malware distribution, posing significant risks to internet users and organisations' Cyber Security posture
Conclusion
Our exploration of DNS in Application Layer reminds us of its profound impact on our digital lives. DNS quietly bridges the gap between human intent and digital connectivity. It ensures a seamless online experience, enabling us to surf the web, communicate, and access services effortlessly. Yet, DNS also faces challenges like security risks and performance optimisation. Understanding and appreciating DNS's significance is essential in this digital domain. It is a technology that empowers us to navigate the vast digital field, connecting us to the world with just a click.
Learn essential security practices for domains and hosting environments with our Introduction to Domain Names and Web Hosting Course – join today!
Frequently Asked Questions

Some Domain Name Server troubleshooting techniques include checking the DNS configuration for errors, ensuring the server is responding to requests, and using tools like ‘nslookup’ or ‘dig’ to diagnose issues with DNS resolution.

The security concerns with DNS include vulnerabilities to DNS spoofing attacks, where attackers redirect traffic by falsifying DNS data, and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, which can overload servers and disrupt service.

The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs, videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA.

The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass, a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.

The Knowledge Academy offers various IT Support and Solution Training including BIND DNS Administration, MacOS Mojave Troubleshooting and Support Training, and Security Management, Planning and Asset Protection Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into What are Network Protocols?
Our IT Infrastructure & Networking Blogs cover a range of topics offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Business Improvement skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Infrastructure & Networking Resources Batches & Dates
Date
 BIND DNS Administration Training
BIND DNS Administration Training
Fri 17th Jan 2025
Fri 21st Mar 2025
Fri 16th May 2025
Fri 18th Jul 2025
Fri 19th Sep 2025
Fri 21st Nov 2025







 Top Rated Course
Top Rated Course



 If you wish to make any changes to your course, please
If you wish to make any changes to your course, please


